Abstract
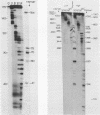
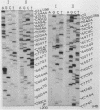
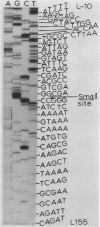
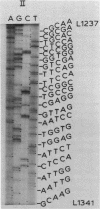
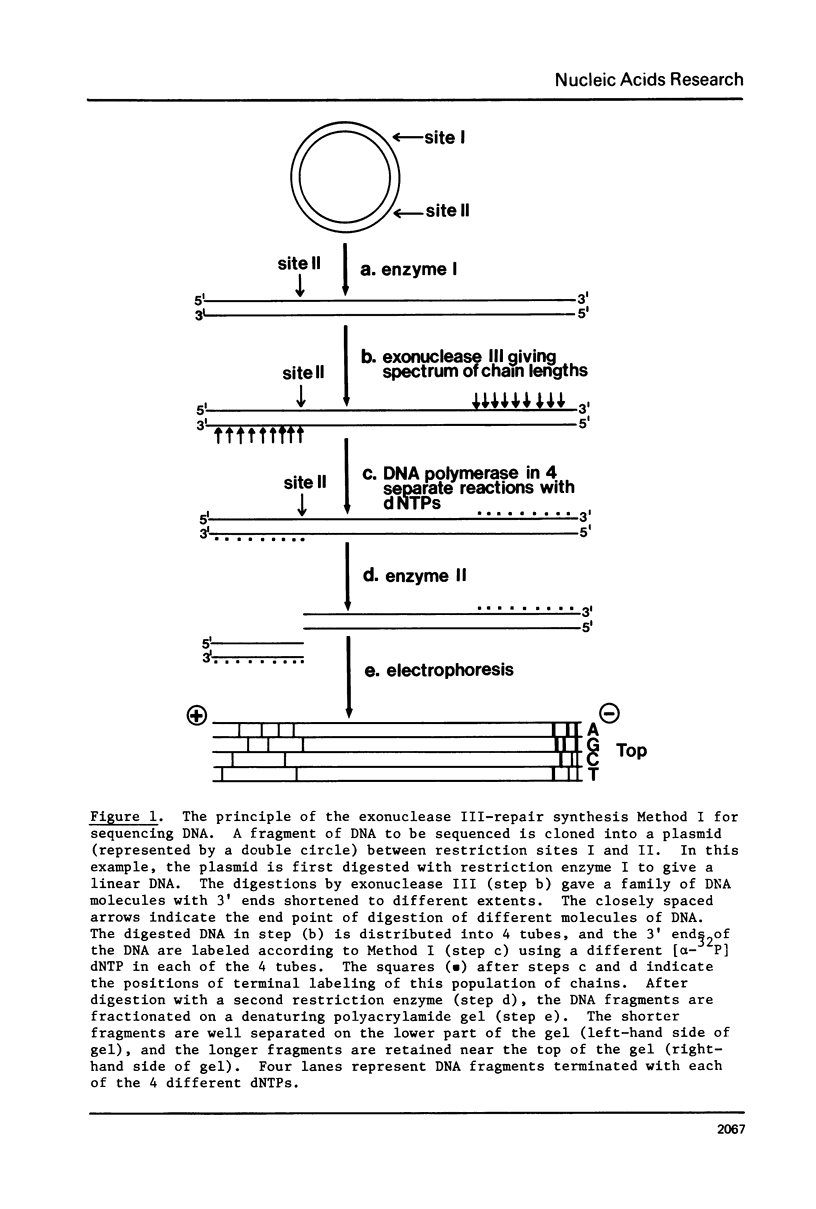
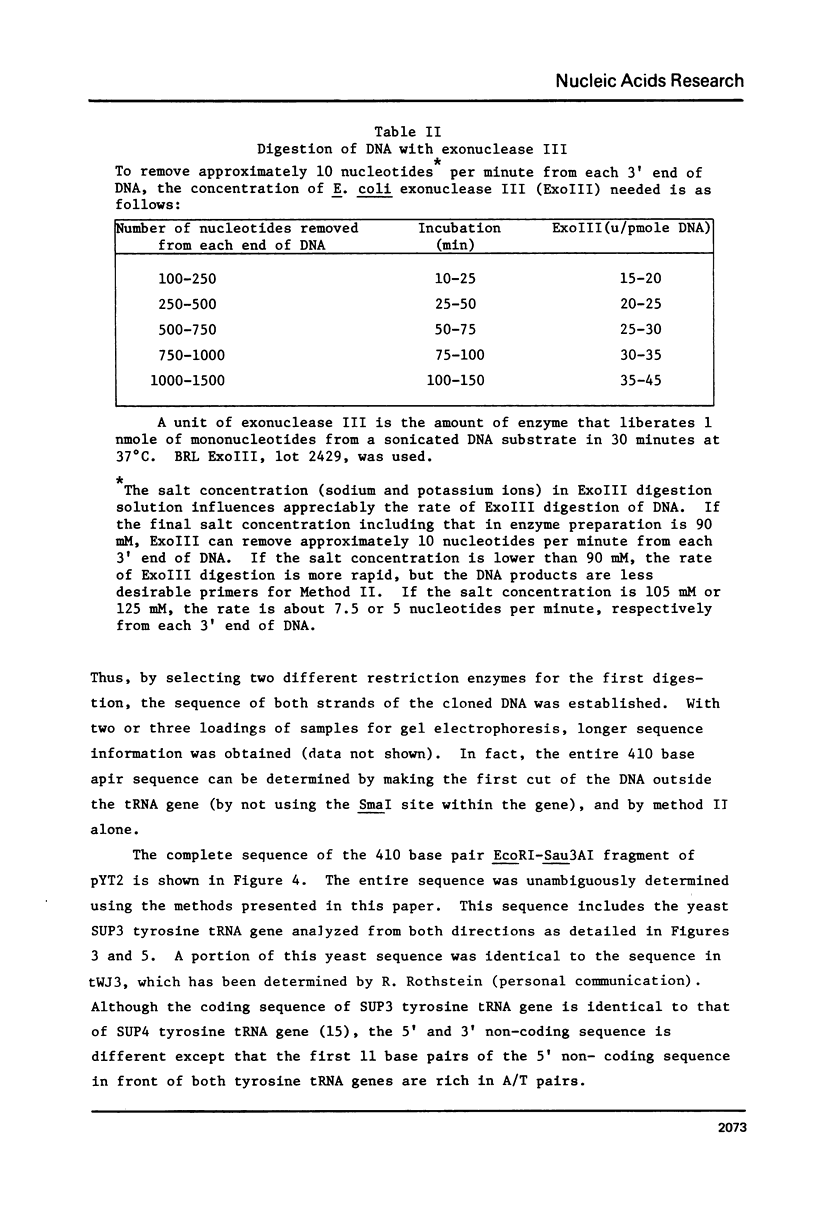
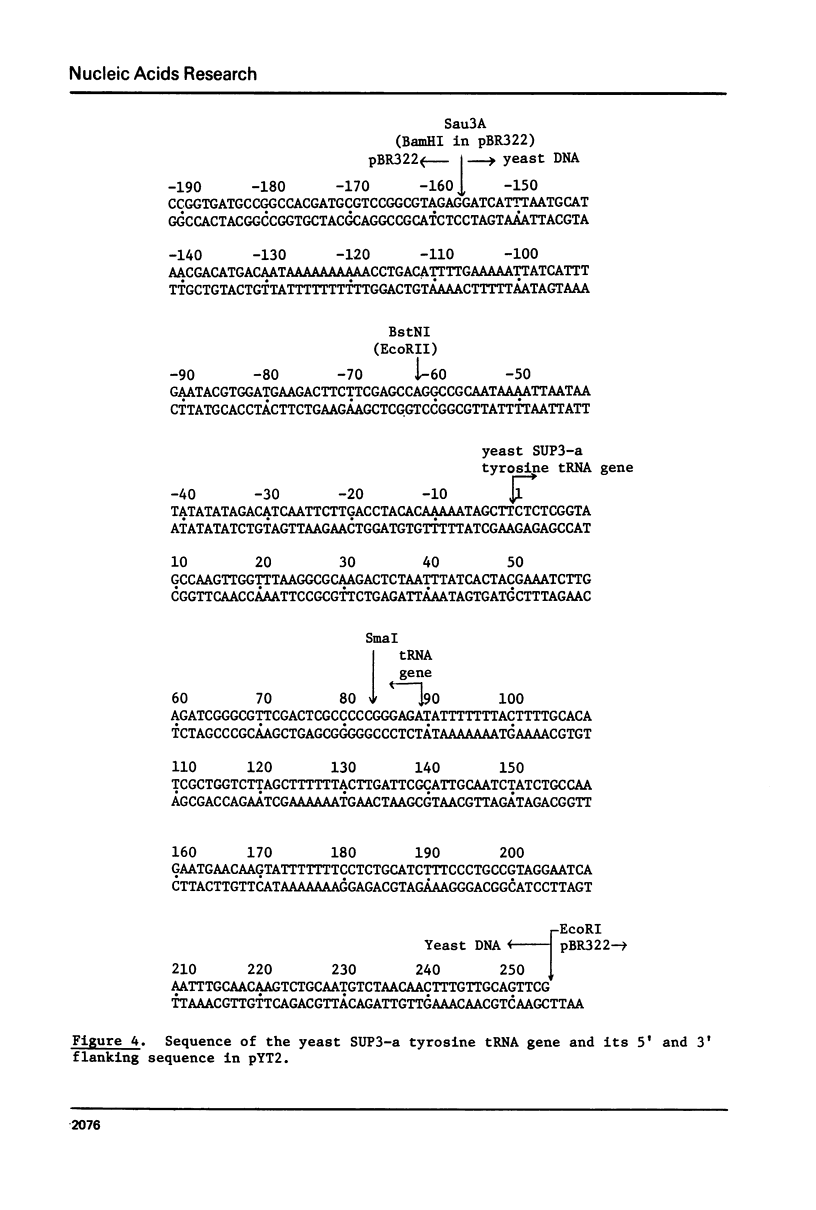
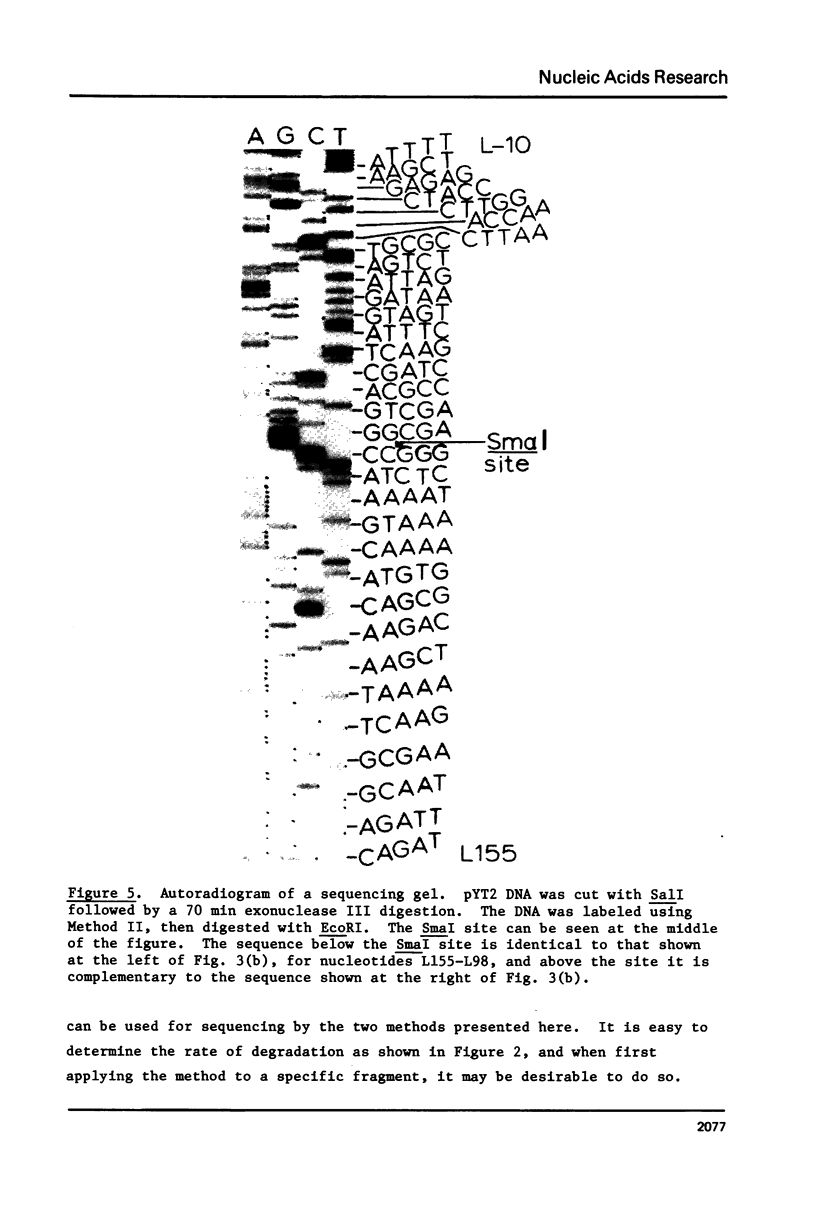
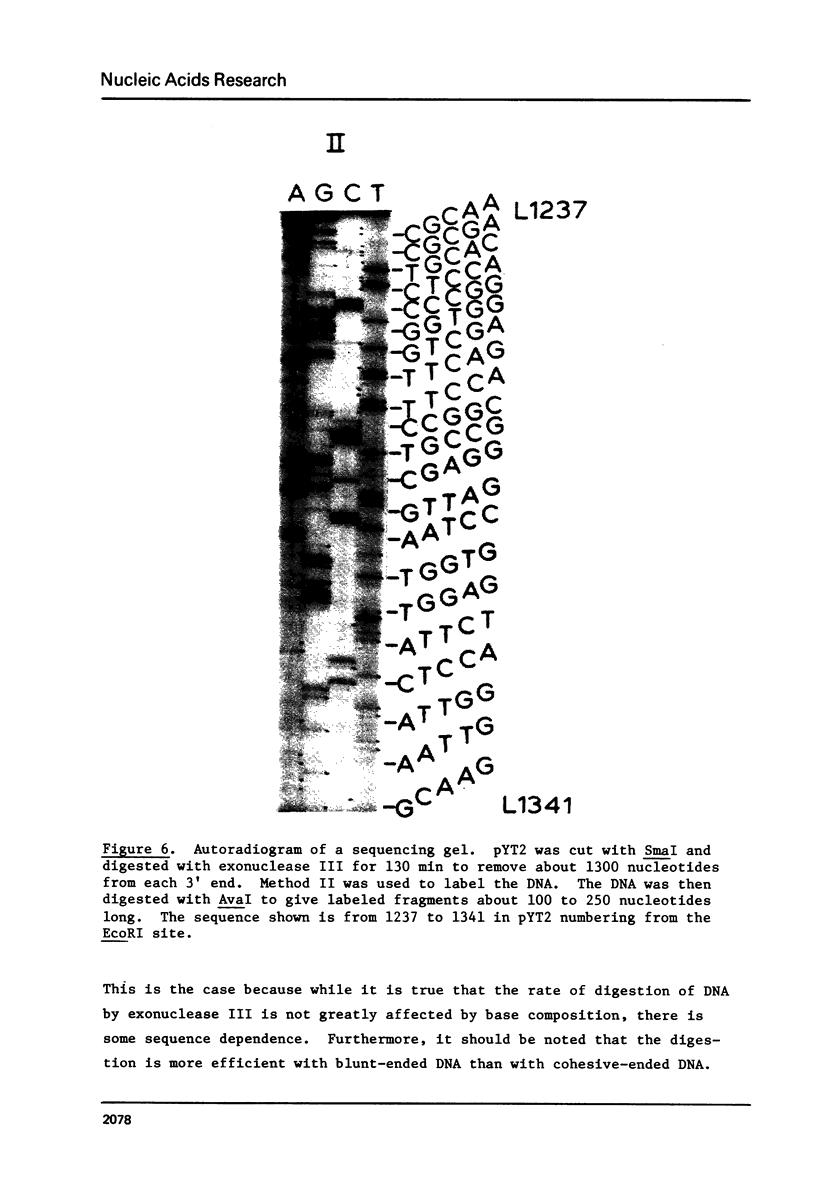
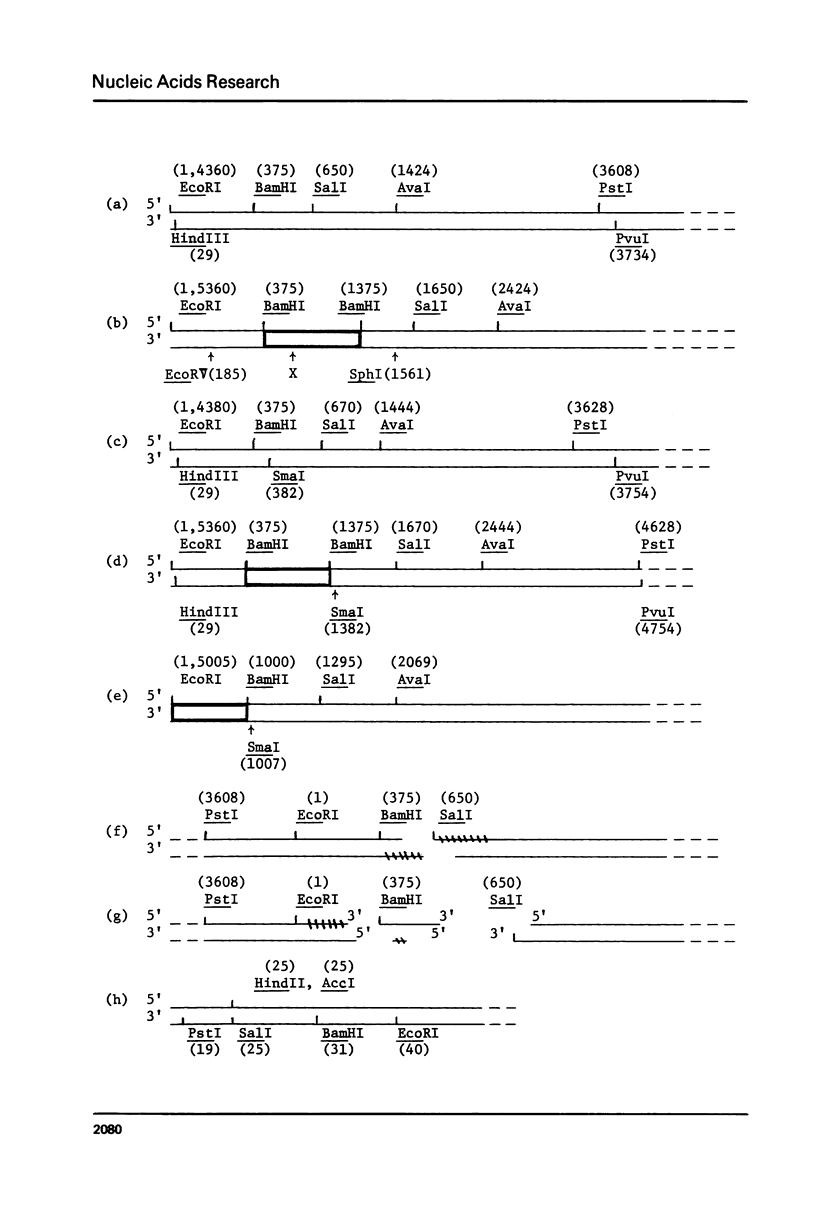
We describe improve enzymatic methods for sequencing method for sequencing DNA. They are based on partial digestion of duplex DNA with exonuclease III to produce DNA molecules with 3' ends shortened to varying lengths, followed by repair synthesis to extend and label the 3' ends. After asymmetrical cleavage of the DNA with a restriction enzyme, the labeled products are separated by gel electrophoresis and the sequence read from the autoradiogram. The entire procedures, beginning with unrestricted DNA and followed through gel