Abstract
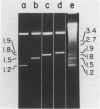
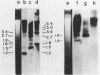
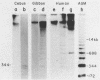
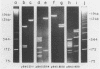
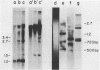
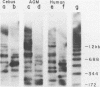
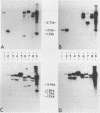
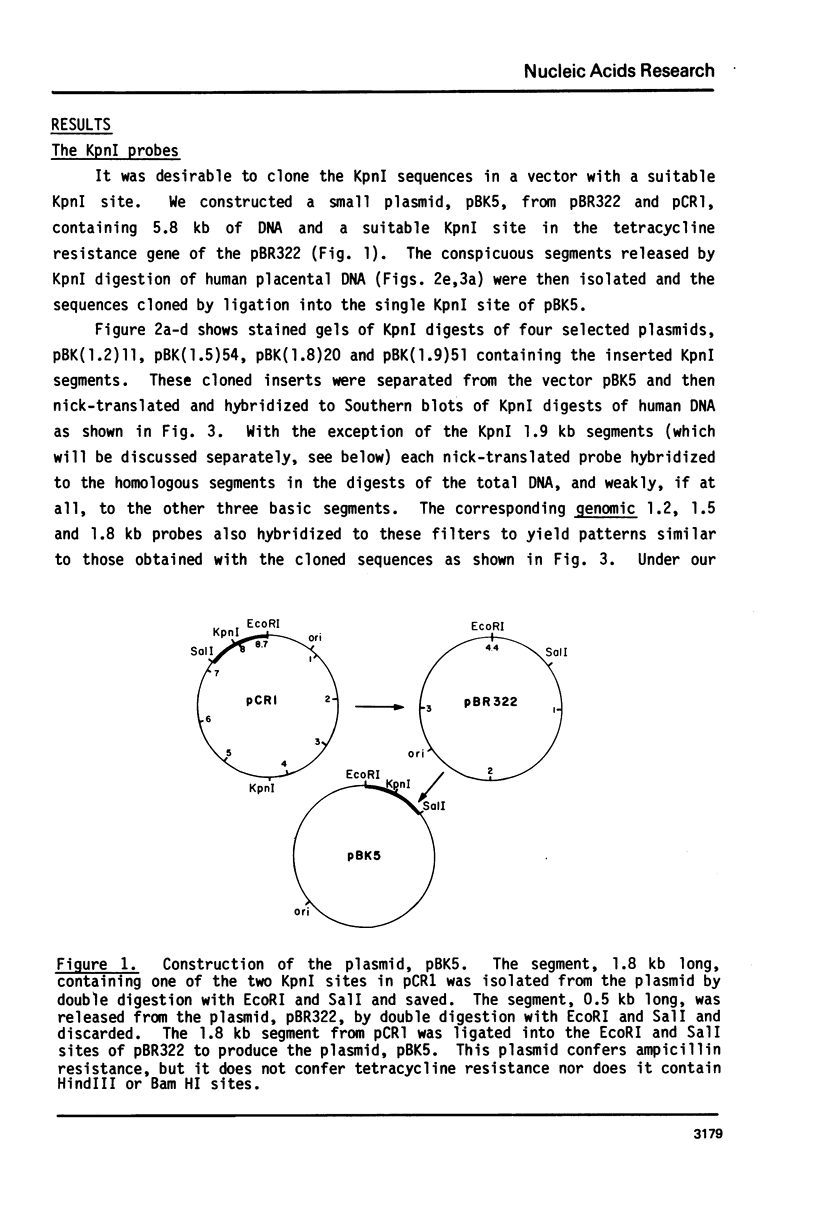
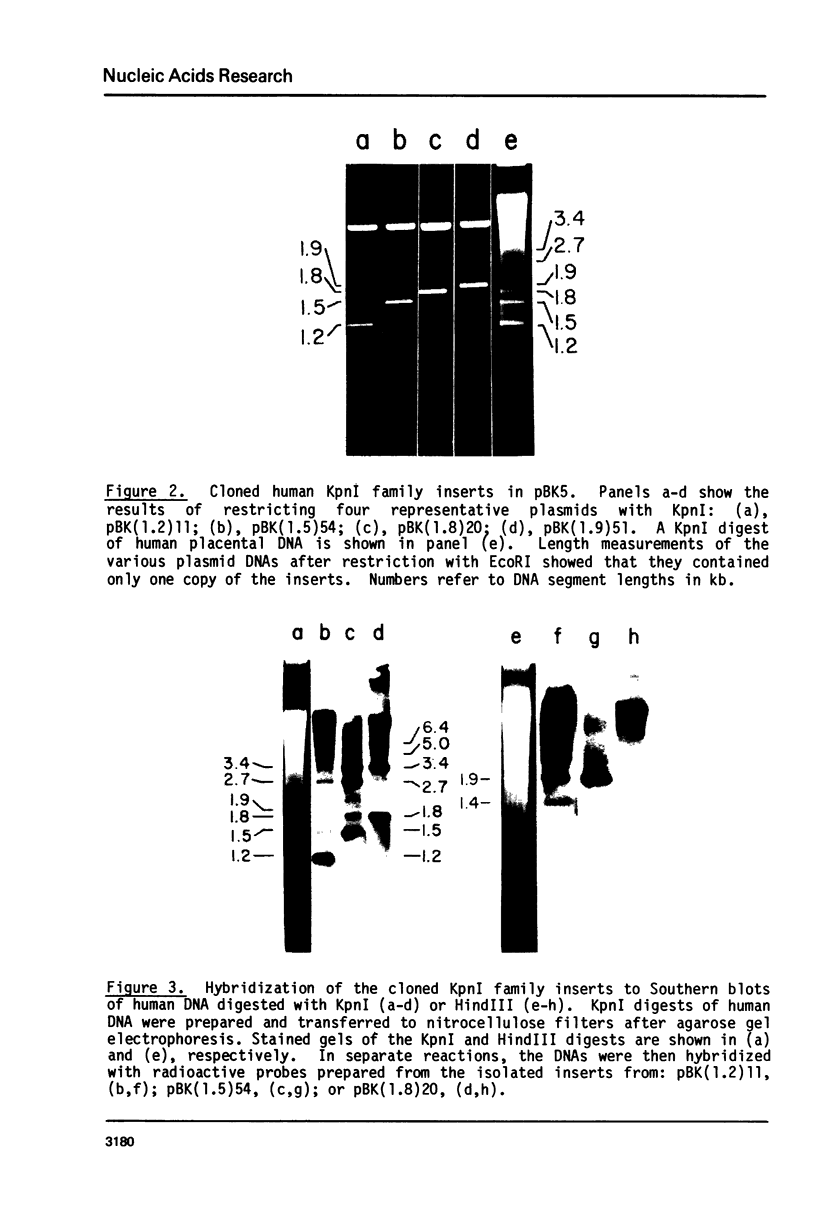
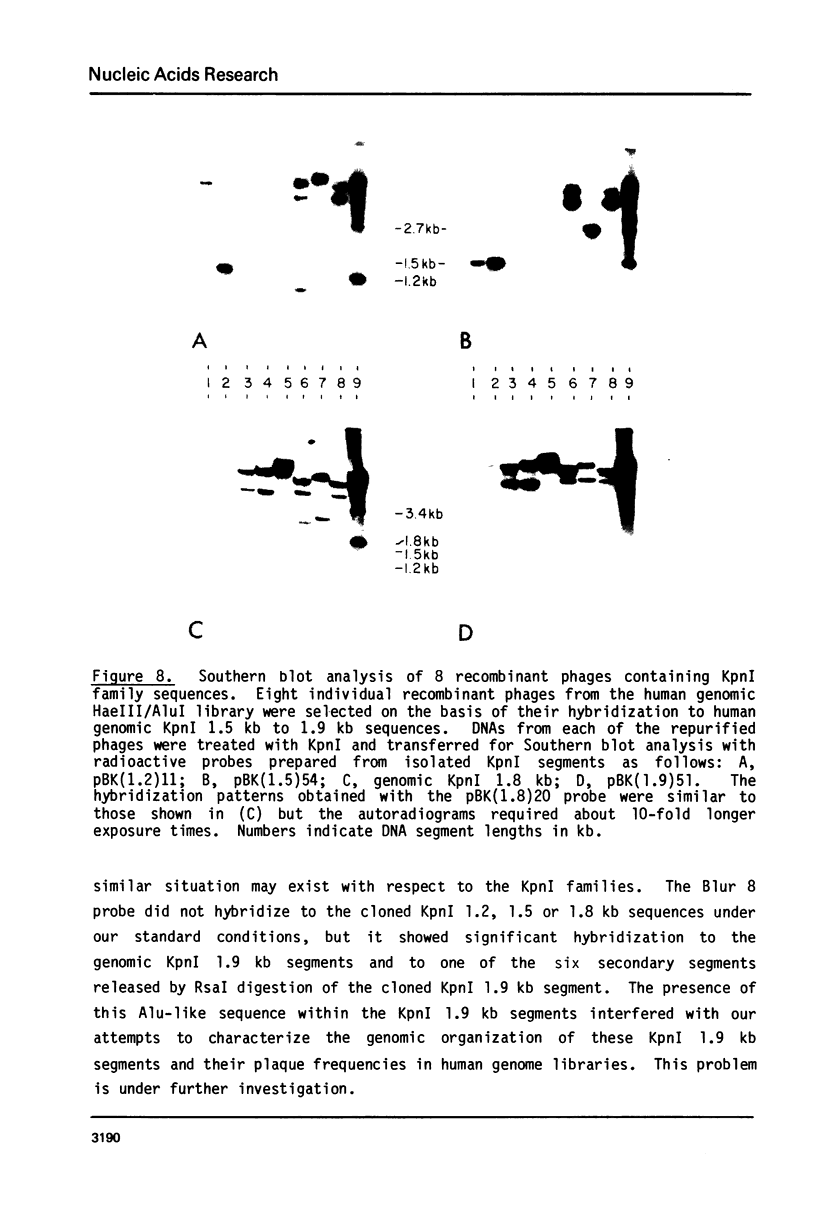
KpnI restriction of DNAs from all anthropoid primates studied releases a conspicuous series of segments representing families of long, interspersed repetitive DNAs termed here the KpnI 1.2, 1.5, 1.8 and 1.9 kb families. Human KpnI 1.2 to 1.9 kb segments representative of these families were isolated and separately cloned in the KpnI site of a plasmid pBK5, specially constructed for this purpose. The KpnI clones did not cross-hybridize with cloned, primate alphoid sequences, suggesting that the KpnI families represent sequences separate and distinct from the alphoid DNAs. Secondary restriction analyses of cloned KpnI segments demonstrated microheterogeneity among individual members within the same KpnI family. Autoradiograms of capuchin monkey, AGM and human DNA cleaved with HaeIII, AluI or RsaI and hybridized to various cloned human KpnI sequences demonstrated a remarkable conservatism and relative simplicity in the organization of the KpnI families in the genomes of these widely divergent primates. The KpnI 1.2 kb and 1.5 kb families occur in high frequency (15%) among all plaques in two recombinant human genome libraries. Evidence is presented suggesting that the bulk of the KpnI families occur in the genome as clusters or congeries of higher molecular weight segments (greater than 2 kb) containing sequences homologous to the low molecular weight segments (1.2 to 1.9 kb).
