Abstract
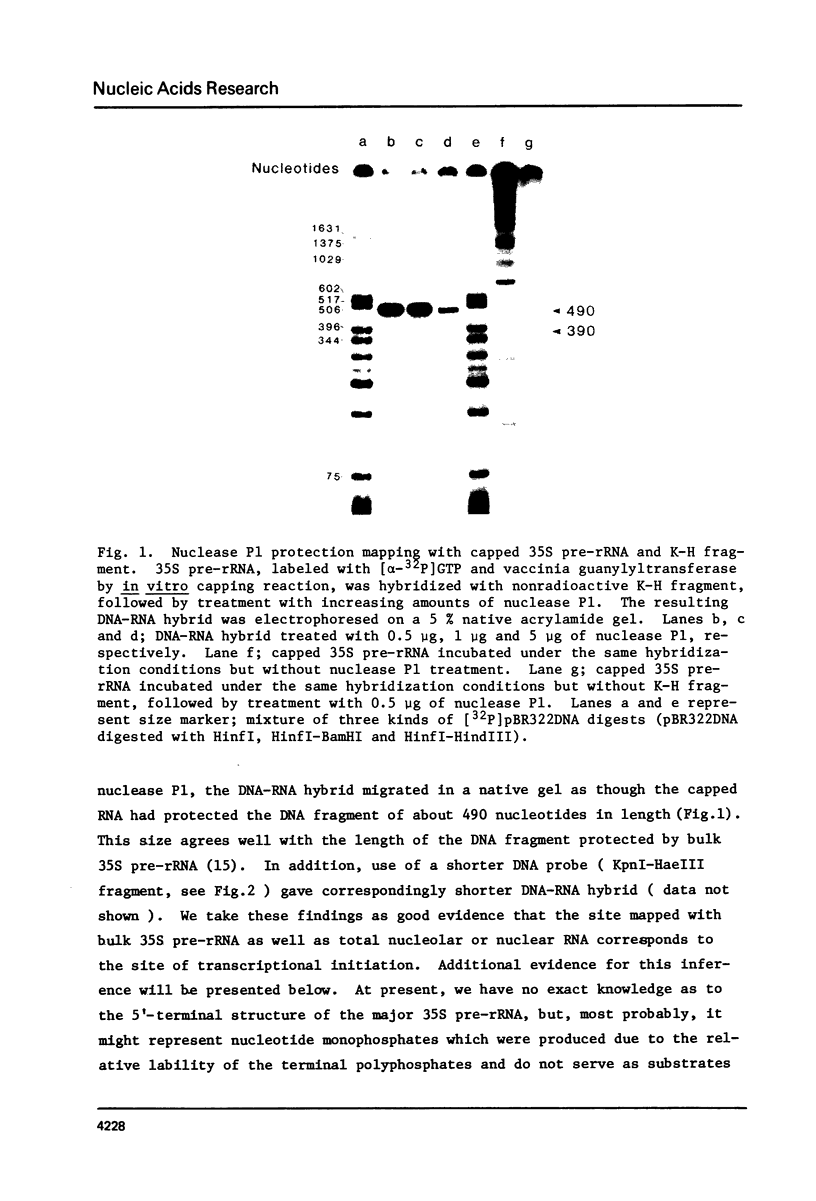
Approximately 700 nucleotide sequences surrounding the transcription initiation site were determined with a cloned rDNA fragment of Tetrahymena pyriformis and the transcription initiation site was localized on these sequences using purified 35S pre-rRNA. A considerable portion of the 35S pre-rRNA was found to be capped in vitro. The 32P-labeled, capped 35S pre-rRNA, on nucleus P1 protection mapping, gave the protection band which is identical in size with that obtained with bulk 35S pre-rRNA. Both reverse transcription extension and nuclease P1 mapping localized the 5'-end of the 35S pre-rRNA at the same adenine nucleotide, 496 base pairs upstream from the HindIII site of the cloned rDNA fragment. Furthermore, sequencing of the 5'-terminal region of the in vitro capped 35S pre-rRNA unambiguously confirmed the above result. The strategy adopted in the present experiment could serve as a general procedure for determining the transcription initiation point even in cases where the concentration of the primary transcript is low.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach R., Allet B., Crippa M. Sequence organization of the spacer in the ribosomal genes of Xenopus clivii and Xenopus borealis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5311–5330. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach R., Grummt I., Allet B. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation region of the ribosomal transcription unit from mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1559–1569. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert W. A., Kaffenberger W., Krohne G., Franke W. W. Introduction of hidden breaks during rRNA maturation and ageing in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jul 3;87(3):607–616. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert W. A., Kaffenberger W. Regulation of rRNA metabolism in Tetrahymena pyriformis. I. Nutritional shift-down. Eur J Cell Biol. 1980 Apr;21(1):53–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engberg J., Andersson P., Leick V., Collins J. Free ribosomal DNA molecules from Tetrahymena pyriformis GL are giant palindromes. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 25;104(2):455–470. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90281-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Two conserved sequence blocks within eukaryotic tRNA genes are major promoter elements. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):626–631. doi: 10.1038/294626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Mapping of a mouse ribosomal DNA promoter by in vitro transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6093–6102. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Santer M., Steitz J. A., Mans R. J. Conservation of the primary structure at the 3' end of 18S rRNA from eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashinakagawa T., Saiga H., Shintani N., Narushima-Iio M., Mita T. Localization of putative transcription initiation site on the cloned rDNA fragment of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5905–5916. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashinakagawa T., Sezaki M., Kondo S. Isolation of nucleoli from Tetrahymena pyriformis. Dev Biol. 1979 Apr;69(2):601–611. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90314-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaffenberger W., Eckert W. A. Regulation of rRNA metabolism in Tetrahymena pyriformis. II. Nutritional shift-up. Eur J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;21(2):200–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karrer K. M., Gall J. G. The macronuclear ribosomal DNA of Tetrahymena pyriformis is a palindrome. