Abstract
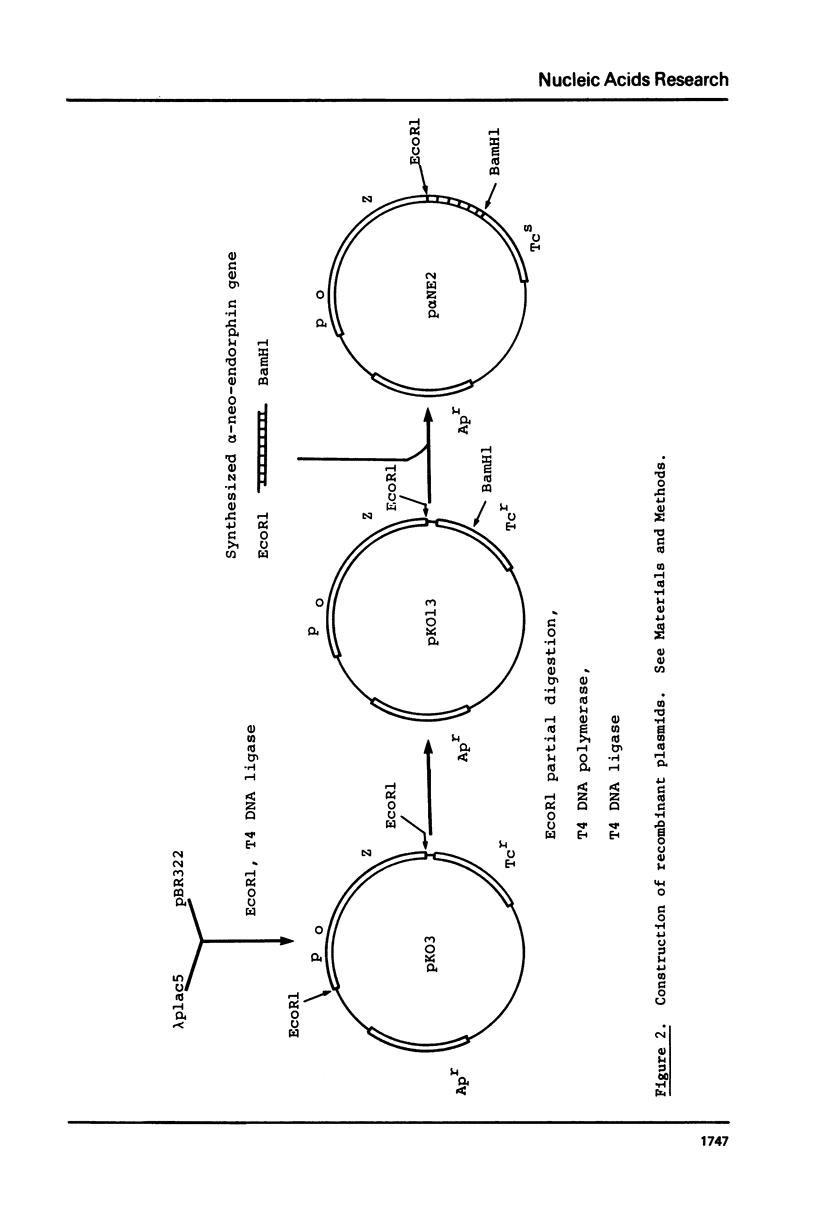
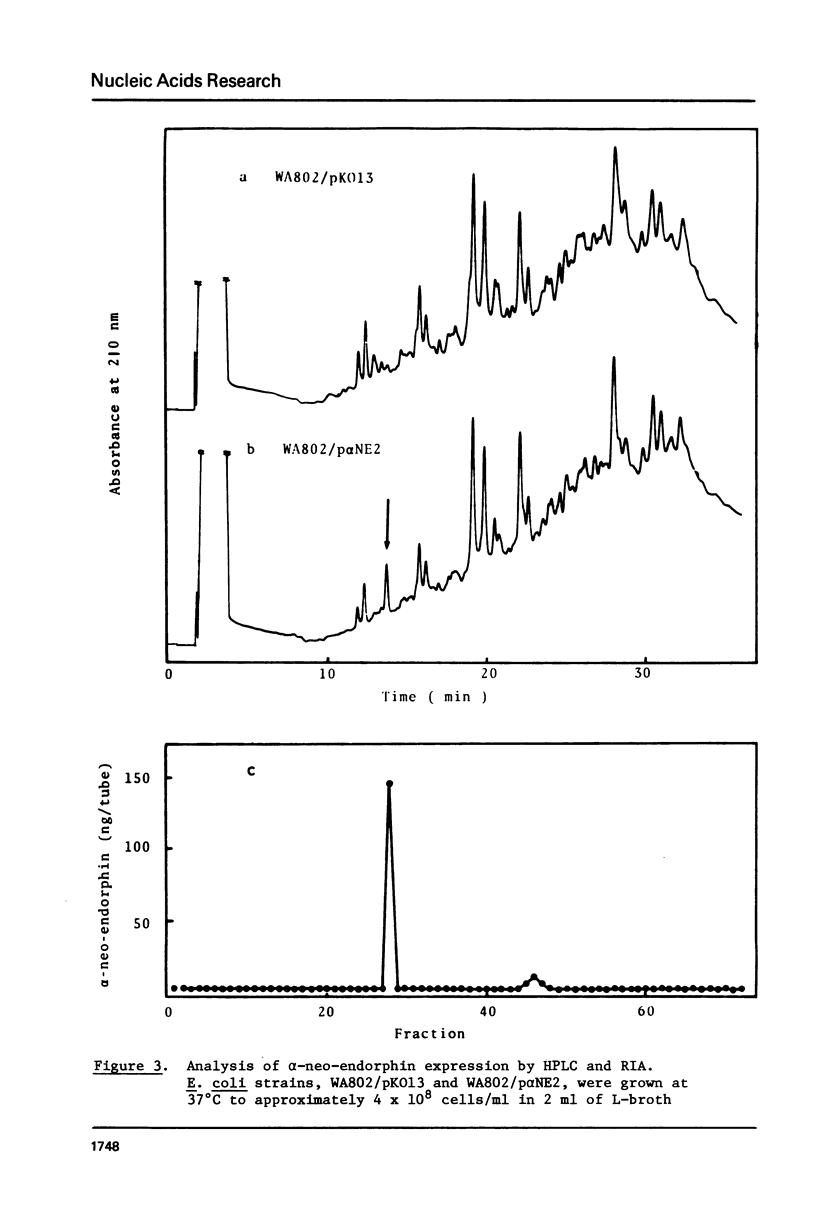
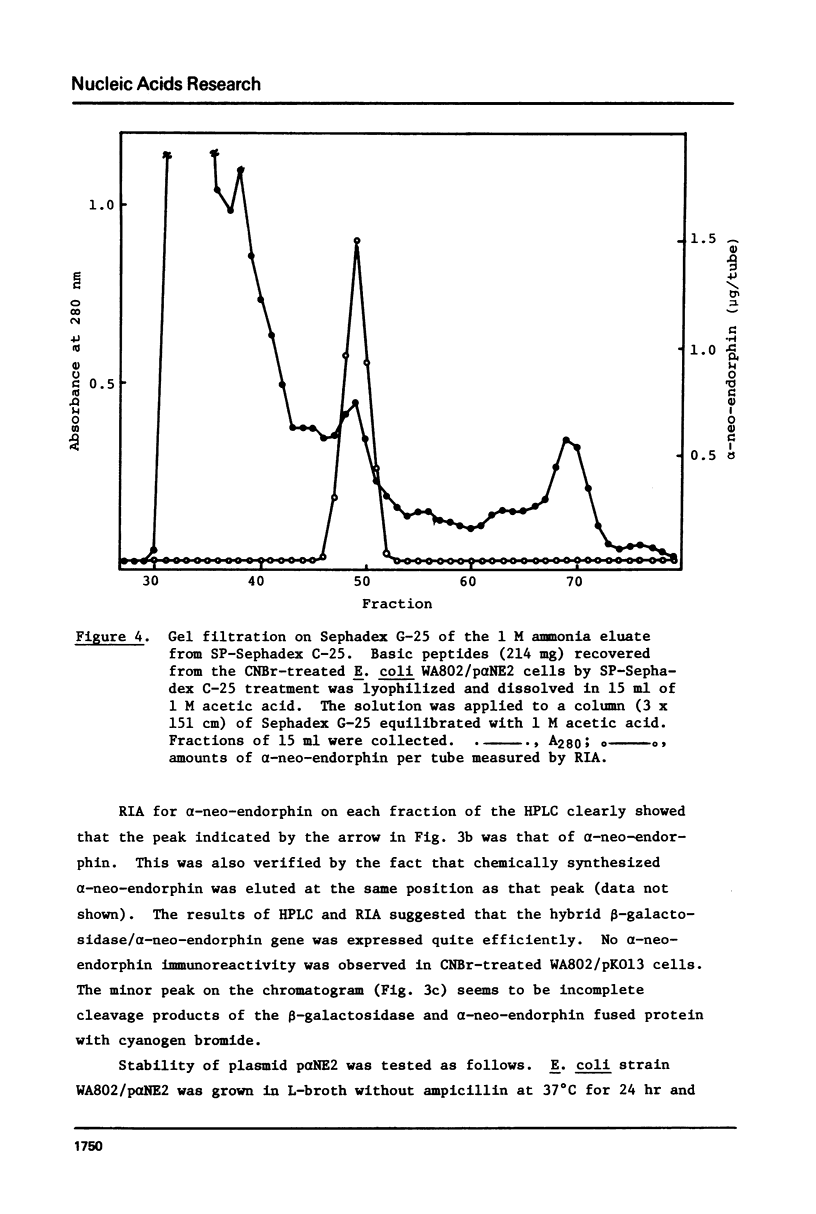
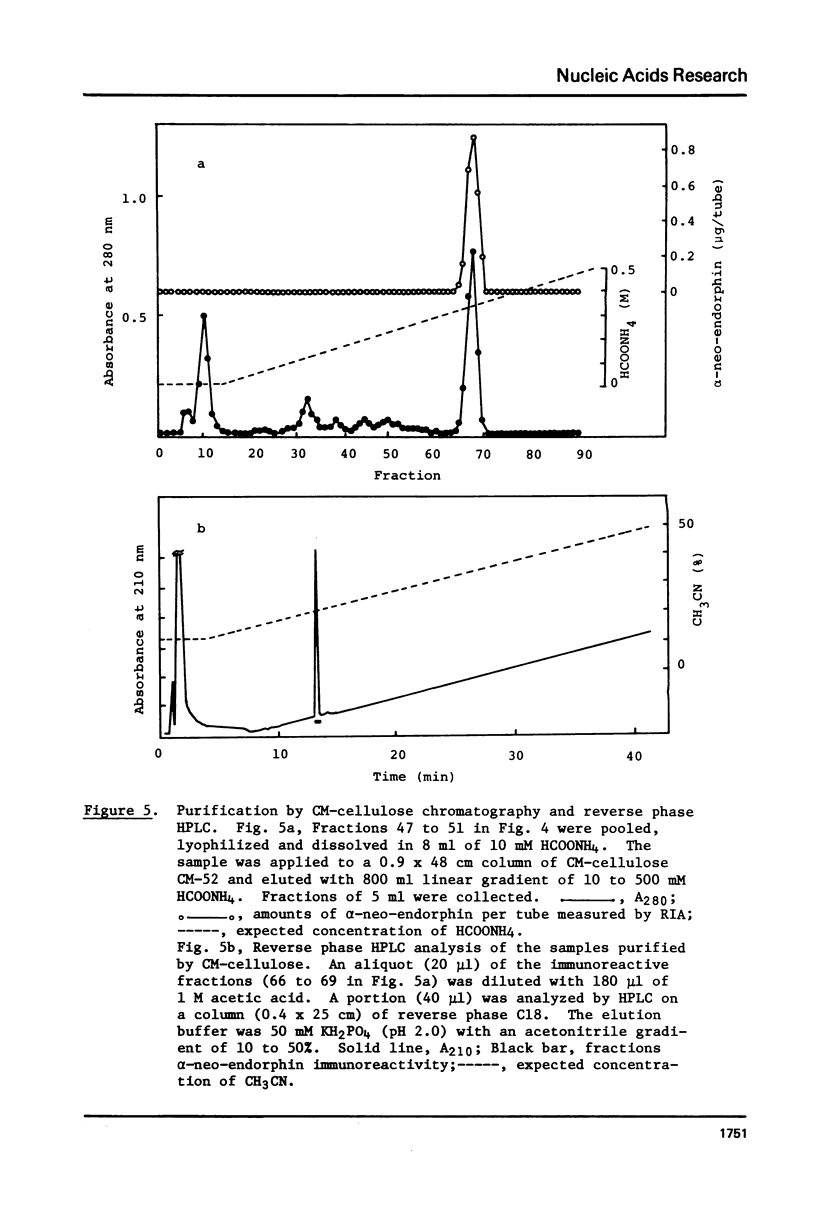
Chemically synthesized alpha-neo-endorphin gene was fused to the Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase gene on the plasmid pKO13. The resulting recombinant DNA was used to transform E. coli cells. Radioimmunoassay for alpha-neo-endorphin in CNBr-treated bacterial cells showed that alpha-neo-endorphin was synthesized at approximately 5 x 10(5) molecules per single E. coli cell. One of the transformants, WA802/p alpha NE2, was used for alpha-neo-endorphin purification. From 10.9 g of wet cells, we isolated 4 mg of chemically pure and biologically active alpha-neo-endorphin.