Abstract
Calculations of the electrostatic field of DNA in two very different double helical conformations, A and Z, are reported and compared with the results previously obtained for B-DNA. Striking contrasts between these fields and the associated electrostatic potentials are brought into evidence. One of the major differences is that while the deepest potentials are generally located in the grooves of DNA, the strongest fields are associated with the phosphate groups. The results of screening the nucleic acids by counterions are also presented.
Full text
PDF






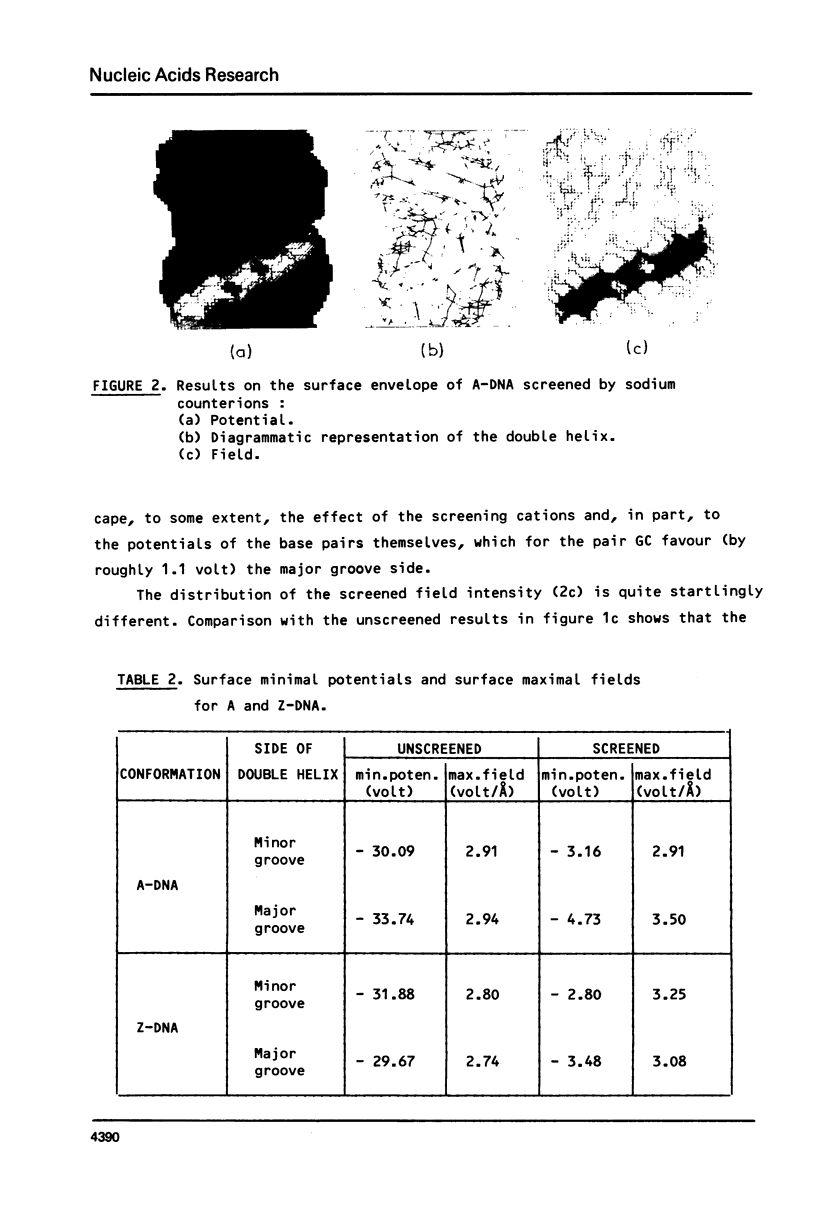





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. Optimised parameters for A-DNA and B-DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1504–1509. doi: 10.1016/0006-291X(72)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleam M. L., Anderson C. F., Record M. T. Relative binding affinities of monovalent cations for double-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3085–3089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavery R., Pullman B., Corbin S. The molecular electrostatic potential and steric accessibility of poly (dA-dT). poly (dA-dT) in various conformations: B-DNA, D-DNA and 'alternating-B' DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6539–6552. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavery R., Pullman B. The molecular electrostatic potential and steric accessibility of A-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 25;9(18):4677–4688. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.18.4677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Port G. N., Pullman A. Quantum-mechanical studies of environmental effects of biomolecules. II. Hydration sites in purines and pyrimidines. FEBS Lett. 1973 Apr 1;31(1):70–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullman A., Pullman B. Molecular electrostatic potential of the nucleic acids. Q Rev Biophys. 1981 Aug;14(3):289–380. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullman B., Perahia D., Cauchy D. The molecular electrostatic potential of the B-DNA helix. VI. The regions of the base pairs in poly (dG.dC) and poly (dA.dT). Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 24;6(12):3821–3829. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.12.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