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 25;104(2):421–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. Accurate transcription of truncated ribosomal DNA templates in a Drosophila cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1501–1505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J. Transcription of Xenopus 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):101–105. doi: 10.1038/295101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. H., Tinoco I., Jr DNA-RNA hybrid duplexes containing oligo(dA:rU) sequences are exceptionally unstable and may facilitate termination of transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2295–2299. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: in vitro and in vivo initiation and processing sites. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Yamamoto O., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. In vitro transcription of a cloned mouse ribosomal RNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6773–6785. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizumoto K., Lipmann F. Transmethylation and transguanylylation in 5'-RNA capping system isolated from rat liver nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4961–4965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Boseley P. G., Birnstiel M. L. More ribosomal spacer sequences from Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 11;8(3):467–485. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanney D. L., McCoy J. W. Characterization of the species of the Tetrahymena pyriformis complex. Trans Am Microsc Soc. 1976 Oct;95(4):664–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles E. G. Isolation of a high specific activity 35S ribosomal RNA precursor from Tetrahymena pyriformis and identification of its 5' terminus, pppAp. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4839–4844. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles E. G., Sutiphong J., Haque S. Structure of the Tetrahymena pyriformis rRNA gene. Nucleotide sequence of the transcription initiation region. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12849–12856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Sollner-Webb B., Wahn H. L. Sites of transcription initiation in vivo on Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5402–5406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., White R. L., Davis R. W. Hybridization of RNA to double-stranded DNA: formation of R-loops. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2294–2298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Ohshima Y., Suzuki Y. Assumed initiation site of fibroin gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4872–4876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urano Y., Kominami R., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. The nucleotide sequence of the putative transcription initiation site of a cloned ribosomal RNA gene of the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6043–6058. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youvan D. C., Hearst J. E. A sequence from Drosophila melanogaster 18S rRNA bearing the conserved hypermodified nucleoside am psi: analysis by reverse transcription and high-performance liquid chromatography. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1723–1741. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]