Abstract
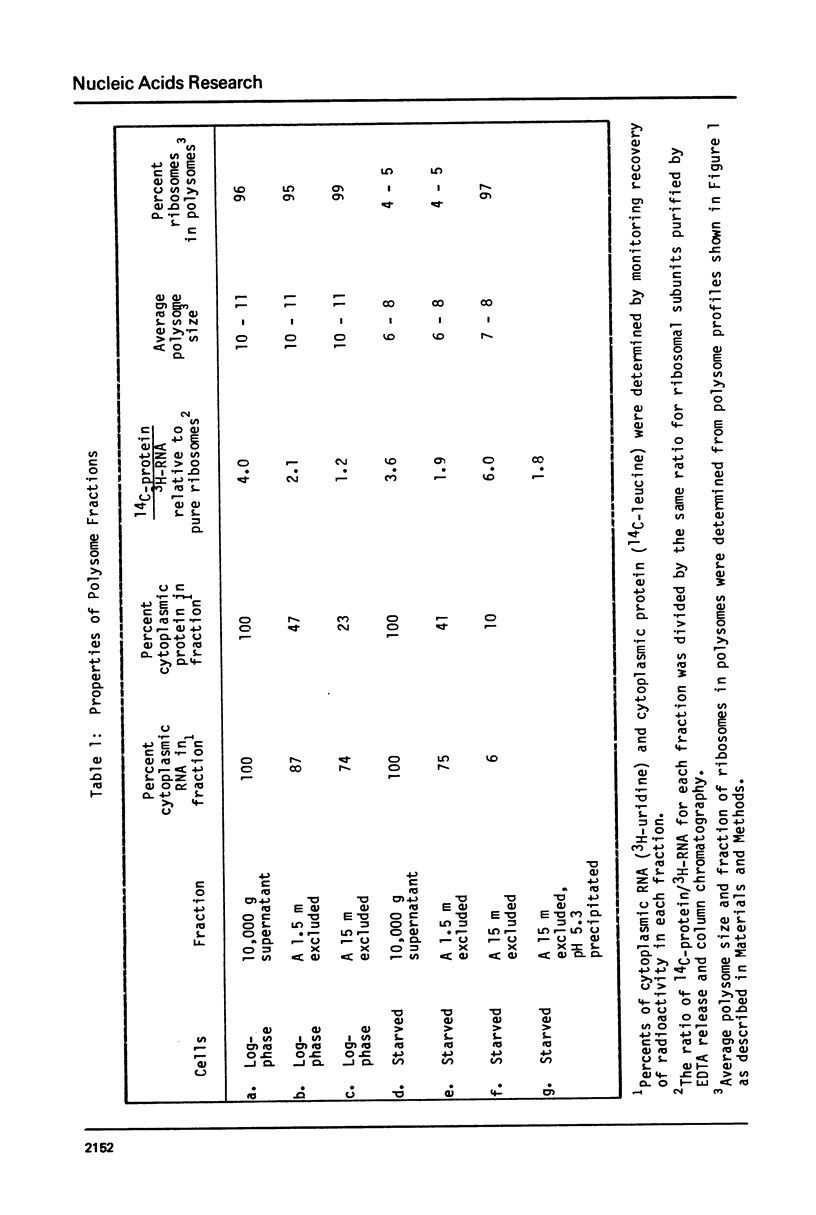
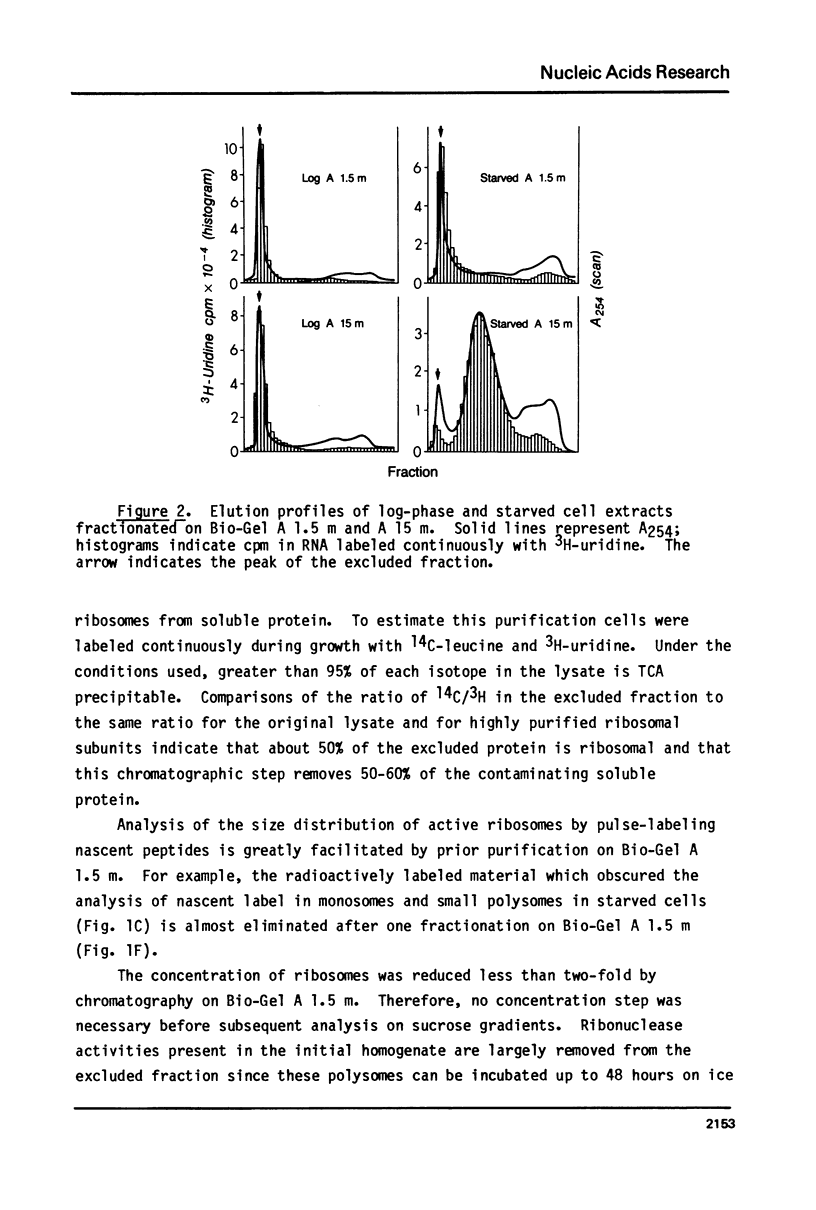
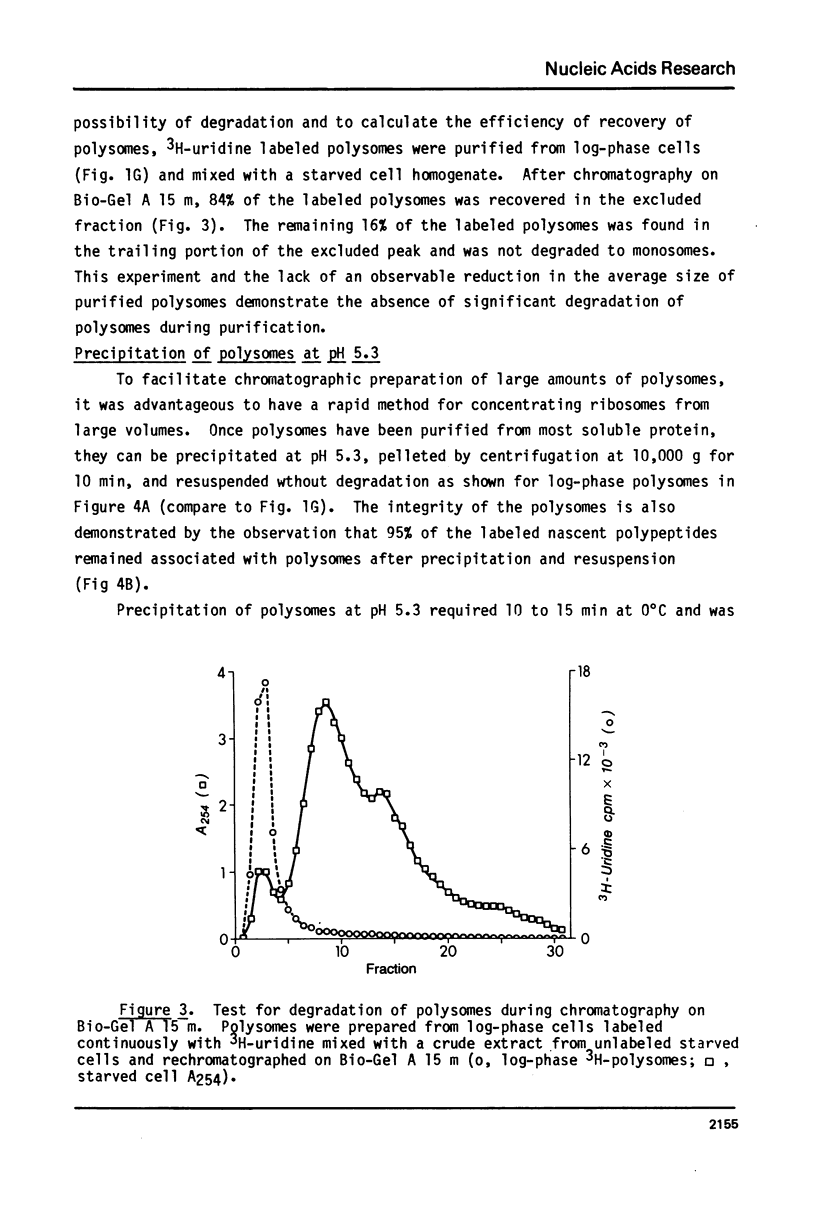
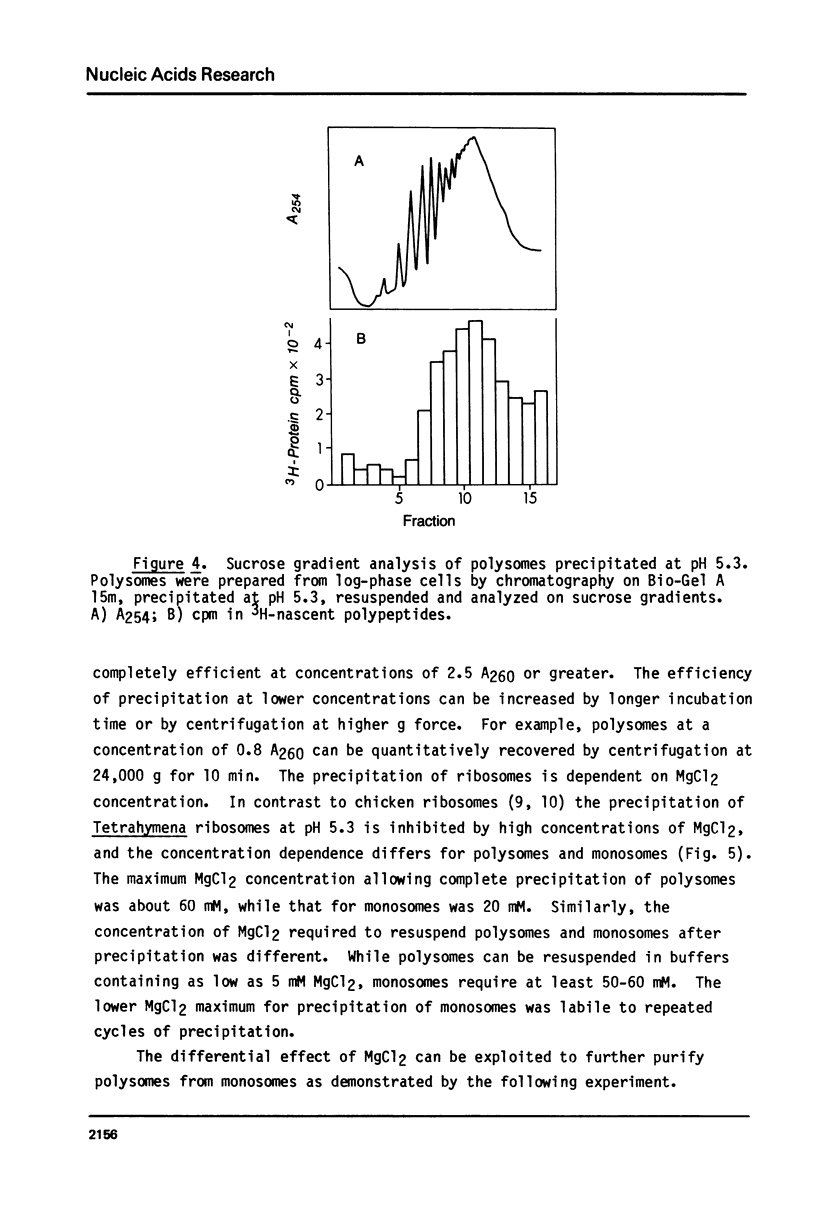
The fraction of ribosomes loaded on polysomes is about 95% in logarithmically growing Tetrahymena thermophila, and about 4% in starved cells. Cytoplasmic extracts from cells in these two physiological states were used to develop column chromatographic methods for the purification of polysomes. Bio-Gel A 1.5 m was found to separate total cytoplasmic ribosomes from many soluble proteins, including RNAse, with no detectable change in the polysome size distribution. Polysomes can be separated from monosomes and non-polysomal mRNA by chromatography on Bio-Gel A 