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. W., Kaufman R. E., Kretschmer P. J., Harrison M., Nienhuis A. W. A family of long reiterated DNA sequences, one copy of which is next to the human beta globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6113–6128. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crampton J. M., Davies K. E., Knapp T. F. The occurrence of families of repetitive sequences in a library of cloned cDNA from human lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3821–3834. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Regulation of gene expression: possible role of repetitive sequences. Science. 1979 Jun 8;204(4397):1052–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.451548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Jolly D. J., Rubin C. M., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Base sequence studies of 300 nucleotide renatured repeated human DNA clones. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Queen C., Singer M. F. Interspersed repeated sequences in the African green monkey genome that are homologous to the human Alu family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5553–5568. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Wallis J. Colony hybridization. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:379–389. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houck C. M., Rinehart F. P., Schmid C. W. A ubiquitous family of repeated DNA sequences in the human genome. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):289–306. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90261-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurnit D. M., Maio J. J. Subnuclear redistribution of DNA species in confluent and growing mammalian cells. Chromosoma. 1973 May 14;42(1):23–36. doi: 10.1007/BF00326328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio J. J., Brown F. L., Musich P. R. Subunit structure of chromatin and the organization of eukaryotic highly repetitive DNA: recurrent periodicities and models for the evolutionary origins of repetitive DNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 15;117(3):637–655. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio J. J., Brown F. L., Musich P. R. Toward a molecular paleontology of primate genomes. I. The HindIII and EcoRI dimer families of alphoid DNAs. Chromosoma. 