Abstract
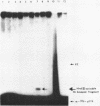
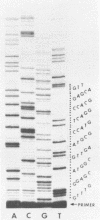
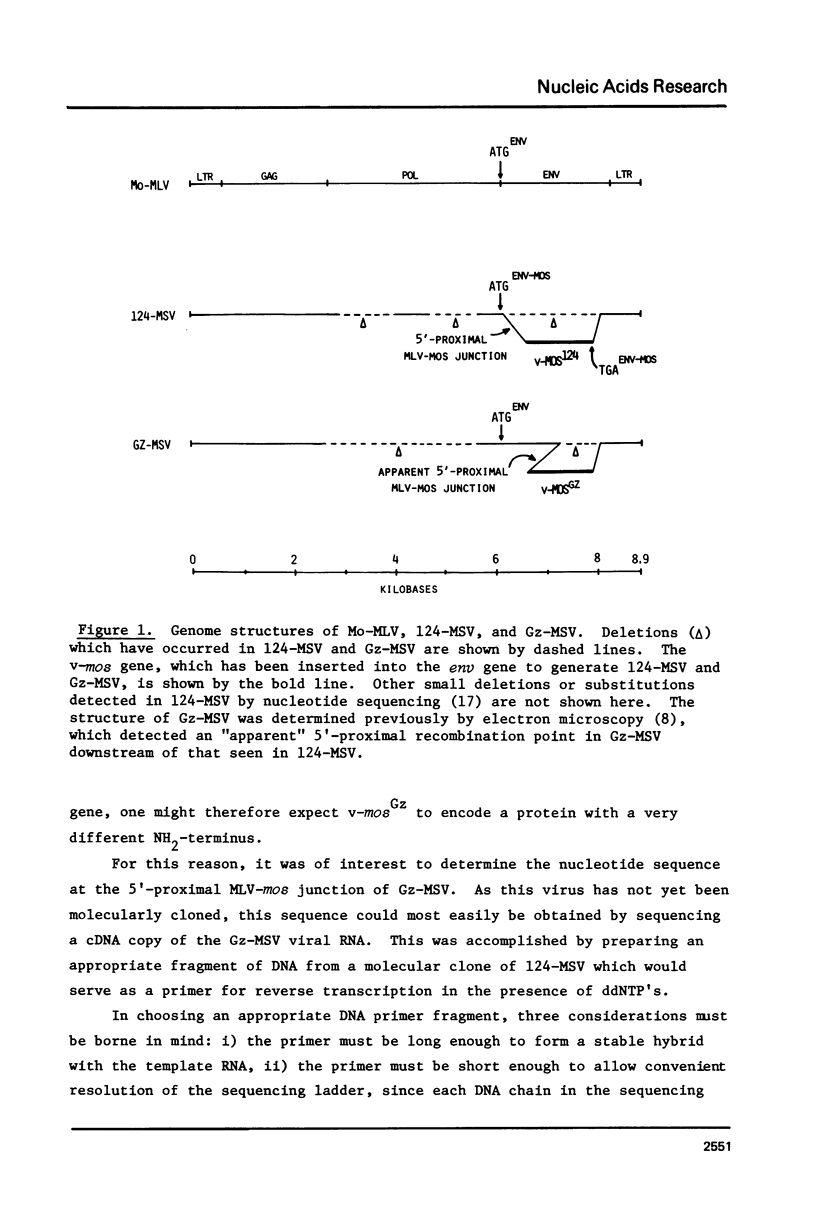
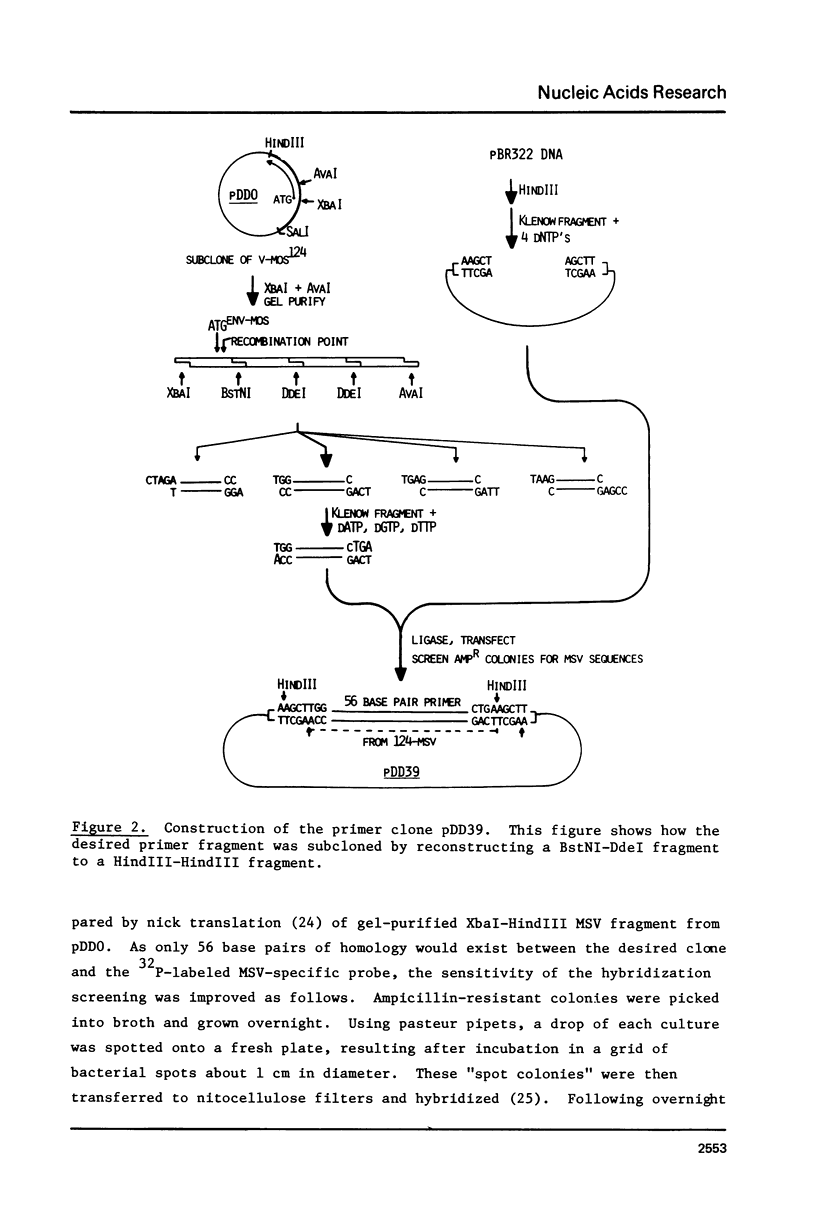
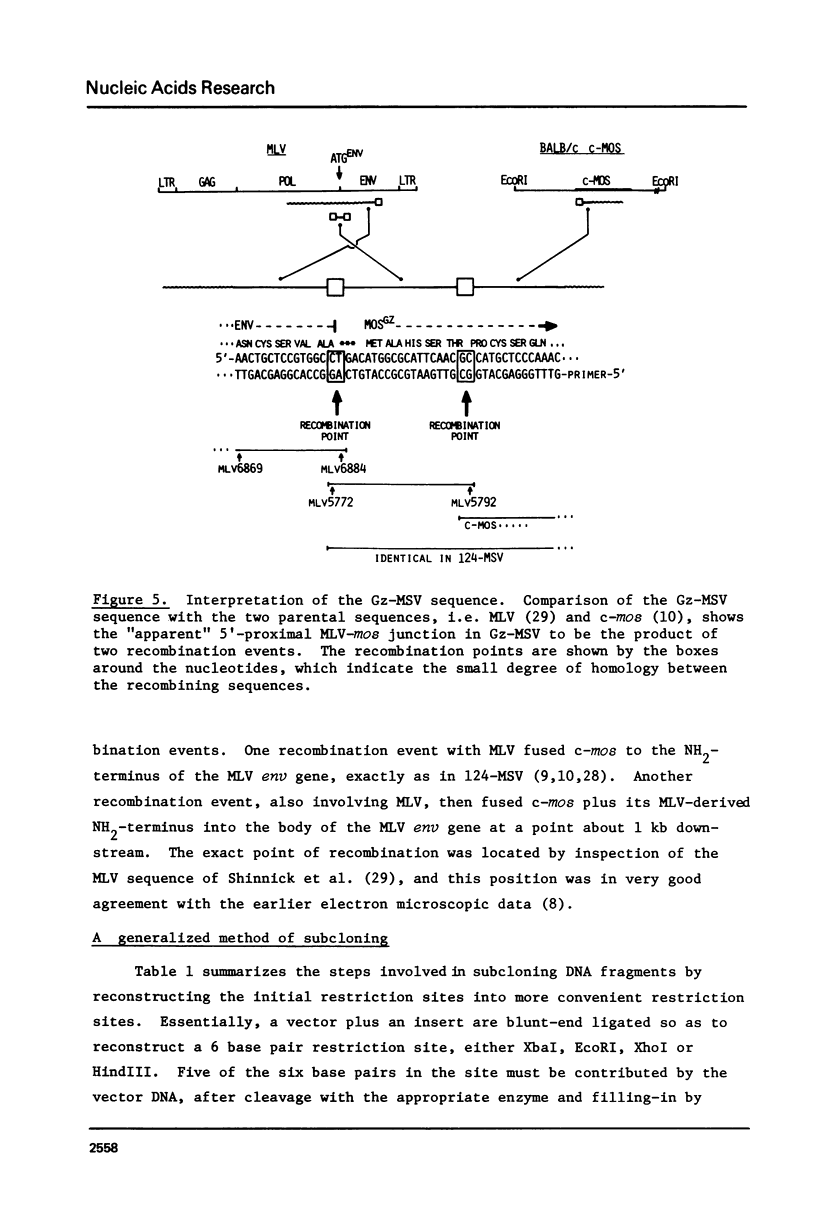
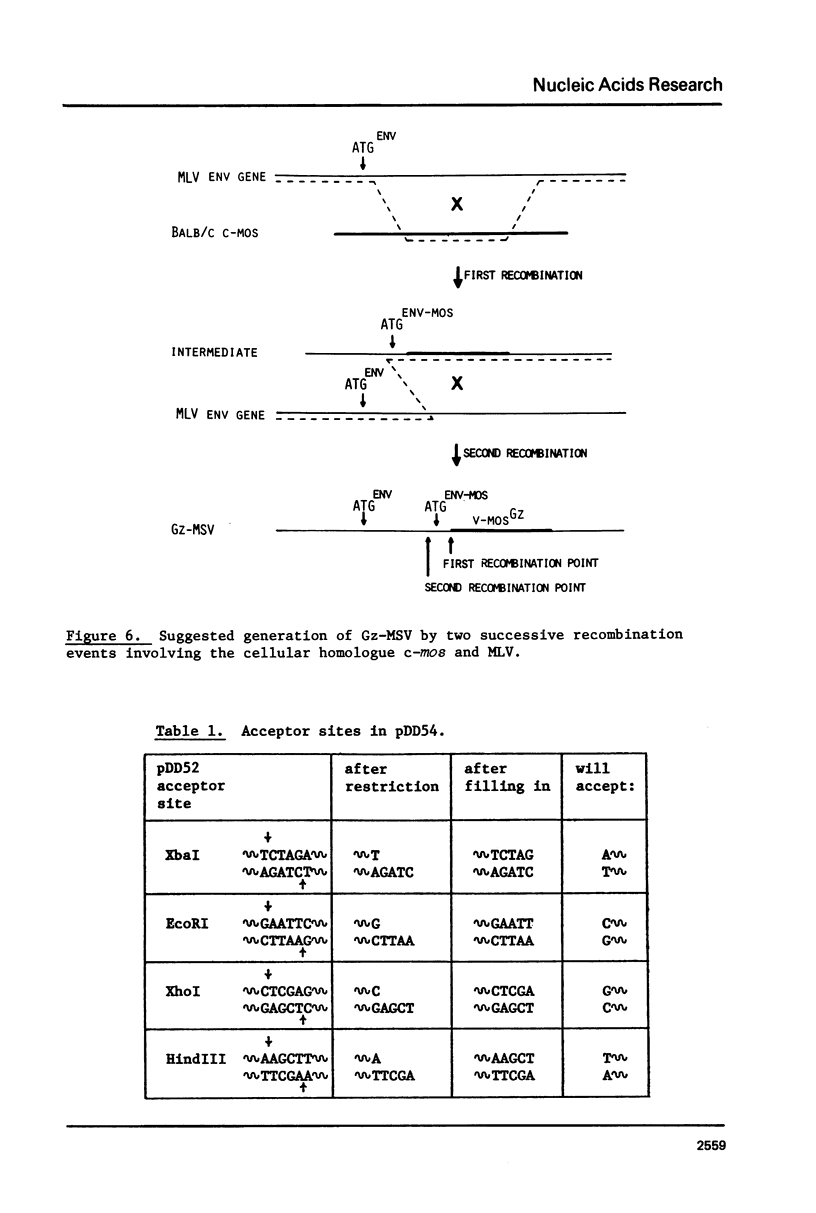
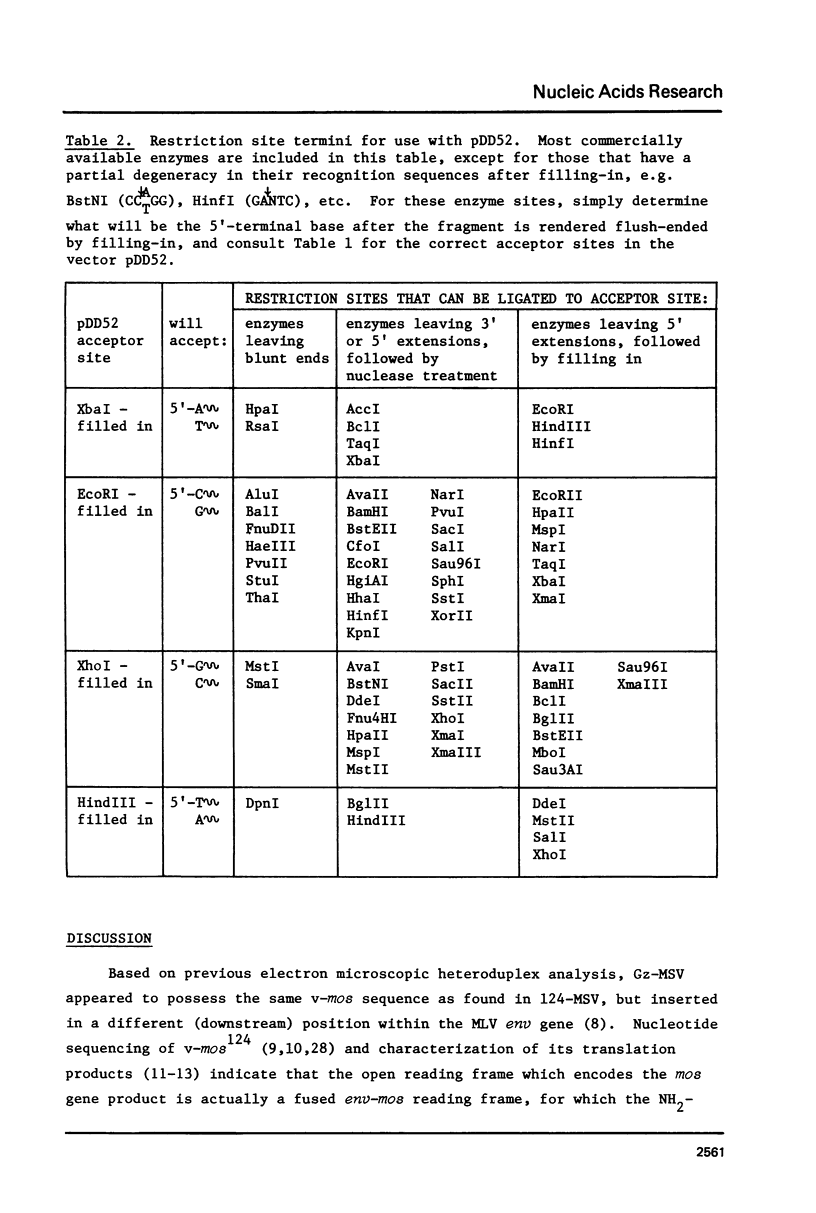
The technique of restriction site reconstruction was generalized so as to allow the subcloning of any DNA fragment and its subsequent reexcision with EcoRI, XbaI, XhoI or HindIII. After excision, the 3' terminus of each strand will be derived from the starting nucleic acid, permitting the use of such fragments as primers for nucleotide sequencing by primer extension methods. The technique was used to subclone a 56 base pair BstNI-DdeI fragment of Moloney murine sarcoma virus (Mo-MSV) as a unique HindIII-HindIII fragment. This fragment then served as a primer to sequence a portion of the RNA genome of Gazdar murine sarcoma virus (Gz-MSV). The nucleotide sequence which was obtained indicated that the transforming gene of Gz-MSV arose by at least two recombination events involving murine leukemia virus (MLV) and the cellular homologue c-mos. This analysis suggests that a virus indistinguishable from Mo-MSV was an intermediate in the formation of Gz-MSV.