Abstract
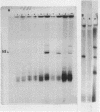
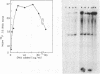
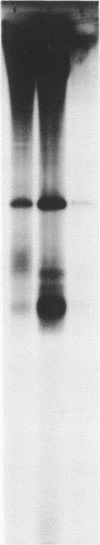
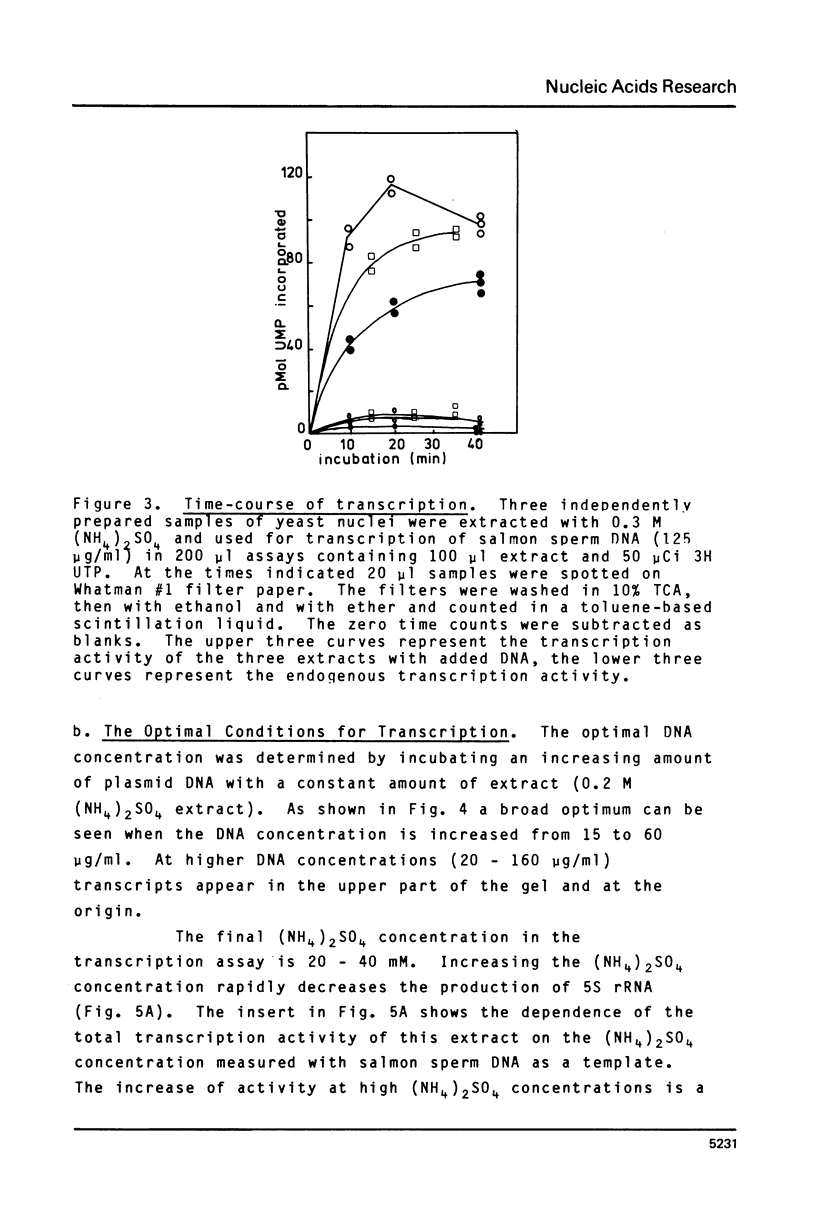
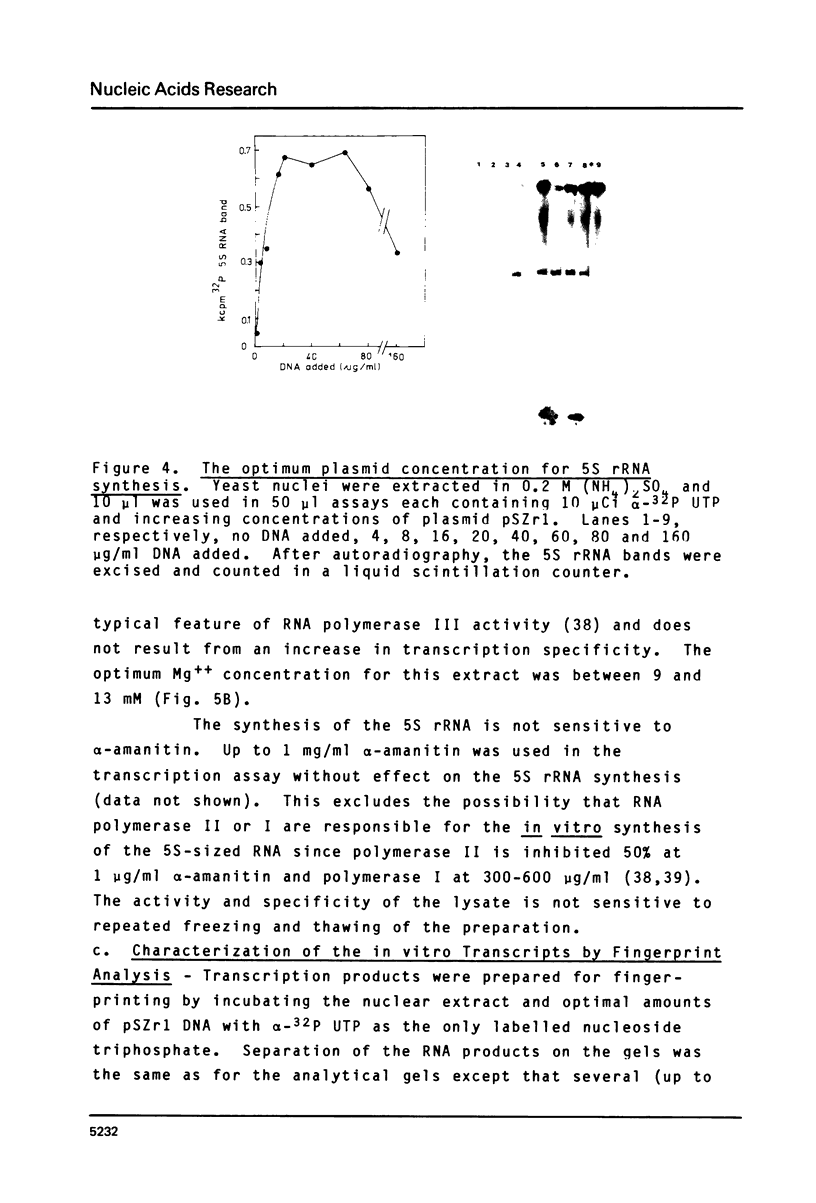
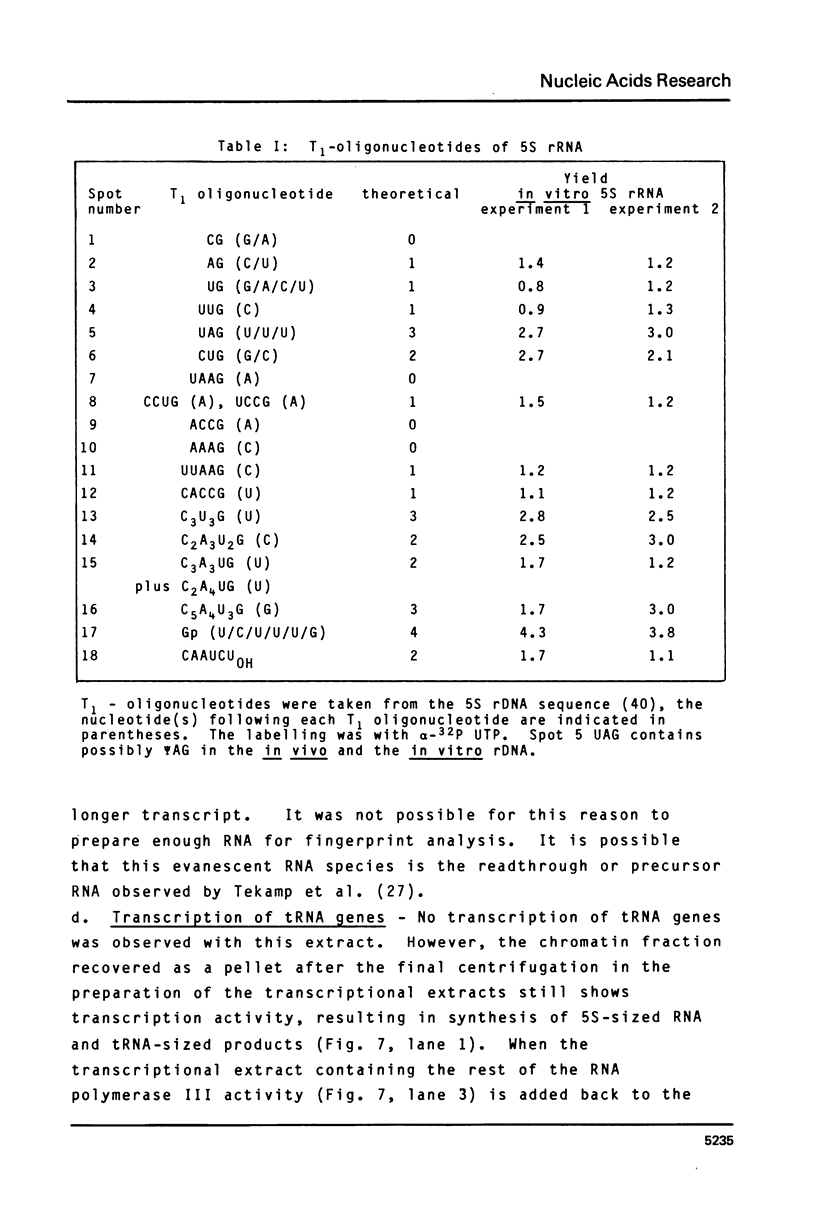
A cell-free extract of yeast nuclei that can specifically transcribe cloned yeast 5S rRNA genes has been developed. Optima for transcription of 5S rDNA were determined and conditions of extract preparation leading to reproducible activities and specificities established. The major in vitro product has the same size and oligonucleotide composition as in vivo 5S rRNA. The in vitro transcription extract does not transcribe yeast tRNA genes. The extract does increase the transcription of tRNA genes packaged in chromatin.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., DeGennaro L. J., Gelfand D. H., Bishop R. J., Valenzuela P., Rutter W. J. Ribosomal RNA genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Physical map of the repeating unit and location of the regions coding for 5 S, 5.8 S, 18 S, and 25 S ribosomal RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8118–8125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Brown D. D., Jordan E. A nuclear extract of Xenopus laevis oocytes that accurately transcribes 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1077–1086. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco D., Schmidt O., Söll D. Two control regions for eukaryotic tRNA gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3365–3368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes D. M., Shenk T. Transcriptional control regions of the adenovirus VAI RNA gene. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber R. L., Gage L. P. Transcription of a cloned Bombyx mori tRNA2Ala gene: nucleotide sequence of the tRNA precursor and its processing in vitro. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):817–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. M., Olson M. V., Hall B. D. Nucleotide sequence of a mutant eukaryotic gene: the yeast tyrosine-inserting ochre suppressor SUP4-o. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5453–5457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Larson D., Hall G. I., Sprague K. U. The primary transcription product of a silkworm alanine tRNA gene: identification of in vitro sites of initiation, termination and processing. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1217–1229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Kressman A., Birnstiel M. L. A split promoter for a eucaryotic tRNA gene. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):573–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Kurjan J. tRNA synthesis: identification of in vivo precursor tRNAs from parental and mutant yeast strains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):1019–1029. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski R. A., Clarkson S. G., Kurjan J., Hall B. D., Smith M. Mutations of the yeast SUP4 tRNATyr locus: transcription of the mutant genes in vitro. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):415–425. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90352-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kressmann A., Hofstetter H., Di Capua E., Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. A tRNA gene of Xenopus laevis contains at least two sites promoting transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1749–1763. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J., Hall B. D., Gillam S., Smith M. Mutations at the yeast SUP4 tRNATyr locus: DNA sequence changes in mutants lacking suppressor activity. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoccia E., Baldi M. I., Carrara G., Fruscoloni P., Benedetti P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Separation of RNA transcription and processing activities from X. laevis germinal vesicles. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):643–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90119-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng S. Y., Parker C. S., Roeder R. G. Transcription of cloned Xenopus 5S RNA genes by X. laevis RNA polymerase III in reconstituted systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):136–140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. Preparation of RNA and ribosomes from yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:45–64. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60951-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D., Engelke D., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. The binding of a transcription factor to deletion mutants of a 5S ribosomal RNA gene. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):665–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt O., Mao J. I., Silverman S., Hovemann B., Söll D. Specific transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes in Xenopus germinal vesicle extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4819–4823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz L. D., Hall B. D. Transcription in yeast: alpha-amanitin sensitivity and other properties which distinguish between RNA polymerases I and III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1029–1033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligy V. L., Thomas D. Y., Miki B. L. Saccharomyces cerevisiae plasmid, Scp or 2 mum: intracellular distribution, stability and nucleosomal-like packaging. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 11;8(15):3371–3391. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.15.3371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman S., Schmidt O., Söll D., Hovemann B. The nucleotide sequence of a cloned Drosophila arginine tRNA gene and its in vitro transcription in Xenopus germinal vesicle extracts. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10290–10294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague K. U., Larson D., Morton D. 5' flanking sequence signals are required for activity of silkworm alanine tRNA genes in homologous in vitro transcription systems. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Wu R. Insertion of a genetic marker into the ribosomal DNA of yeast. Plasmid. 1979 Oct;2(4):536–554. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tekamp P. A., Garcea R. L., Rutter W. J. Transcription and in vitro processing of yeast 5 S rRNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9501–9506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tekamp P. A., Valenzuela P., Maynard T., Bell G. I., Rutter W. J. Specific gene transcription in yeast nuclei and chromatin by added homologous RNA polymerases I and II. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):955–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Bell G. I., Venegas A., Sewell E. T., Masiarz F. R., DeGennaro L. J., Weinberg F., Rutter W. J. Ribosomal RNA genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Physical map and nucleotide sequence of the 5 S ribosomal RNA gene and adjacent intergenic regions. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8126–8135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Hager G. L., Weinberg F., Rutter W. J. Molecular structure of yeast RNA polymerase III: demonstration of the tripartite transcriptive system in lower eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1024–1028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volckaert G., Jou W. M., Fiers W. Analysis of 32P-labeled bacteriophage MS2 RNA by a mini-fingerprinting procedure. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:433–446. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90551-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Luse D. S., Segall J., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate initiation of transcription at the Ad2 major late promotor in a soluble system dependent on purified RNA polymerase II and DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):469–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Segall J., Harris B., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Faithful transcription of eukaryotic genes by RNA polymerase III in systems reconstituted with purified DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6163–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G. J. Adenovirus DNA-directed transcription of 5.5S RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2175–2179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G. Faithful transcription of adenovirus 5.5 S RNA gene by RNA polymerase III in a human KB cell-free extract. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]