1981;83(1):103–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00286019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Wu J. C. Homology between human and simian repeated DNA. Nature. 1978 Nov 2;276(5683):92–94. doi: 10.1038/276092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musich P. R., Brown F. L., Maio J. J. Highly repetitive component alpha and related alphoid DNAs in man and monkeys. Chromosoma. 1980;80(3):331–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00292688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orgel L. E., Crick F. H. Selfish DNA: the ultimate parasite. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):604–607. doi: 10.1038/284604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez F., Burns A. L., Mears J. G., Spence S., Starkman D., Bank A. Isolation and characterization of cloned human fetal globin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1147–1162. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Singer M., Rosenberg M. Highly reiterated sequences of SIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIAN. Science. 1978 Apr 28;200(4340):394–402. doi: 10.1126/science.205944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P., Chyn R., Chirgwin J., Cordell B., Goodman H. M., Permut M. A. Polymorphism in the 5'-flanking region of the human insulin gene and its possible relation to type 2 diabetes. Science. 1981 Sep 4;213(4512):1117–1120. doi: 10.1126/science.6267694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeckpeper B. J., Willard H. F., Smith K. D. Isolation and characterization of cloned human DNA fragments carrying reiterated sequences common to both autosomes and the X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1853–1872. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. Gel electrophoresis of restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:152–176. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer R. E., Singer M. F., McCutchan T. F. Sequence relationships between single repeat units of highly reiterated African Green monkey DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):169–181. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]