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Goeddel D. V., Heyneker H. L., Hozumi T., Arentzen R., Itakura K., Yansura D. G., Ross M. J., Miozzari G., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. Direct expression in Escherichia coli of a DNA sequence coding for human growth hormone. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):544–548. doi: 10.1038/281544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Kleid D. G., Bolivar F., Heyneker H. L., Yansura D. G., Crea R., Hirose T., Kraszewski A., Itakura K., Riggs A. D. Expression in Escherichia coli of chemically synthesized genes for human insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):106–110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura K., Hirose T., Crea R., Riggs A. D., Heyneker H. L., Bolivar F., Boyer H. W. Expression in Escherichia coli of a chemically synthesized gene for the hormone somatostatin. Science. 1977 Dec 9;198(4321):1056–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.412251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay E., Bambara R., Padmanabhan R., Wu R. DNA sequence analysis: a general, simple and rapid method for sequencing large oligodeoxyribonucleotide fragments by mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Mar;1(3):331–353. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangawa K., Matsuo H. alpha-Neo-endorphin : a "big" Leu-enkephalin with potent opiate activity from porcine hypothalami. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jan 15;86(1):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90394-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangawa K., Minamino N., Chino N., Sakakibara S., Matsuo H. The complete amino acid sequence of alpha-neo-endorphin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 15;99(3):871–878. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91244-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Inoue A., Kita T., Nakamura M., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Numa S. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA for bovine corticotropin-beta-lipotropin precursor. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):423–427. doi: 10.1038/278423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Zar M. A. The origin of acetylcholine released from guinea-pig intestine and longitudinal muscle strips. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):13–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polisky B., Bishop R. J., Gelfand D. H. A plasmid cloning vehicle allowing regulated expression of eukaryotic DNA in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3900–3904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



