Abstract
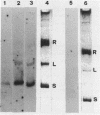
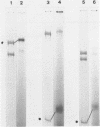
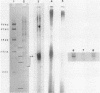
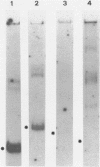
Clones of the yeast Tyl element and 2 microns plasmid have been selectively transcribed in vitro by partially or completely purified yeast RNA polymerase II. Electrophoretic analysis of whole and restricted ternary transcription complexes allows the localization of the in vitro actively transcribed regions of the analyzed genes. The DNA regions that actively promote in vitro transcription correspond to the nucleotide sequence that in the Tyl element encompasses the in vivo transcription initiation sites and that in the 2 micrometer plasmid encompasses the starting codons of two oppositely oriented potential protein coding frames. The transcription assay that we describe herein may be applied to analyze rapidly the in vitro transcription of clones genes, to localize transcription initiation sites on supercoiled templates and to evaluate the differential in vitro promoter strength in RNA polymerase II served genes. Data obtained with RNA polymerase II at two different stages of purification are presented in parallel. Studies with a completely purified enzyme should certainly be preferred although the use of a partially purified RNA polymerase II may be convenient and may reveal factors which affect specificity.
Full text
PDF



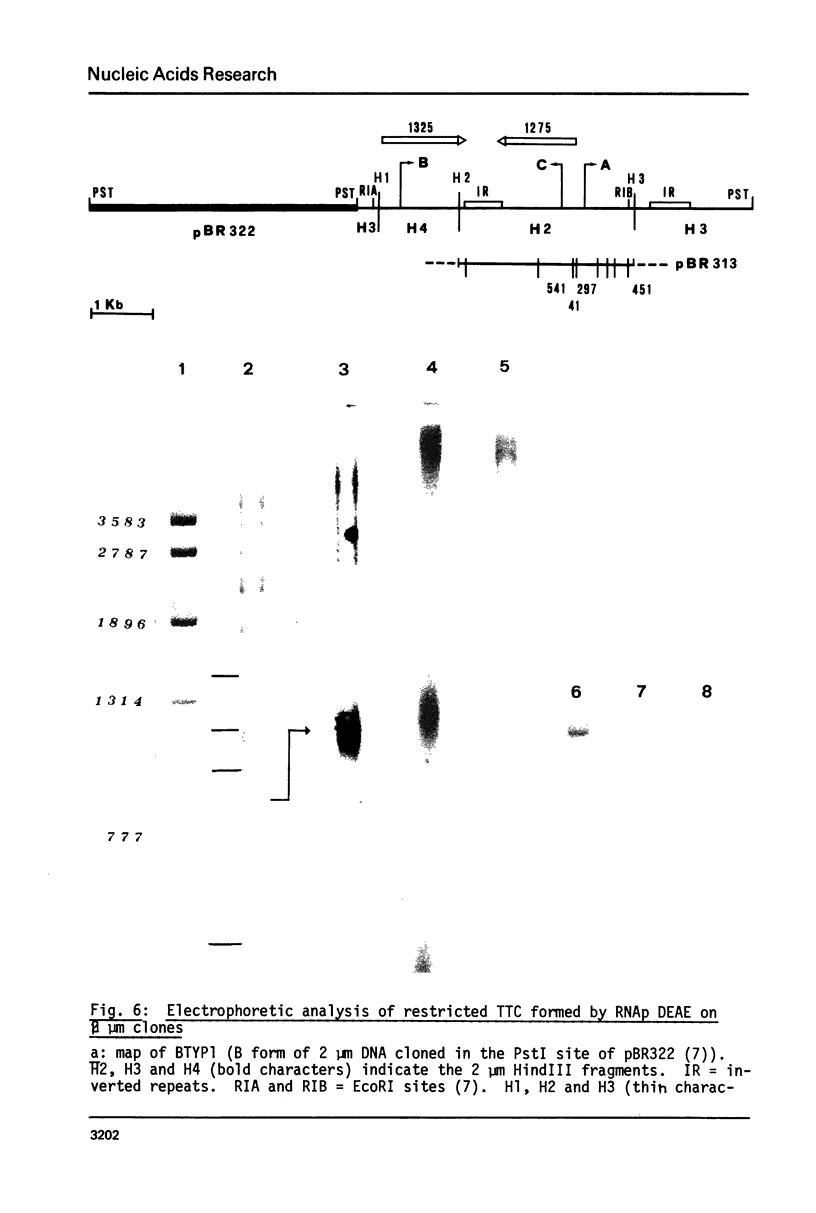



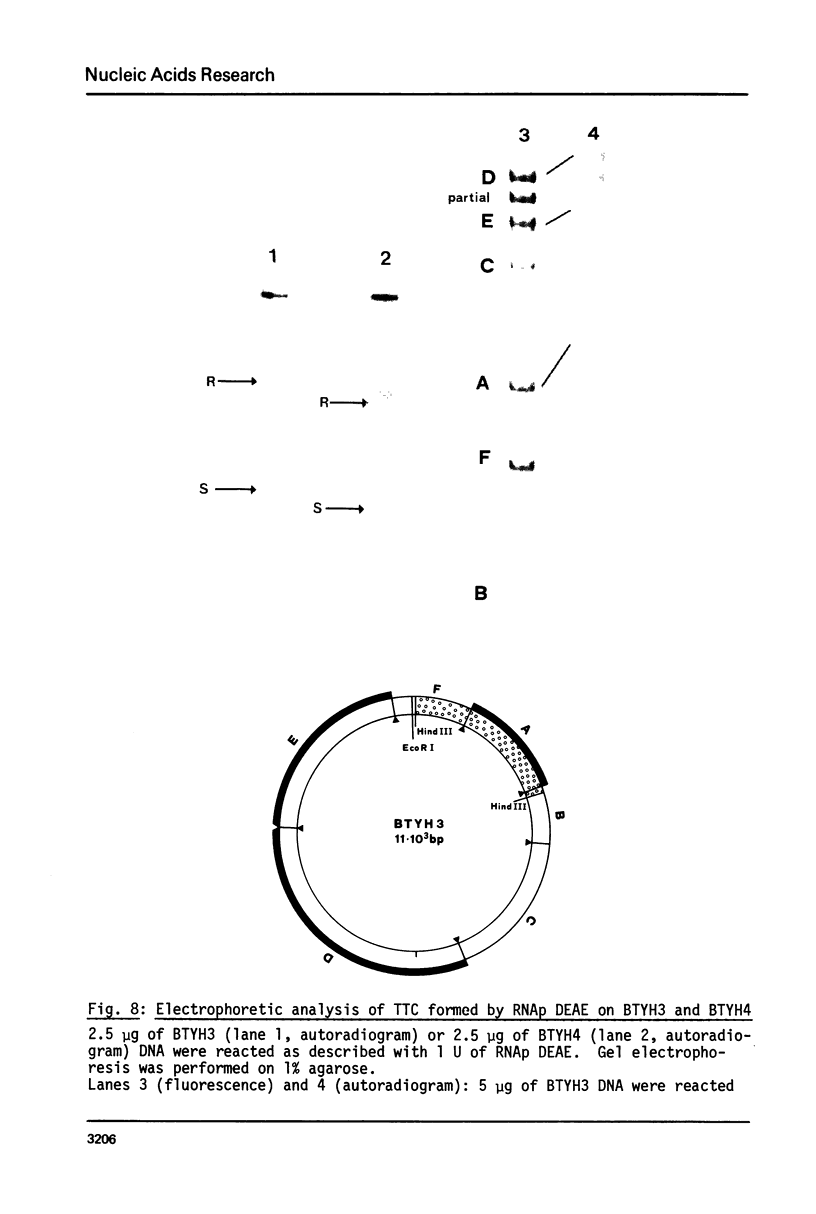



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballario P., Buongiorno-Nardelli M., Carnevali F., Di Mauro E., Pedone F. Selective in vitro transcription by purified yeast RNA polymerase II on cloned 2 micron DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):3959–3978. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.3959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Atkins J. F., McGill C., Chow L. Identification and mapping of the transcriptional and translational products of the yeast plasmid, 2mu circle. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):827–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buongiorno-Nardelli M., Ballario P., Di Mauro E. Binding of sea-urchin RNA polymerase II on homologous histone genes. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):171–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. R., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. Evidence for transposition of dispersed repetitive DNA families in yeast. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):739–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelm B. K., Geiduschek E. P. Gel electrophoretic separation of transcription complexes: an assay for RNA polymerase selectivity and a method for promoter mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1851–1867. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder R. T., St John T. P., Stinchcomb D. T., Davis R. W., Scherer S., Davis R. W. Studies on the transposable element Ty1 of yeast. I. RNA homologous to Ty1. II. Recombination and expression of Ty1 and adjacent sequences. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):581–591. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. L., Donelson J. E. Nucleotide sequence of the yeast plasmid. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):860–865. doi: 10.1038/286860a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg C. P. Mapping of regions on cloned Saccharomyces cerevisiae 2-mum DNA coding for polypeptides synthesized in Escherichia coli minicells. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jun 1;162(1):23–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00333847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lescure B., Williamson V., Sentenac A. Efficient and selective initiation by yeast RNA polymerase B in a dinucleotide-primed reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):31–45. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Luse D. S., Segall J., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate initiation of transcription at the Ad2 major late promotor in a soluble system dependent on purified RNA polymerase II and DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):469–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]