Abstract
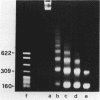
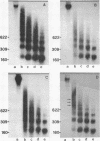
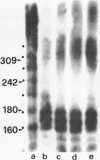
We have investigated the nucleosomal organization of ribosomal genes in the acellular slime mold Physarum polycephalum. When probed with staphylococcal nuclease, the ribosomal genes appear to be uniformly packed in nucleosomes, in an arrangement which is indistinguishable from the pattern obtained with bulk chromatin. During this study, an unusual pattern of digestion was obtained from a DNA region immediately upstream of the initiation site of rRNA transcription, in addition to the nucleosomal profile, a second regular ladder of fragments with a repeat length of 30-40 basepairs was generated from this region. We established that this pattern of degradation reflects the strong preference of staphylococcal nuclease for certain nucleotide arrangements on the DNA, rather than a particular chromatin configuration. These observations clearly show that great caution needs to be exerted whenever data from staphylococcal nuclease digestions are interpreted in terms of chromatin structure.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryan P. N., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Nucleosome arrangement on tRNA genes of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90387-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. L., Bellard M., Chambon P. Biochemical evidence of variability in the DNA repeat length in the chromatin of higher eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4382–4386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fittler F., Zachau H. G. Subunit structure of alpha-satellite DNA containing chromatin from African green monkey cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):1–13. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Kindle K. L., Davidson N., Kindle K. L. The actin genes of Drosophila: a dispersed multigene family. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90511-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Bloomer L. S. Nonrandom alignment of nucleosomes on 5S RNA genes of X. laevis. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):751–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90438-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Wyler T., Seebeck T., Braun R. Processing of ribosomal precursor RNAs in Physarum polycephalum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2647–2664. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Altenburger W. Sequence specific cleavage of DNA by micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2643–2658. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Allfrey V. G., Bradbury E. M., Matthews H. R. Altered nucleosome structure containing DNA sequences complementary to 19S and 26S ribosomal RNA in Physarum polycephalum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1116–1120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene M. A., Corces V., Lowenhaupt K., Elgin S. C. DNase I hypersensitive sites in Drosophila chromatin occur at the 5' ends of regions of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):143–146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene M. A., Elgin S. C. Micrococcal nuclease as a probe of DNA sequence organization and chromatin structure. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy A., Frei E., Noll M. Efficient transfer of highly resolved small DNA fragments from polyacrylamide gels to DBM paper. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy A., Noll M. Multiple phases of nucleosomes in the hsp 70 genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6059–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Nucleosome structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1115–1156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohberg J., Rusch H. P. Isolation of the nuclear histones from the Myxomycete, Physarum polycephalum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Nov;134(2):577–589. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samal B., Worcel A., Louis C., Schedl P. Chromatin structure of the histone genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):401–409. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seebeck T., Stalder J., Braun R. Isolation of a minichromosome containing the ribosomal genes from Physarum polycephalum. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 6;18(3):484–490. doi: 10.1021/bi00570a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Larsen A., Engel J. D., Dolan M., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Tissue-specific DNA cleavages in the globin chromatin domain introduced by DNAase I. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90631-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Seebeck T., Braun R. Accessibility of the ribosomal genes to micrococcal nuclease in Physarum polycephalum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 27;561(2):452–463. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90153-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker P. W., Hazen E. E., Jr, Cotton F. A. Staphylococcal nuclease reviewed: a prototypic study in contemporary enzymology. I. Isolation; physical and enzymatic properties. Mol Cell Biochem. 1978 Dec 22;22(2-3):67–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00496235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M., Braun R. The replication of ribosomal DNA in Physarum polycephalum. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Nov 1;80(2):557–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Bonner W. M. Separation of basal histone synthesis from S-phase histone synthesis in dividing cells. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90415-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]