Abstract
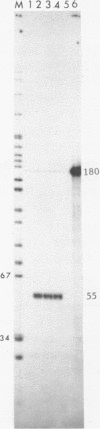
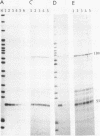
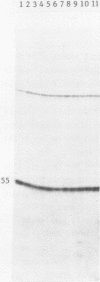
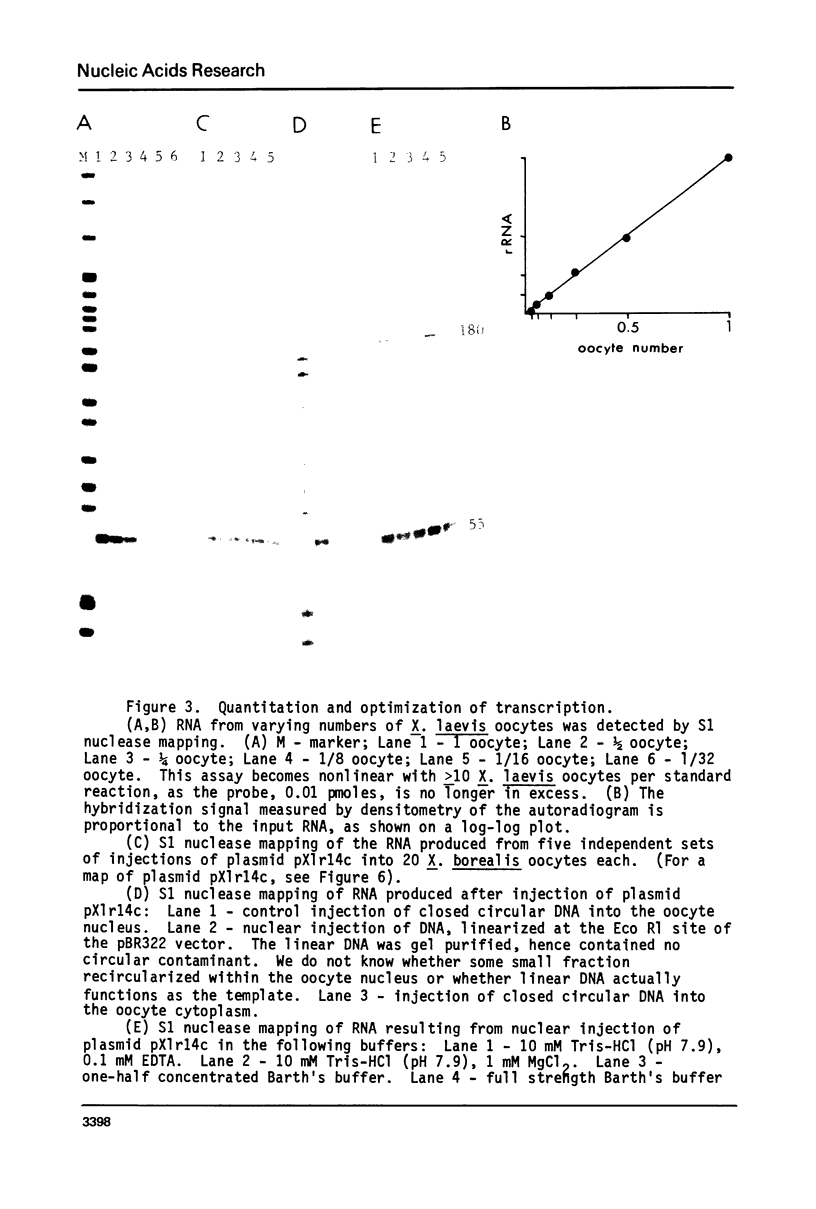
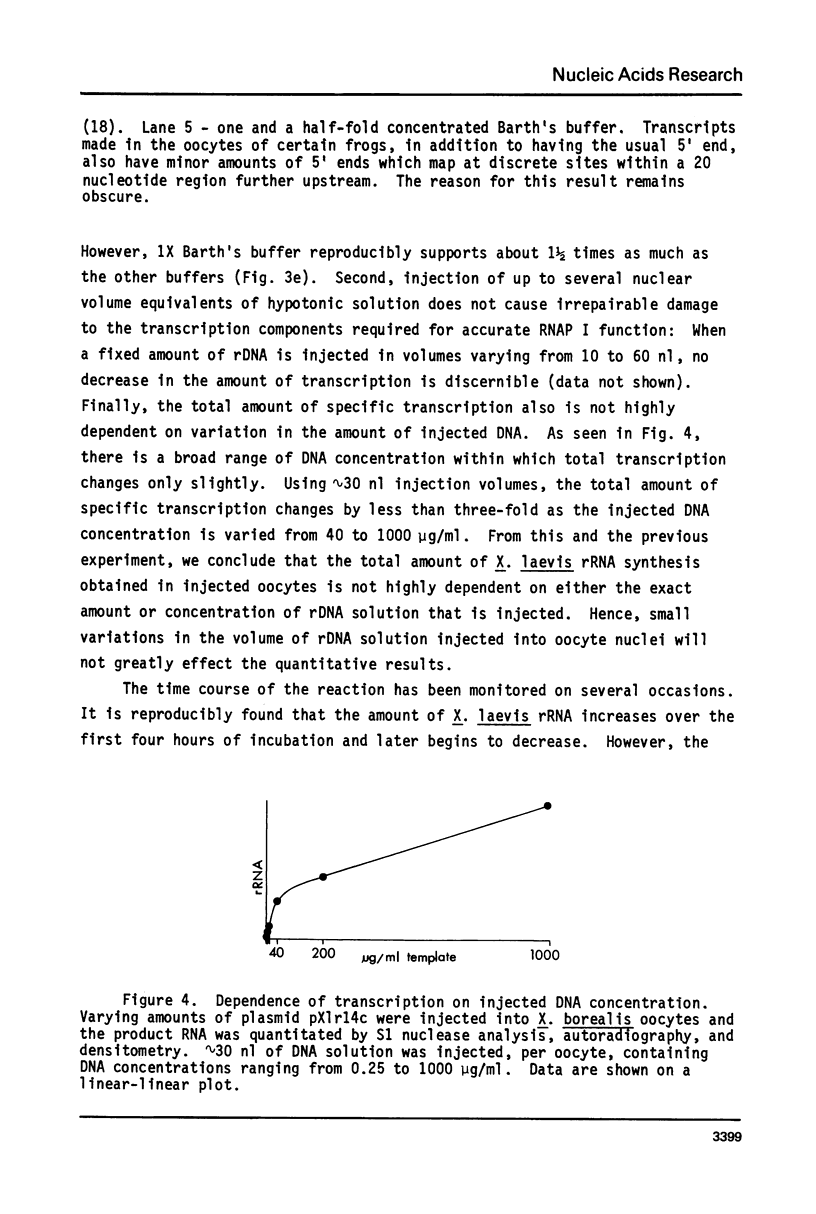
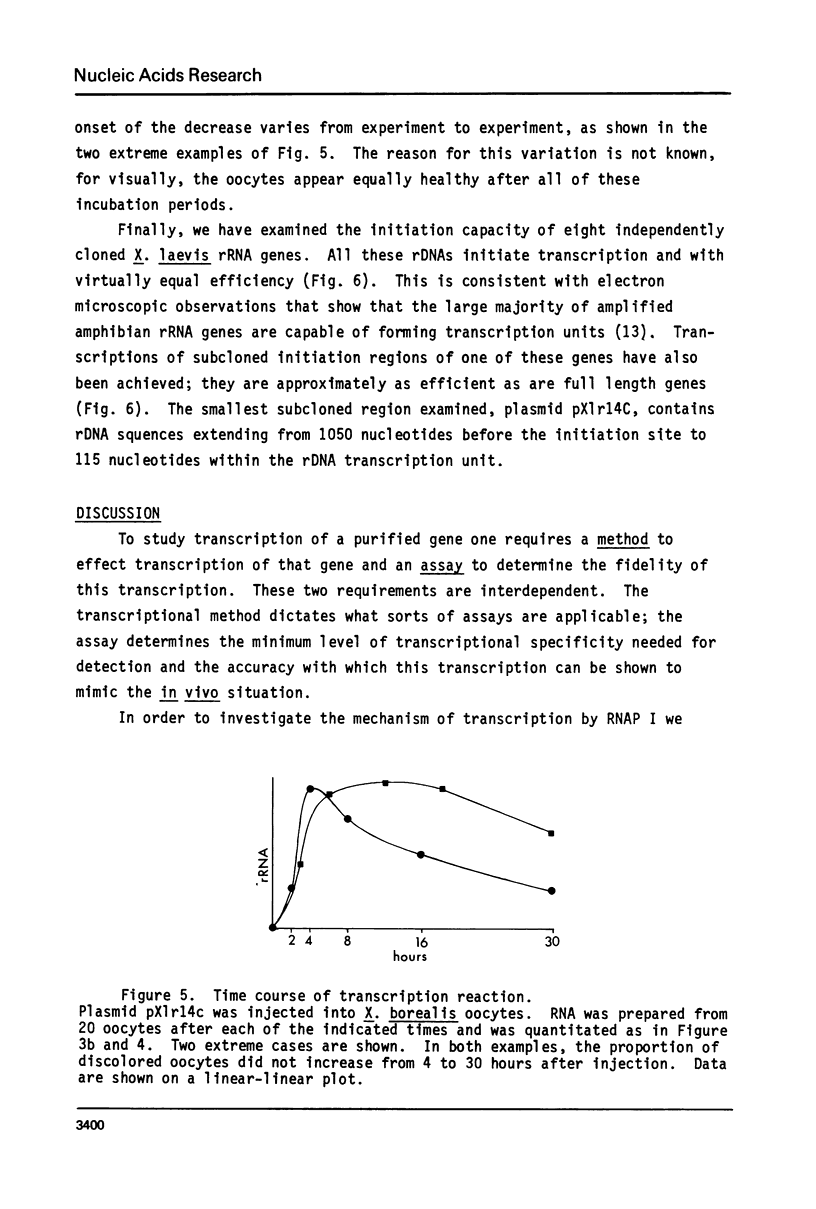
We have demonstrated faithful transcriptional initiation of cloned Xenopus rRNA genes upon injection into Xenopus oocytes. This observation has been made possible by the use of an S1 nuclease assay that is both sensitive and quantitative. In order to detect rRNA synthesis from the injected template above the large background of rRNA endogenously present in oocytes, the divergence of ribosomal DNA sequences between two Xenopus species was utilized. Cloned X. laevis ribosomal DNA was injected into the nuclei of X. borealis oocytes. Total oocyte RNA was then isolated and hybridized to a radioactive DNA probe that over laps the 5' end of X. laevis rRNA; endogenous rRNA of the X. borealis oocytes does not hybridize to the probe. RNA/DNA hybrids were treated with S1 nuclease and protected fragments were sized by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. RNA made from the injected rDNA protects the same region of probe as does authentic X. laevis precursor rRNA. Thus, transcription appears to initiate on the cloned, microinjected X. laevis rDNA at the same site as is used in vivo. This synthesis is not impaired by coinjection of an amount of alpha-amanitin sufficient to inhibit RNA polymerase II and III; therefore the reaction is mediated by RNA polymerase I. The amount of transcription may be reproducibly quantitated and we have varied a number of parameters in order to maximize transcriptional expression of the injected rDNA. Eight independently isolated X. laevis rDNA clones as well as several subcloned initiation regions of these genes are all accurately transcribed at approximately equal efficiency. This assay should facilitate analysis of several aspects of rRNA transcription, including deleniation of the Xenopus RNA polymerase I promoter location.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach R., Allet B., Crippa M. Sequence organization of the spacer in the ribosomal genes of Xenopus clivii and Xenopus borealis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5311–5330. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebee T. J., Butterworth P. H. Template specificities of Xenopus laevis RNA polymerases. Selective transcription of ribosomal cistrons by RNA polymerase A. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 15;45(2):395–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Brown D. D., Jordan E. A nuclear extract of Xenopus laevis oocytes that accurately transcribes 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1077–1086. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P., Moss T., Mächler M., Portmann R., Birnstiel M. Sequence organization of the spacer DNA in a ribosomal gene unit of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan P., Reeder R. H., Dawid I. B. Restriction analysis of the nontranscribed spacers of Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):599–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Gurdon J. B. Cloned single repeating units of 5S DNA direct accurate transcription of 5S RNA when injected into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2849–2853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsheit A. B., Davidson N., Brown D. D. An electron microscope heteroduplex study of the ribosomal DNAs of Xenopus laevis and Xenopus mulleri. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 5;90(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Scheer U., Spring H., Trendelenburg M. F., Krohne G. Morphology of transcriptional units of rDNA. Evidence for transcription in apparent spacer intercepts and cleavages in the elongating nascent RNA. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jul;100(2):233–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Spacer DNA sequences upstream of the T-A-T-A-A-A-T-A sequence are essential for promotion of H2A histone gene transcription in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7102–7106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Brown D. D. The transcription of 5 S DNA injected into Xenopus oocytes. Dev Biol. 1978 Dec;67(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipskind R. A., Reeder R. H. Initiation of ribosomal RNA chains in homogenates of oocyte nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7896–7906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Reeder R. H. Preferential transcription of Xenopus laevis ribosomal RNA in interspecies hybrids between Xenopus laevis and Xenopus mulleri. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 25;80(2):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. L., Manley J. L. DNA sequence required for initiation of transcription in vitro from the major late promoter of adenovirus 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):820–824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kressmann A., Clarkson S. G., Telford J. L., Birnstiel M. L. Transcription of xenopus tDNAmet1 and sea urchin histone DNA injected into the Xenopus oocyte nucleus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1077–1082. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R. Expression of the herpes thymidine kinase gene in Xenopus laevis oocytes: an assay for the study of deletion mutants constructed in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5931–5948. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. L., Jr, Beatty B. R. Visualization of nucleolar genes. Science. 1969 May 23;164(3882):955–957. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3882.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst E., Kressmann A., Birnstiel M. L. Expression of sea urchin histone genes in the oocyte of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 15;135(3):709–732. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90173-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Brown D. D. Transcription of the ribosomal RNA genes of an amphibian by the RNA polymerase of a bacterium. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):361–377. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rungger D., Achermann H., Crippa M. Transcription of spacer sequences in genes coding for ribosomal RNA in Xenopus cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3957–3961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. Pancreatic DNAase cleavage sites in nuclei. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trendelenburg M. F., Gurdon J. B. Transcription of cloned Xenopus ribosomal genes visualised after injection into oocyte nuclei. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):292–294. doi: 10.1038/276292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]