Abstract
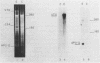
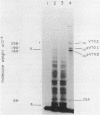
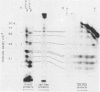
A clone for vitellogenin, a major avian, estrogen responsive egg yolk protein, was isolated from the cDNA library of estrogen-induced rooster liver. Two forms of plasma vitellogenin, vitellogenin I (VTG I) and vitellogenin II (VTG II), distinguishable on the basis of their unique partial proteolysis maps, have been characterized and their corresponding hepatic precursor forms identified. We have used this criterion to specifically characterize which vitellogenin protein had been cloned. Partial proteolysis maps of BTG I and VTG II standards, synthesized in vivo, were compared to maps of protein synthesized in vitro using RNA hybrid-selected by the vitellogenin plasmid. Eight major digest fragments were found common to the in vitro synthesized vitellogenin and the VTG II standard while no fragments were observed to correspond to the VTG I map. A restriction map of the VTG II cDNA clone permits comparison to previously described cDNA and genomic vitellogenin clones.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ab G., Roskam W. G., Dijkstra J., Mulder J., Willems M., Van der Ende A., Gruber M. Estradiol-induced synthesis of vitellogenin. III. The isolation and characterization of vitellogenin messenger RNA from avian liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 12;454(1):67–78. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90355-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christmann J. L., Grayson M. J., Huang R. C. Comparative study of hen yolk phosvitin and plasma vitellogenin. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 12;16(14):3250–3256. doi: 10.1021/bi00633a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozens P. J., Cato A. C., Jost J. P. Characterization of cloned complementary DNA covering more than 6000 nucleotides (97%) of avian vitellogenin mRNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Dec;112(3):443–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeley R. G., Gordon J. I., Burns A. T., Mullinix K. P., Binastein M., Goldberg R. F. Primary activation of the vitellogenin gene in the rooster. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8310–8319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeley R. G., Mullinix D. P., Wetekam W., Kronenberg H. M., Meyers M., Eldridge J. D., Goldberger R. F. Vitellogenin synthesis in the avian liver. Vitellogenin is the precursor of the egg yolk phosphoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):9060–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Maurhofer S., Jaggi R. B., Wyler T., Wahli W., Ryffel G. U., Weber R. Isolation and translation in vitro of four related vitellogenin mRNAs of estrogen-stimulated Xenopus laevis. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;105(1):17–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergen J. P., Stern R. H., Wensink P. C. Filter replicas and permanent collections of recombinant DNA plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2115–2136. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Burns A. T., Christmann J. L., Deeley R. G. Cloning of a double-stranded cDNA that codes for a portion of chicken preproalbumin. A general method for isolating a specific DNA sequence from partially purified mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8629–8639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Deeley R. G., Burns A. T., Paterson B. M., Christmann J. L., Goldberger R. F. In vitro translation of avian vitellogenin messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8320–8327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haff L. A., Bogorad L. Poly(adenylic acid)-containing RNA from plastids of maize. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):4110–4115. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Pehling G. Organization of vitellogenin polysomes, size of the mRNA and polyadenylate fragment. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 16;62(2):299–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Udell D. S., Deeley R. G. Characterization of the estrogen-responsive domain of avian liver and cloning of double-stranded cDNA derived from estrogen-inducible RNA species. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6781–6786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo S. C., Lampen J. O. Tunicamycin--an inhibitor of yeast glycoprotein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 May 7;58(1):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90925-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lizardi P. M., Mahdavi V., Shields D., Candelas G. Discontinuous translation of silk fibroin in a reticulocyte cell-free system and in intact silk gland cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6211–6215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Wu R. Terminal transferase-catalyzed addition of nucleotides to the 3' termini of DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):43–62. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Calvo J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the E coli gene coding for dihydrofolate reductase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2255–2274. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck D. K., Lennarz W. J. Evidence for the participation of saccharide-lipids in the synthesis of the oligosaccharide chain of ovalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1007–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., Smith D. F. Vitellogenesis: a versatile model for hormonal regulation of gene expression. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1979;35:47–95. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571135-7.50006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Ryffel G. U., Weber R. Vitellogenesis and the vitellogenin gene family. Science. 1981 Apr 17;212(4492):298–304. doi: 10.1126/science.7209528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Wyler T., Jaggi R. B., Weber R., Ryffel G. U. Vitellogenin in Xenopus laevis is encoded in a small family of genes. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Y., Williams D. L. Biosynthesis of the vitellogenins. Identification and characterization of nonphosphorylated precursors to avian vitellogenin I and vitellogenin II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3837–3846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Y., Williams D. L. Identificiation, purification, and characterization of two distinct avian vitellogenins. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 15;19(8):1557–1563. doi: 10.1021/bi00549a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Ab G., Gruber M. The nucleotide sequence of the very low density lipoprotein II mRNA from chicken. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):489–501. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Roskam W., Arnberg A., van der Zwaag-Gerritsen J., Ab G., Gruber M. Purification of the mRNA for chicken very low density lipoproteinII and molecular cloning of its full-length double-stranded cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2147–2163. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., van der Zwaag-Gerritsen J., Mulder J., Ab G., Gruber M. Translation in vivo and in vitro of mRNAs coding for vitellogenin, serum albumin and very-low-density lipoprotein II from chicken liver. A difference in translational efficiency. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar;114(3):635–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A., Cato A. C., Cozens P. J., Mattaj I. W., Jost J. P. Isolation and fine structure organisation of an avian vitellogenin gene coding for the major estrogen-inducible mRNA. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]