electrophoresis, takes only one day for sequencing both strands of the DNA molecule. These methods are especially suitable for sequencing DNA cloned in plasmid vectors, and they greatly extend the usefulness of the dideoxynucleotide chain termination method of Sanger et al. (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74, 5463, 1977). Using these methods we have determined the sequence of a 410 base pair fragment which includes the yeast SUP3 tyrosine tRNA gene.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donelson J. E., Wu R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of deoxyribonucleic acid. VI. Determination of 3'-terminal dnucleotide sequences of several species of duplex deoxyribonucleic acid using Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4654–4660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. M., Olson M. V., Hall B. D. Nucleotide sequence of a mutant eukaryotic gene: the yeast tyrosine-inserting ochre suppressor SUP4-o. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5453–5457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Lehman I. R., Kaiser A. D. An exonuclease induced by bacteriophage lambda. I. Preparation of the crystalline enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):672–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON C. C., LEHMAN I. R., KORNBERG A. A DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID PHOSPHATASE-EXONUCLEASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. II. CHARACTERIZATION OF THE EXONUCLEASE ACTIVITY. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J., Lau L. F., Bahl C. P., Narang S. A., Wu R. Synthetic adaptors for cloning DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:98–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Koenen M., Otto K., Müller-Hill B. pUR222, a vector for cloning and rapid chemical sequencing of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4087–4098. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier P. H., Cortese R. A fast and simple method for sequencing DNA cloned in the single-stranded bacteriophage M13. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 25;129(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif I., Khoury G., Dhar R. A rapid enzymatic DNA sequencing technique: determination of sequence alterations in early simian virus 40 temperature sensitive and deletion mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2225–2240. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J. The use of exonuclease III for preparing single stranded DNA for use as a template in the chain terminator sequencing method. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Mar;6(3):831–848. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.3.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Ruben G., Siegel B., Jay E., Spielman P., Tu C. P. Synchronous digestion of SV40 DNA by exonuclease III. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):734–740. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Taylor E. Nucleotide sequence analysis of DNA. II. Complete nucleotide sequence of the cohesive ends of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 14;57(3):491–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Tu C. D., Padmanabhan R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of DNA. XII. The chemical synthesis and sequence analysis of a dodecadeoxynucleotide which binds to the endolysin gene of bacteriophage lambda. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 19;55(4):1092–1099. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zain B. S., Roberts R. J. Sequences from the beginning of the fiber messenger RNA of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):341–352. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]