Abstract
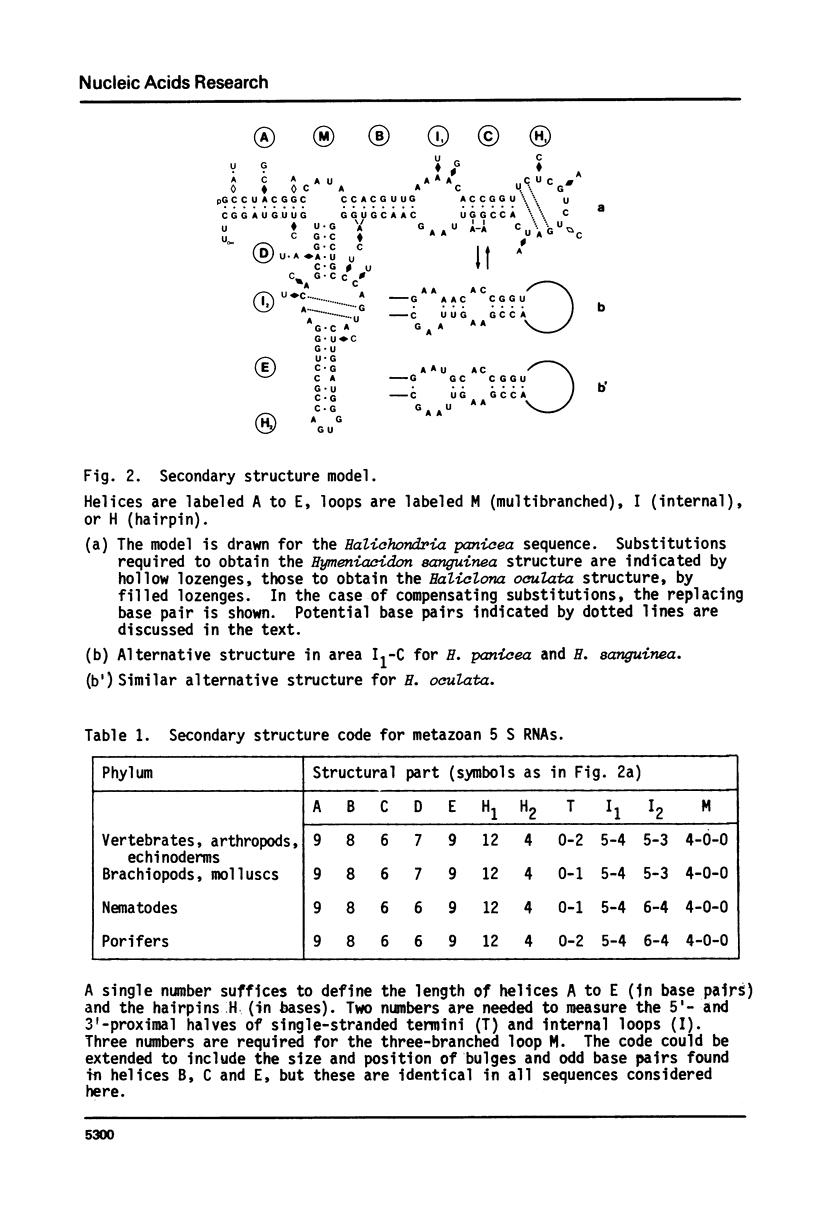
We have determined the nucleotide sequences of 5 S ribosomal RNAs isolated from the sponges Halichondria panicea, Hymeniacidon sanguinea, and Haliclona oculata. The structures can be fitted in a universal five-helix secondary structure model (De Wachter, Chen and Vandenberghe (1982) Biochimie 64, 311-329) applicable to all 5 S RNAs hitherto sequenced. The base pairing scheme proves to be extremely conserved throughout the metazoan kingdom, yet four slightly different variants of the model may be distinguished among the 5 S RNAs from the seven animal phyla investigated until now.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butler M. H., Wall S. M., Luehrsen K. R., Fox G. E., Hecht R. M. Molecular relationships between closely related strains and species of nematodes. J Mol Evol. 1981;18(1):18–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01733207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wachter R., Chen M. W., Vandenberghe A. Conservation of secondary structure in 5 S ribosomal RNA: a uniform model for eukaryotic, eubacterial, archaebacterial and organelle sequences is energetically favourable. Biochimie. 1982 May;64(5):311–329. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diels L., De Baere R., Vandenberghe A., De Wachter R. The sequence of 5S ribosomal RNA of the crustacean Artemia salina. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):5141–5144. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.5141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A. Collection of published 5S and 5.8S RNA sequences and their precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):r93–115. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.762-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay R. M., Spencer D. F., Schnare M. N., Doolittle W. F., Gray M. W. Comparative sequence analysis as an approach to evaluating structure, function, and evolution of 5S and 5.8S ribosomal RNAs. Can J Biochem. 1982 Apr;60(4):480–489. doi: 10.1139/o82-057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninio J. Prediction of pairing schemes in RNA molecules-loop contributions and energy of wobble and non-wobble pairs. Biochimie. 1979;61(10):1133–1150. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(80)80227-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Takemura S. Structure and function of 5S ribosomal ribonucleic acid from Torulopsis utilis. II. Partial digestion with ribonucleases and derivation of the complete sequence. J Biochem. 1974 Nov;76(5):935–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. Use of in vitro 32P labeling in the sequence analysis of nonradioactive tRNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:58–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Gauss D. H. Compilation of tRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):r1–55. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. A., Luehrsen K. R., Woese C. R., Pace N. R. An unusual 5S rRNA, from Sulfolobus acidocaldarius, and its implications for a general 5S rRNA structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6129–6137. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Dyer T. A., Brownlee G. G. An improved direct RNA sequence method; its application to Vicia faba 5.8S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1259–1272. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Wegnez M. R., Hearst J. E. Determination of the secondary structure of Drosophila melanogaster 5 S RNA by hydroxymethyltrimethylpsoralen crosslinking. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 15;147(3):417–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90493-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troutt A., Savin T. J., Curtiss W. C., Celentano J., Vournakis J. N. Secondary structure of Bombyx mori and Dictyostelium discoideum 5S rRNA from S1 nuclease and cobra venom ribonuclease susceptibility, and computer assisted analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):653–664. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


