Abstract
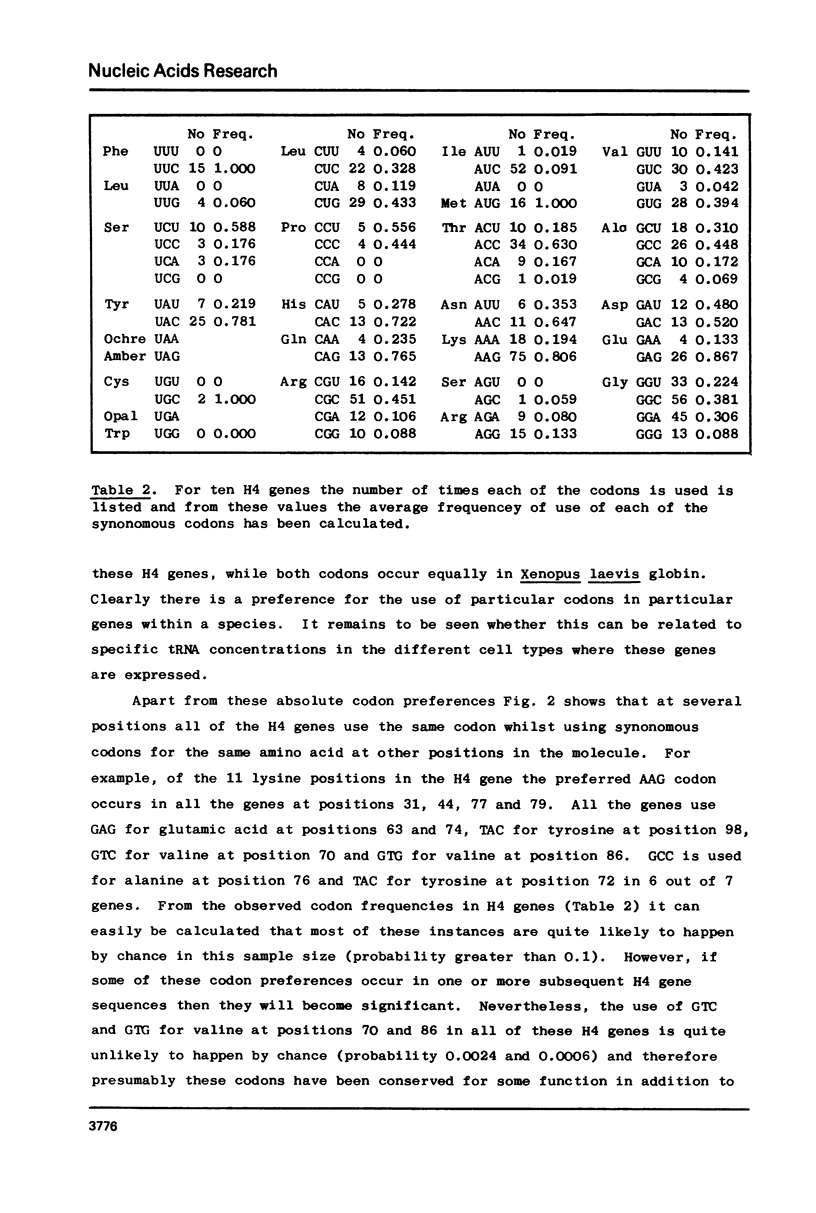
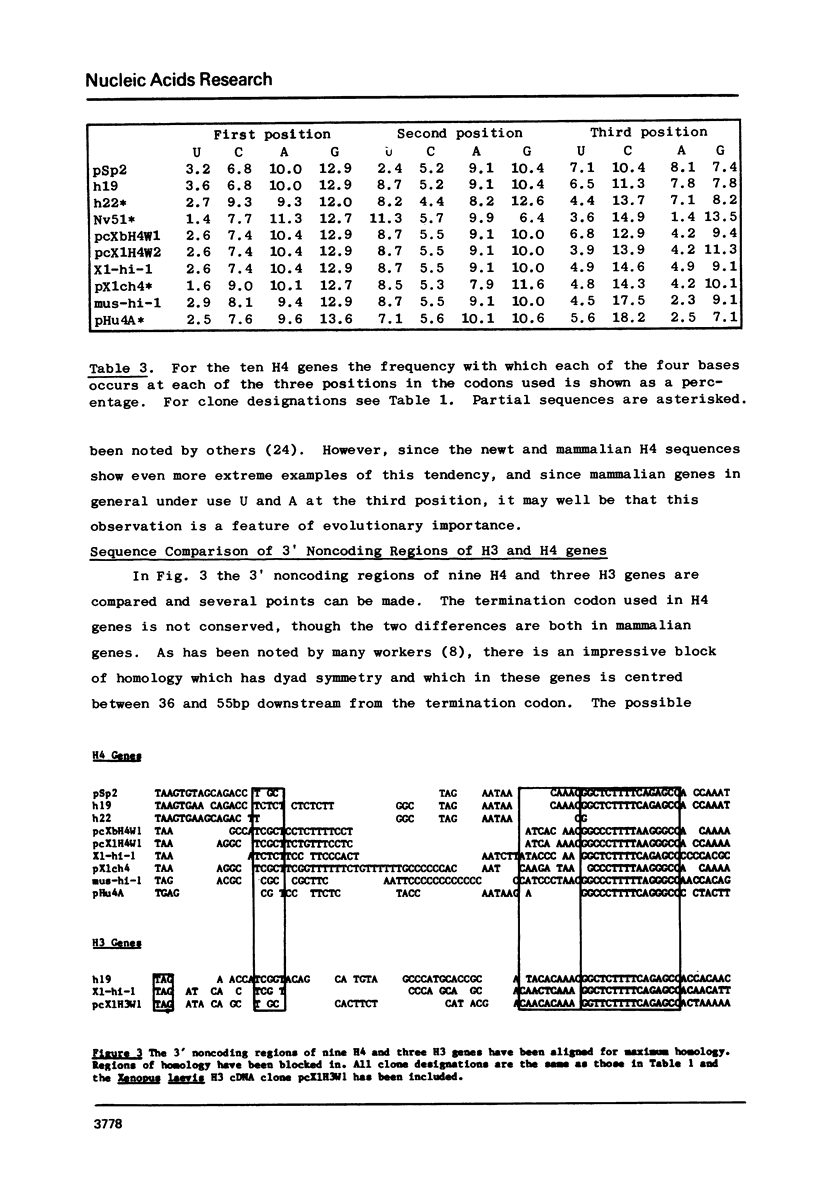
Ovarian poly (A) + RNA from Xenopus laevis and Xenopus borealis was used to construct two cDNA libraries which were screened for histone sequences. cDNA clones to H4 mRNA were obtained from both species and an H3 cDNA clone from Xenopus laevis. The complete DNA sequences of these clones have been determined and are presented. These new sequences are compared with other H3 and H4 DNA sequences both in the coding and 3' noncoding regions. We find that there is considerable non-random codon usage in ten H4 genes. In addition there are some sequence similarities in the 3' noncoding regions of H3 and H4 genes.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Busslinger M., Portmann R., Irminger J. C., Birnstiel M. L. Ubiquitous and gene-specific regulatory 5' sequences in a sea urchin histone DNA clone coding for histone protein variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):957–977. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Rusconi S., Birnstiel M. L. An unusual evolutionary behaviour of a sea urchin histone gene cluster. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):27–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01119.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs G., Levy S., Kedes L. H. Rapid purification of biologically active individual histone messenger RNAs by hybridization to cloned DNA linked to cellulose. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):208–213. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson S. G., Smith H. O., Schaffner W., Gross K. W., Birnstiel M. L. Integration of eukaryotic genes for 5S RNA and histone proteins into a phage lambda receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2617–2632. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman A., Byers M. J., Primrose S. B., Lyons A. Rapid purification of plasmid DNAs by hydroxyapatite chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 2;91(1):303–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. D., Dodgson J. B. Histone genes are clustered but not tandemly repeated in the chicken genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2856–2860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R. Nucleic acid sequence similarities: 'poly(A) tendency'. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 1;121(2):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80340-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Diamond K. E., Knoppel E., Grunstein J. E. Comparison of the early histone H4 gene sequence of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus with maternal, early, and late histone H4 mRNA sequences. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1216–1223. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Zernik M., Roeder R. G. The structure of the human histone genes: clustered but not tandemly repeated. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg I. Histones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:159–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RIBOSOMAL RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:266–269. doi: 10.1042/bj0960266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Chang A. C., Houseman D., Cohen S. N. Isolation of histone genes from unfractionated sea urchin DNA by subculture cloning in E. coli. Nature. 1975 Jun 12;255(5509):533–538. doi: 10.1038/255533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorman A. F., de Boer P. A., de Laaf R. T., van Dongen W. M., Destrée O. H. Primary structure of the histone H3 and H4 genes and their flanking sequences in a minor histone gene cluster of Xenopus laevis. FEBS Lett. 1981 Dec 21;136(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazato H., Edmonds M. The isolation and purification of rapidly labeled polysome-bound ribonucleic acid on polythymidylate cellulose. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3365–3367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. G., Barber C., Carey N. H., Hallewell R. A., Threlfall G., Emtage J. S. Complete nucleotide sequence of an influenza virus haemagglutinin gene from cloned DNA. Nature. 1979 Nov 29;282(5738):471–477. doi: 10.1038/282471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C., Cappello J., Cochran M. D., Armentrout R. W., Brown R. D. Partial sequence analysis of Xenopus alpha- and beta-globin mRNA as determined from recombinant DNA plasmids. Dev Biol. 1980 Jul;78(1):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90326-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Kunz G., Daetwyler H., Telford J., Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. Genes and spacers of cloned sea urchin histone DNA analyzed by sequencing. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):655–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90249-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Birnstiel M. L. Structure and expression in L-cells of a cloned H4 histone gene of the mouse. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 5;151(4):607–625. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Williams J. G. Quantitative analysis of specific labelled RNA'S using DNA covalently linked to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):195–203. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. C., Erba H. P., Gall J. G. Characterization of a cloned histone gene cluster of the newt Notophthalamus viridescens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2281–2295. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodland H. R. Histone synthesis during the development of Xenopus. FEBS Lett. 1980 Nov 17;121(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zernik M., Heintz N., Boime I., Roeder R. G. Xenopus laevis histone genes: variant H1 genes are present in different clusters. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90557-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