15 m without size selection. These methods can easily be adapted to large scale preparations of polysomes, even from cells where a small fraction of the ribosomes is on polysomes. A method is described for reversible precipitation of polysomes and monosomes from dilute solutions at pH 5.3 which greatly facilitates polysome isolation. Hybridization of 3H-labeled polyU to RNA isolated from column fractions has been used to demonstrate that purification of EDTA released polysomal mRNA can be performed using the column chromatography procedures described here. These methods have been employed to demonstrate that most of the cytoplasmic mRNA in log-phase Tetrahymena is loaded onto polysomes while most of the mRNA is starved cells exists in a non-polysomal form.
Full text
PDF







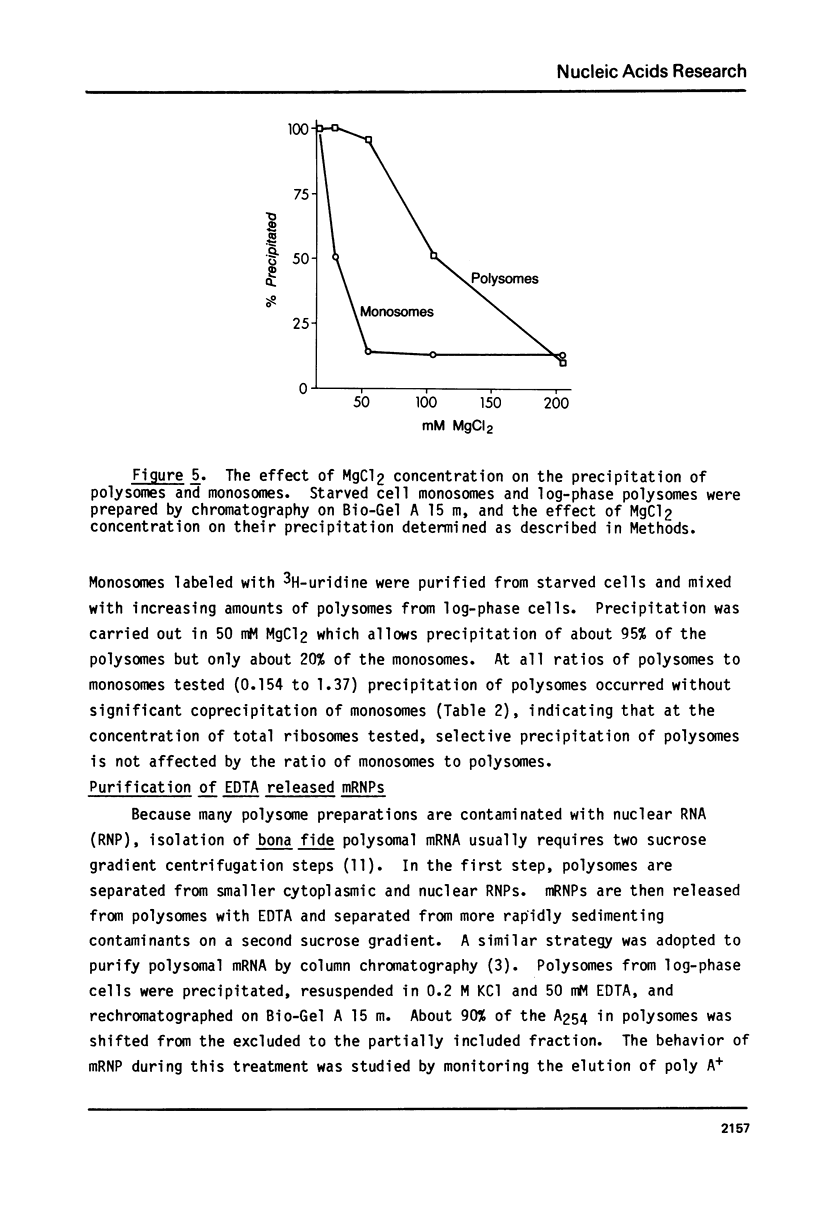
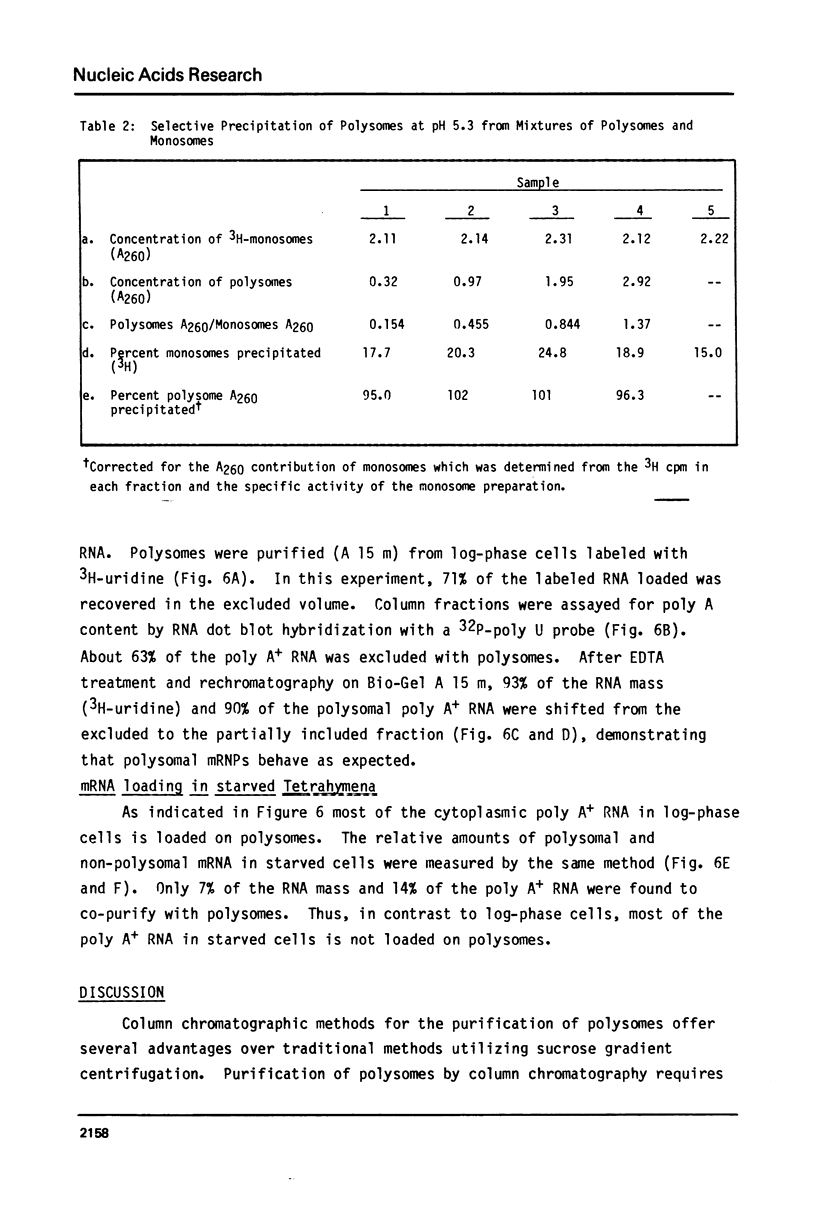
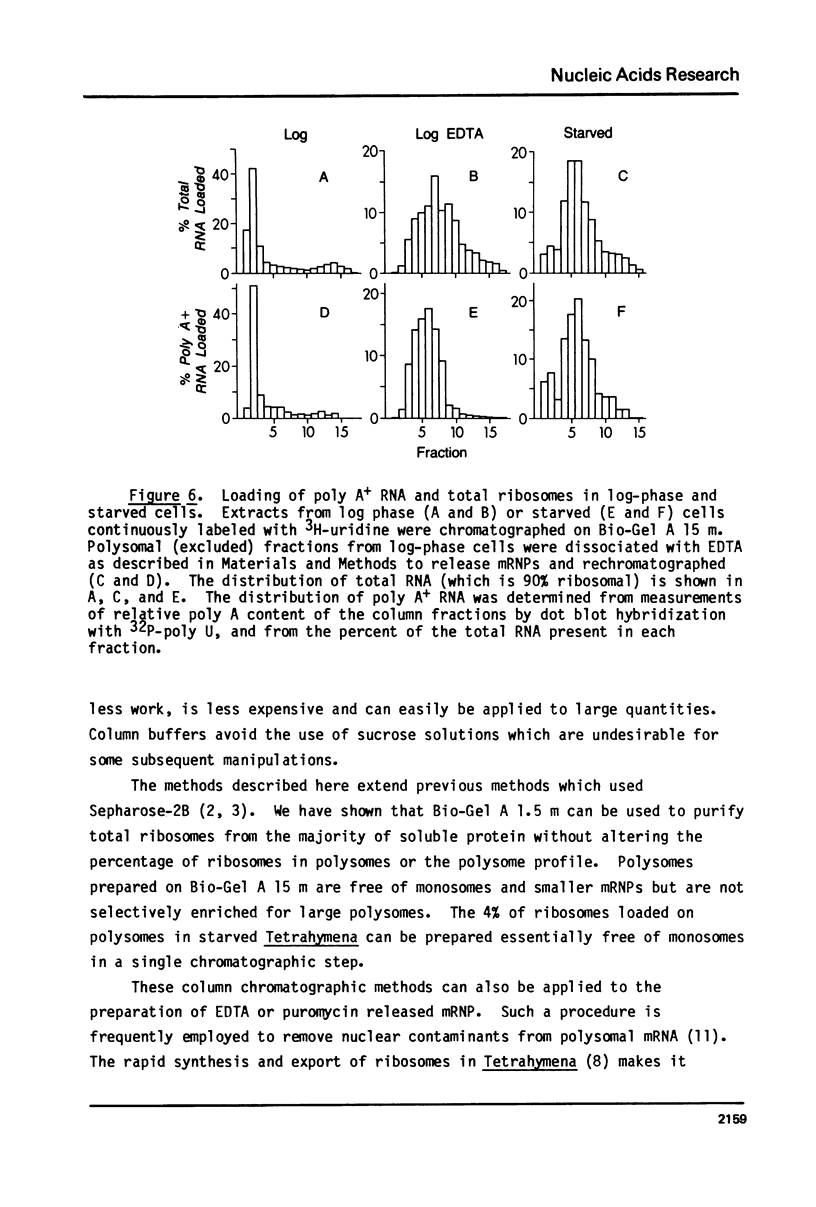


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Detection of poly A+ RNA in sea urchin eggs and embryos by quantitative in situ hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2819–2840. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bast R. E., Garfield S. A., Gehrke L., Ilan J. Coordination of ribosome content and polysome formation during estradiol stimulation of vitellogenin synthesis in immature male chick livers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3133–3137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns P. J., Brussard T. B. Pair formation in tetrahymena pyriformis, an inducible developmental system. J Exp Zool. 1974 Jun;188(3):337–344. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401880309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galau G. A., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. A measurement of the sequence complexity of polysomal messenger RNA in sea urchin embryos. Cell. 1974 May;2(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg R. L., Bruns P. J. Ribosome biosynthesis in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Regulation in response to nutritional changes. J Cell Biol. 1976 Nov;71(2):383–394. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Kaumeyer J. F., Young E. M., Raff R. A. A test for masked message: the template activity of messenger ribonucleoprotein particles isolated from sea urchine eggs. Dev Biol. 1978 Apr;63(2):279–298. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleinick N. L., Rustad R. C., Kuncio G. S. Studies on the radiation-induced dissociation and reassociation of polysomes in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 11;366(2):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90335-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Magnesium precipitation of ribonucleoprotein complexes. Expedient techniques for the isolation of undergraded polysomes and messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3606–3615. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Digan M. E., Mahowald A. P., Scott M., Craig E. A. Two clusters of genes for major chorion proteins of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):905–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swiderski R. E., Johnson S. A., Larkins B. A., Graham D. E. Sequential Sepharose chromatographic isolation of polysomes and polysomal RNAs depleted in nuclear RNA from Xenopus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3685–3701. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Wallace B. J., Herzog E. L., Davis B. D. Properties of initiation-free polysomes of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):609–615. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