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baralle F. Complete nucleotide sequence of the 5' noncoding region of human alpha-and beta-globin mRNA. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1085–1095. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bina-Stein M., Thoren M., Salzman N., Thomspon J. A. Rapid sequence determination of late simian virus 40 16S mRNA leader by using inhibitors of reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):731–735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer K., Reddy E. P., Aaronson S. A. Translational products of Moloney murine sarcoma virus RNA: identification of proteins encoded by the murine sarcoma virus src gene. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):704–711. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.704-711.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue D. J., Hunter T. Expression of transforming region of Moloney murine sarcoma virus in Escherichia coli as a fusion protein with small tumor antigen of polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):800–804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue D. J., Sharp P. A., Weinberg R. A. Comparative study of different isolates of murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):1015–1027. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.1015-1027.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti L., Sgaramella V. Temperature dependence of the joining by T4 DNA ligase of termini produced by type II restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):85–93. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Chopra H. C., Sarma P. S. Properties of a murine sarcoma virus isolated from a tumor arising in an NZW-NZB F 1 hybrid mouse. I. Isolation and pathology of tumors induced in rodents. Int J Cancer. 1972 Jan 15;9(1):219–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Piatak M., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Determination of RNA sequences by primer directed synthesis and sequencing of their cDNA transcripts. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):580–595. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McReynolds L., O'Malley B. W., Nisbet A. D., Fothergill J. E., Givol D., Fields S., Robertson M., Brownlee G. G. Sequence of chicken ovalbumin mRNA. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):723–728. doi: 10.1038/273723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moloney J. B. A virus-induced rhabdomyosarcoma of mice. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Sep;22:139–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation and preservation of competent bacterial cells by freezing. