Abstract
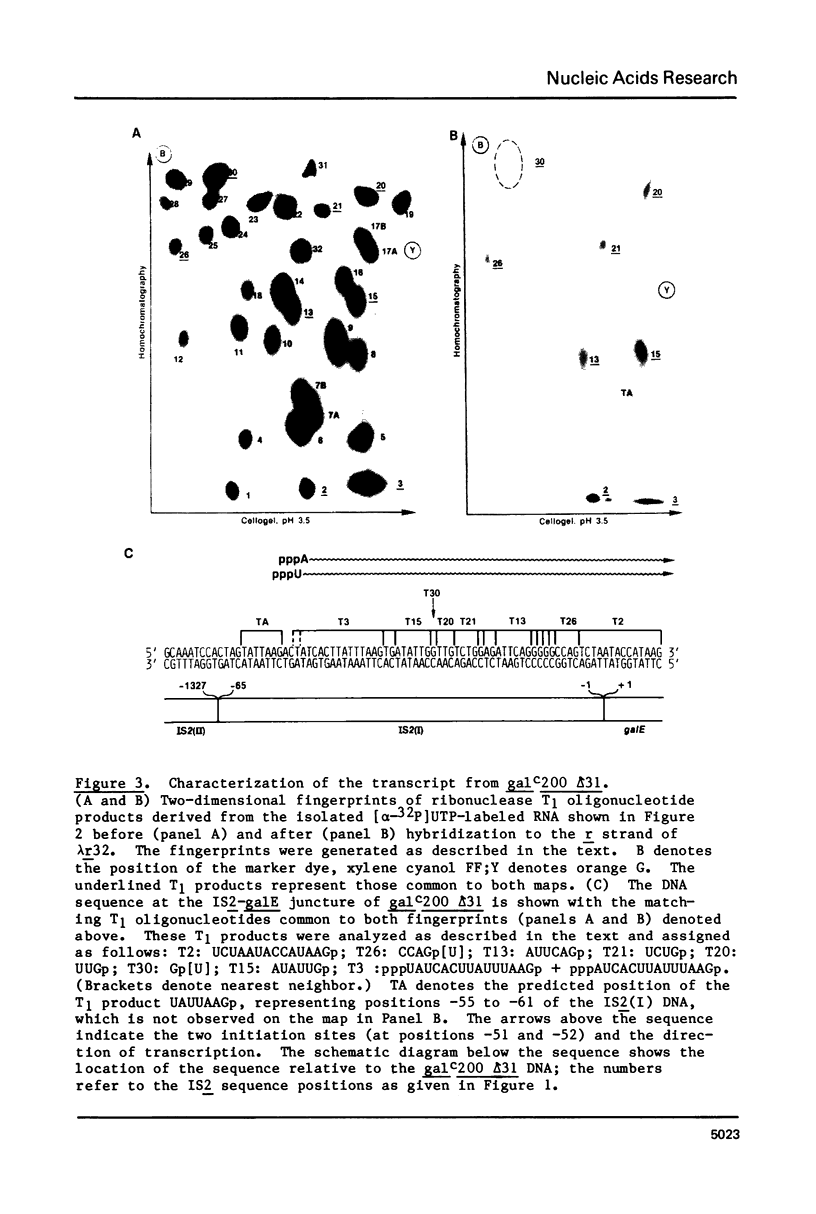
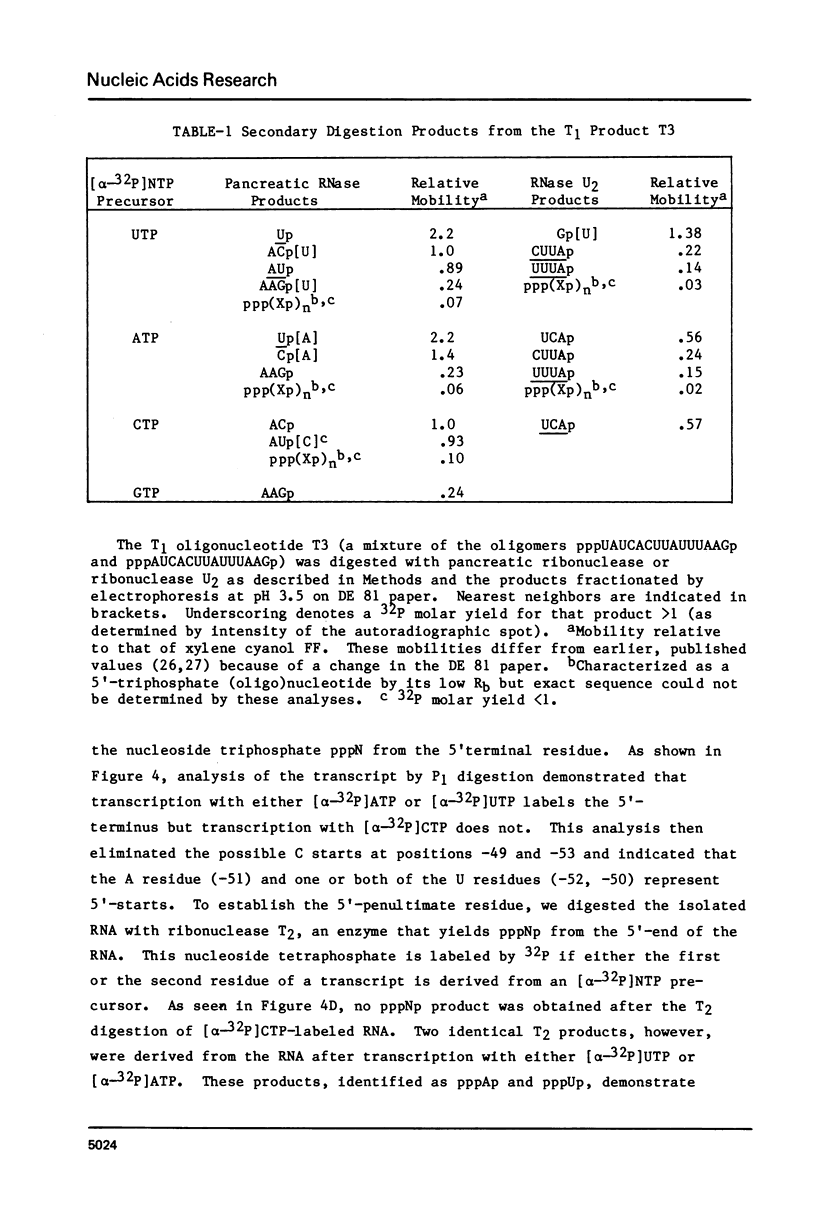
Insertion of the insertion sequence Is2(I) directly before the galE gene of the galactose operon results in a Gal minus phenotype (1, 2). The Gal-constitutive allele galc200 (and its deletion derivative galc200 delta 31) arise from such a Gal minus mutant by the insertion of LS2(II) DNA within the LS2(I) sequence (3). We have transcribed in vitro a DNA template representing the IS2-galE region of galc200 delta 31. Gal-directed transcription initiates at two sites within the IS2(I) sequence, 51 and 52 bp from the IS2-galE junction. The promoter for these transcripts, Pgal200 delta 31, is composed of a novel joint between a -10 region from the IS2(I) DNA and a -35 region contributed by the IS2(II) insertion. No promoters intrinsic to the 121 bp of the IS2(II) sequence also present on the template were detected. The relevance of Pgal200 delta 31 to the Galc phenotype of galc200 and to general mechanisms for the constitutive expression of genes adjacent to IS2 is discussed.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed A., Johansen E. Reversion of the gal3 mutation of Escherichia coli: partial deletion of the insertion sequence. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Dec 31;142(4):263–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00271251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed A., Scraba D. The nature of the gal3 mutation of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1975;136(3):233–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00334018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besemer J., Görtz G., Charlier D. Deletions and DNA rearrangements within the transposable DNA element IS2. A model for the creation of palindromic DNA by DNA repair synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5825–5833. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyen A., Charlier D., Crabeel M., Cunin R., Palchaudhuri S., Glansdorff N. Studies on the control region of the bipolar argECBH operon of Escherichia coli. I. Effect of regulatory mutations and IS2 insertions. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 May 3;161(2):185–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00274187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Miller J. H. Transposable elements. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashel M., Lazzarini R. A., Kalbacher B. An improved method for thin-layer chromatography of nucleotide mixtures containing 32P-labelled orthophosphate. J Chromatogr. 1969 Mar 11;40(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96624-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlier D., Crabeel M., Palchaudhuri S., Cunin R., Boyen A., GLANSDORFF N. Heteroduplex analysis of regulatory mutations and of insertions (IS1, IS2, IS5) in the bipolar argECBH operon of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 May 3;161(2):175–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00274186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Crombrugghe B., Adhya S., Gottesman M., Pastan I. Effect of Rho on transcription of bacterial operons. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 28;241(113):260–264. doi: 10.1038/newbio241260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius H., Charlier D., Besemer J. The structure of unstable constitutive revertants of mutant galOP-308::IS2-I. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(2):391–397. doi: 10.1007/BF00425470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiss M., Adyha S., Court D. L. Isolation of plaque-forming, galactose-transducing strains of phage lambda. Genetics. 1972 Jun;71(2):189–206. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiandt M., Szybalski W., Malamy M. H. Polar mutations in lac, gal and phage lambda consist of a few IS-DNA sequences inserted with either orientation. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(3):223–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00333860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., Saedler H. DNA sequence of the mini-insertion IS2--6 and its relation to the sequence of IS2. Nature. 1978 Oct 19;275(5681):611–617. doi: 10.1038/275611a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., Sommer H., Saedler H. Nucleotide sequence of the transposable DNA-element IS2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Mar;6(3):1111–1122. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.3.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch H. J., Starlinger P., Brachet P. Two kinds of insertions in bacterial genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(3):191–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00333858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. D., Lazzarini R. A. The 5' terminal nucleotide of RNA from vesicular stomatitis virus defective interfering particles. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):863–866. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90508-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. D., Selsing E., Wells R. D. A rapid microscale technique for isolation of recombinant plasmid DNA suitable for restriction enzyme analysis. Plasmid. 1980 Jan;3(1):88–91. doi: 10.1016/s0147-619x(80)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M., Radding C. M. Nucleotide sequence of a ribonucleic acid transcribed in vitro from lambda phage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 25;246(16):5120–5139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosharrafa E., Pilacinski W., Zissler J., Fiandt M., Szybalski W. Insertion sequence IS2 near the gene for prophage lambda excision. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Aug 10;147(1):103–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00337943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musso R. E., Di Lauro R., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Dual control for transcription of the galactose operon by cyclic AMP and its receptor protein at two interspersed promoters. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisseley S. P., Anderson W. B., Gottesman M. E., Perlman R. L., Pastan I. In vitro transcription of the gal operon requires cyclic adenosine monophosphate and cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor protein. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4671–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Ghosal D., Sommer H., Saedler H. Development of a system useful for studying the formation of unstable alleles of IS2. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 May 23;173(1):15–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00267686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilacinski W., Mosharrafa E., Edmundson R., Zissler J., Fiandt M., Szybalski W. Insertion sequence IS2 associated with int-constitutive mutants of bacteriophage lambda. Gene. 1977;2(2):61–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez R. L., West R. W., Heyneker H. L., Bolivar F., Boyer H. W. Characterizing wild-type and mutant promoters of the tetracycline resistance gene in pBR313. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3267–3287. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saedler H., Heiss B. Multiple copies of the insertion-DNA sequences IS1 and IS2 in the chromosome of E. coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 May 9;122(3):267–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00278602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saedler H., Reif H. J., Hu S., Davidson N. IS2, a genetic element for turn-off and turn-on of gene activity in E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;132(4):265–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00268569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer H., Cullum J., Saedler H. IS2-43 and IS2-44: new alleles of the insertion sequence IS2 which have promoter activity. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Aug;175(1):53–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00267855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starlinger P. IS elements and transposons. Plasmid. 1980 May;3(3):241–259. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz A., Ratzkin B., Carbon J. Control of expression of a cloned yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) gene (trp5) by a bacterial insertion element (IS2). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6172–6176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartell R. M., Reznikoff W. S. Cloning DNA restriction endonuclease fragments with protruding single-stranded ends. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90329-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Mudryj M., DiLauro R., Gottesman M. Specificity of the bacteriophage lambda N gene product (pN): nut sequences are necessary and sufficient for antitermination by pN. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1145–1151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]