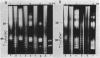
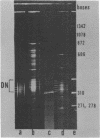
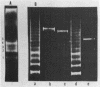
Abstract
A series of mono- and dinucleosomal DNAs characterized by an about ten-base periodicity in the size were revealed in the micrococcal nuclease digests of Drosophila chromatin which have 180 +/- 5 base pair (bp) nucleosomal repeat. 20, 30, and 40 bp spacers were found to be predominant in chromatin by trimming DNA in dinucleosomes to the core position. Among several identified mononucleosomes (MN), MN170, MN180 and MN190 were isolated from different sources (the figures indicate the DNA length in bp). The presence of the 10, 20, and 30 bp long spacers was shown in these mononucleosomes by crosslinking experiments. The interaction of histone H3 with the spacer in the Drosophila MN180 particle was also shown by the crosslinking /5/. We conclude from these results that the 10 n bp long intercore DNA (n = 2, 3 and 4) is organized by histone H3, in particular, and together with the core DNA forms a continuous superhelix. Taken together, these data suggest that Drosophila chromatin consists of the regularly aligned and tightly packed MN180, as a repeating unit, containing 10 and 20 bp spacers at the ends of 180 bp DNA. Within the asymmetric and randomly oriented in chromatin MN180, the cores occupy two alternative positions spaced by 10 bp.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J., Cowling G. J., Harborne N., Cattini P., Craigie R., Gould H. Regulation of the higher-order structure of chromatin by histones H1 and H5. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):279–288. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belyavsky A. V., Bavykin S. G., Goguadze E. G., Mirzabekov A. D. Primary organization of nucleosomes containing all five histones and DNA 175 and 165 base-pairs long. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 25;139(3):519–536. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90144-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. The organization of histones and DNA in chromatin: evidence for an arginine-rich histone kernel. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):333–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh T., Brutlag D. Sequence and sequence variation within the 1.688 g/cm3 satellite DNA of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 5;135(2):465–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90447-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Omori A., Zachau H. G. Non-random arrangement of nucleosomes in satellite I containing chromatin of rat liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5377–5390. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolchinskii A. M., Vashakidze R. P., Evgen'ev M. B., Mirzabekov A. D. Klonirovanie i izuchenie vstavochnykh posledovatel'nostei v gene 28S ribosomnoi RNA Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1982 Mar-Apr;16(2):302–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Structure of chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:931–954. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levina E. S., Bavykin S. G., Shick V. V., Mirzabekov A. D. The method of crosslinking histones to DNA partly depurinated at neutral pH. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy A., Noll M. Chromatin fine structure of active and repressed genes. Nature. 1981 Jan 15;289(5794):198–203. doi: 10.1038/289198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy A., Noll M. Multiple phases of nucleosomes in the hsp 70 genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6059–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Rau D. C., Charney E., Felsenfeld G. Orientation of the nucleosome within the higher order structure of chromatin. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Internal structure of the chromatin subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1573–1578. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Kornberg R. D. Action of micrococcal nuclease on chromatin and the location of histone H1. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 25;109(3):393–404. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder B. A., Crawford L. V. The arrangement of nucleosomes in nucleoprotein complexes from polyoma virus and SV40. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):35–49. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prunell A., Kornberg R. D. Relation of nucleosomes to DNA sequences. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):103–108. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley D., Weintraub H. Nucleosomal DNA is digested to repeats of 10 bases by exonuclease III. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):281–293. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samal B., Worcel A., Louis C., Schedl P. Chromatin structure of the histone genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):401–409. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shick V. V., Belyavsky A. V., Bavykin S. G., Mirzabekov A. D. Primary organization of the nucleosome core particles. Sequential arrangement of histones along DNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 25;139(3):491–517. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Structure of the chromatosome, a chromatin particle containing 160 base pairs of DNA and all the histones. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 12;17(25):5524–5531. doi: 10.1021/bi00618a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Koller T., Klug A. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):403–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Bakayev V. V., Georgiev G. P. Heterogeneity of chromatin subunits in vitro and location of histone H1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Feb;3(2):477–492. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weischet W. O., Allen J. R., Riedel G., Van Holde K. E. The effects of salt concentration and H-1 depletion on the digestion of calf thymus chromatin by micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(5):1843–1862. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittig B., Wittig S. A phase relationship associates tRNA structural gene sequences with nucleosome cores. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1173–1183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90230-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcel A., Benyajati C. Higher order coiling of DNA in chromatin. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):83–100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90187-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]