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:326–331. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oskarsson M., McClements W. L., Blair D. G., Maizel J. V., Vande Woude G. F. Properties of a normal mouse cell DNA sequence (sarc) homologous to the src sequence of Moloney sarcoma virus. Science. 1980 Mar 14;207(4436):1222–1224. doi: 10.1126/science.6243788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page G. S., Smith S., Goodman H. M. DNA sequence of the rat growth hormone gene: location of the 5' terminus of the growth hormone mRNA and identification of an internal transposon-like element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 11;9(9):2087–2104. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.9.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang R. H., Phillips L. A., Haapala D. K. Characterization of Gazdar murine sarcoma virus by nucleic acid hybridization and analysis of viral expression in cells. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):551–556. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.551-556.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Hunter T., Beemon K. In vitro translation of virion RNA from Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):91–103. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90486-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Lai M. H., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Analysis of transforming gene products from Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90365-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Stiles J. I., Bahl C. P., Wu R. Specific binding of a synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide to yeast cytochrome c mRNA. Nature. 1977 Jan 6;265(5589):61–63. doi: 10.1038/265061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Cameron J. R., Davis R. W. Viable molecular hybrids of bacteriophage lambda and eukaryotic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4579–4583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., Galleshaw J. A., Jonas V., Berns A. J., Doolittle R. F., Donoghue D. J., Verma I. M. Nucleotide sequence and formation of the transforming gene of a mouse sarcoma virus. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):258–262. doi: 10.1038/289258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Galleshaw J. A., Verma I. M. Nucleotide sequence of the genome of a murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90364-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]