Abstract
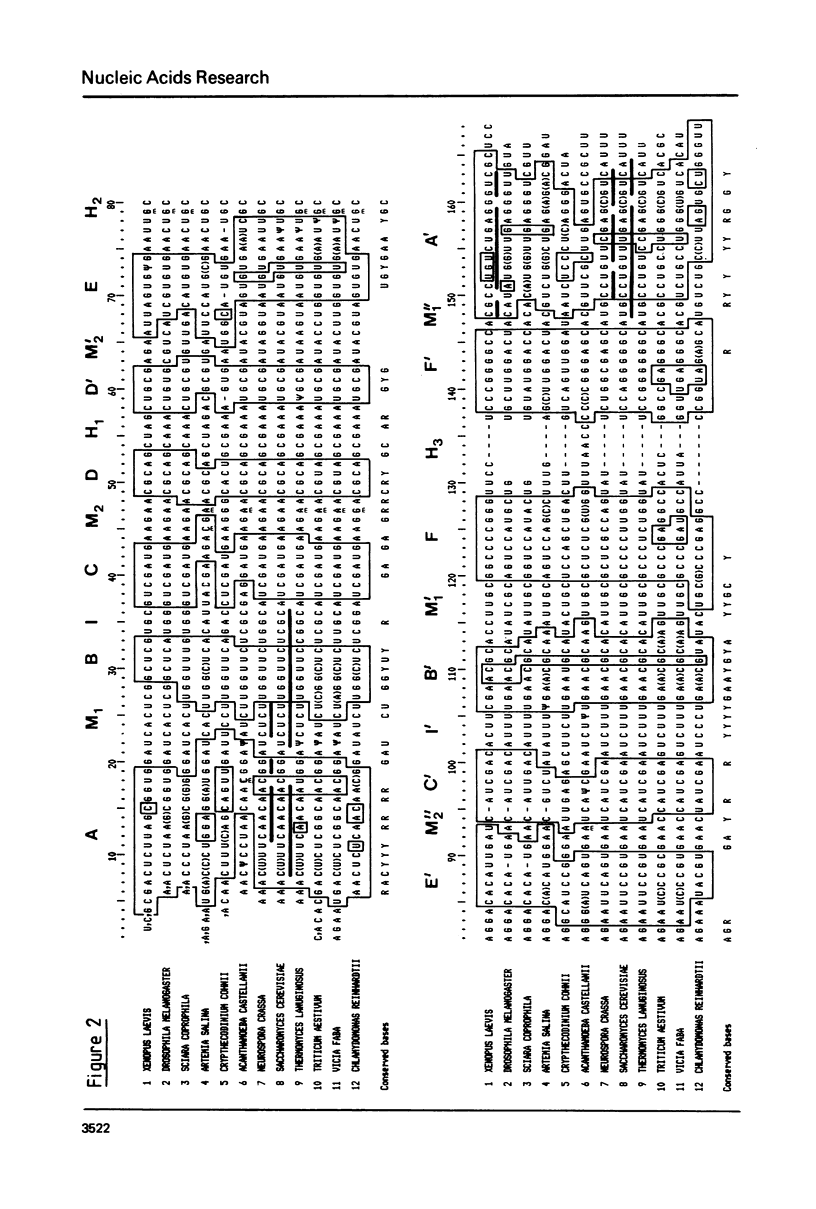
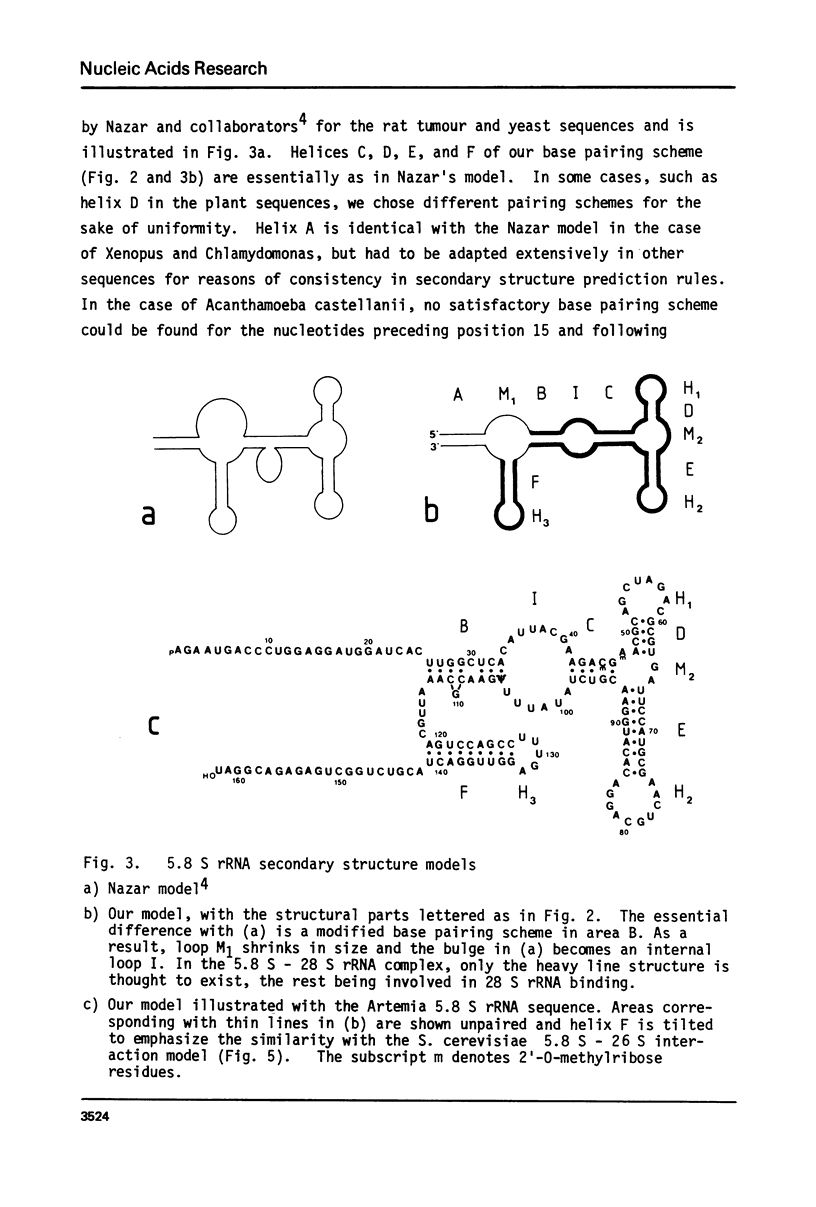
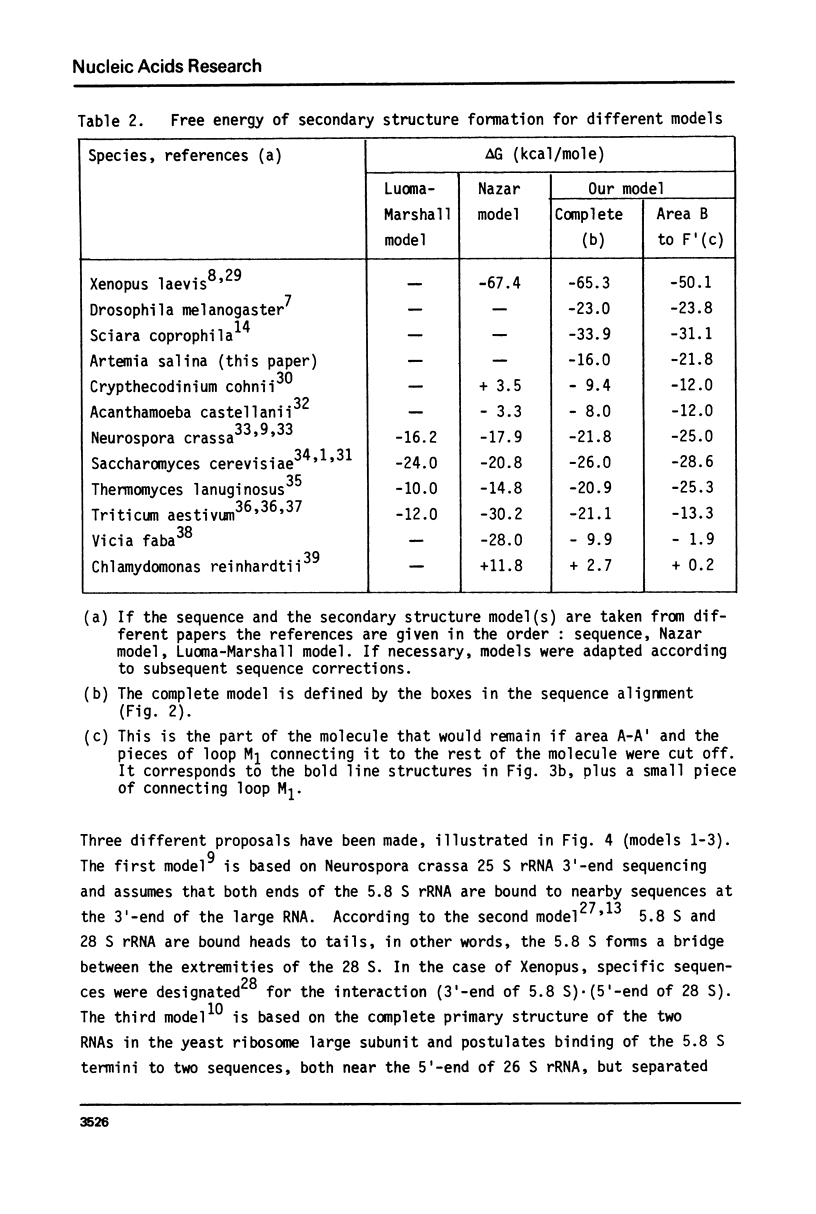
We report the primary structure of 5.8 S rRNA from the crustacean Artemia salina. The preparation shows length heterogeneity at the 5'-terminus, but consists of uninterrupted RNA chains, in contrast to some insect 5.8 S rRNAs, which consist of two chains of unequal length separated in the gene by a short spacer. The sequence was aligned with those of 11 other 5.8 S rRNAs and a general secondary structure model derived. It has four helical regions in common with the model of Nazar et al. (J. Biol. Chem. 250, 8591-8597 (1975)), but for a fifth helix a different base pairing scheme was found preferable, and the terminal sequences are presumed to bind to 28 S rRNA instead of binding to each other. In the case of yeast, where both the 5.8 S and 26 S rRNA sequences are known, the existence of five helices in 5.8 S rRNA is shown to be compatible with a 5.8 S - 26 S rRNA interaction model.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branlant C., Krol A., Machatt M. A., Pouyet J., Ebel J. P., Edwards K., Kössel H. Primary and secondary structures of Escherichia coli MRE 600 23S ribosomal RNA. Comparison with models of secondary structure for maize chloroplast 23S rRNA and for large portions of mouse and human 16S mitochondrial rRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4303–4324. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L., Rochaix J. D. Nucleotide sequence and structure of cytoplasmic 5S RNA and 5.8S RNA of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1291–1299. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A. Collection of published 5S and 5.8S RNA sequences and their precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):r93–115. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.762-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford P. J., Mathieson T. The nucleotide sequences of 5.8-S ribosomal RNA from Xenopus laevis and Xenopus borealis. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 1;87(1):199–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Woese C. R. 5S RNA secondary structure. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):505–507. doi: 10.1038/256505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotz C., Zwieb C., Brimacombe R., Edwards K., Kössel H. Secondary structure of the large subunit ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli, Zea mays chloroplast, and human and mouse mitochondrial ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3287–3306. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Maden B. E. Nucleotide sequence through the 18S-28S intergene region of a vertebrate ribosomal transcription unit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5993–6005. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G., Klotz L. C., Blanken R. L., Loeblich A. R., 3rd An evaluation of the phylogenetic position of the dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii based on 5S rRNA characterization. J Mol Evol. 1981;17(6):334–337. doi: 10.1007/BF01734355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacq B. Sequence homologies between eukaryotic 5.8S rRNA and the 5' end of prokaryotic 23S rRNa: evidences for a common evolutionary origin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2913–2932. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan B. R., Latil-Damotte M., Jourdan R. Coding and spacer sequences in the 5.8S-2S region of Sciara coprophila ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3565–3573. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. M., Cox R. A. The nucleotide sequence at the 3'-end of Neurospora crassa 25S-rRNA and the location of a 5.8S-rRNA binding site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1111–1121. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luoma G. A., Marshall A. G. Laser Raman evidence for new cloverleaf secondary structures for eukaryotic 5.8S RNA and prokaryotic 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4901–4905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay R. M., Doolittle W. F. Nucleotide sequences of Acanthamoeba castellanii 5S and 5.8S ribosomal ribonucleic acids: phylogenetic and comparative structural analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3321–3334. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay R. M., Spencer D. F., Doolittle W. F., Gray M. W. Nucleotide sequences of wheat-embryo cytosol 5-S and 5.8-S ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Dec;112(3):561–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar R. N. A 5.8 S rRNA-like sequence in prokaryotic 23 S rRNA. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 6;119(2):212–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar R. N., Sitz T. O., Busch H. Structural analyses of mammalian ribosomal ribonucleic acid and its precursors. Nucleotide sequence of ribosomal 5.8 S ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8591–8597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar R. N., Wildeman A. G. Altered features in the secondary structure of Vicia faba 5.8s rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5345–5358. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninio J. Prediction of pairing schemes in RNA molecules-loop contributions and energy of wobble and non-wobble pairs. Biochimie. 1979;61(10):1133–1150. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(80)80227-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace N. R., Walker T. A., Schroeder E. Structure of the 5.8S RNA component of the 5.8S-28S ribosomal RNA junction complex. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 29;16(24):5321–5328. doi: 10.1021/bi00643a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis G. N., Jordan B. R., Wurst R. M., Vournakis J. N. Sequence and secondary structure of Drosophila melanogaster 5.8S and 2S rRNAs and of the processing site between them. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2213–2238. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinck L., Pinck M. Sequence homology at the 3'-ends of alfalfa mosaic virus RNAs. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):61–65. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80463-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipas J. M., McMahon J. E. Method for predicting RNA secondary structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2017–2021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. The nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5.8 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3860–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W. Globin mRNA sequences: analysis of base pairing and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):985–1002. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence and conserved features of the 5.8 S rRNA coding region of Neurospora crassa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2561–2567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiegler P., Carbon P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C. A general secondary-structure model for procaryotic and eucaryotic RNAs from the small ribosomal subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Dec;120(3):487–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Dyer T. A., Brownlee G. G. An improved direct RNA sequence method; its application to Vicia faba 5.8S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1259–1272. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberghe A., Nelles L., De Wachter R. High-pressure liquid chromatography analysis of oligo- and monoribonucleotide mixtures, with special reference to ribosomal RNA constituents. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 15;107(2):369–376. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Klootwijk J., de Regt V. C., Planta R. J., Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P. The primary and secondary structure of yeast 26S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6935–6952. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Klootwijk J., van Heerikhuizen H., Planta R. J. The nucleotide sequence of the intergenic region between the 5.8S and 26S rRNA genes of the yeast ribosomal RNA operon. Possible implications for the interaction between 5.8S and 26S rRNA and the processing of the primary transcript. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):4847–4862. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.4847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Nazar R. N. Studies on the secondary structure of 5.8 S rRNA from a thermophile, Thermomyces lanuginosus. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5675–5682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Nazar R. N. Studies on the secondary structure of wheat 5.8 S rRNA. Conformational changes in the A + U-rich stem during ribosome assembly. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jan;121(2):357–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Gupta R., Siegel R. B., Stahl D. A., Kop J., Crawford N., Brosius J., Gutell R., Hogan J. J. Secondary structure model for bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA: phylogenetic, enzymatic and chemical evidence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2275–2293. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Ochoa S. A supernatant factor involved in initiation complex formation with eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3059–3063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]