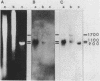
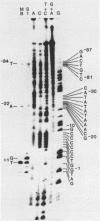
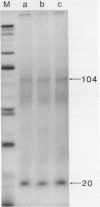
Abstract
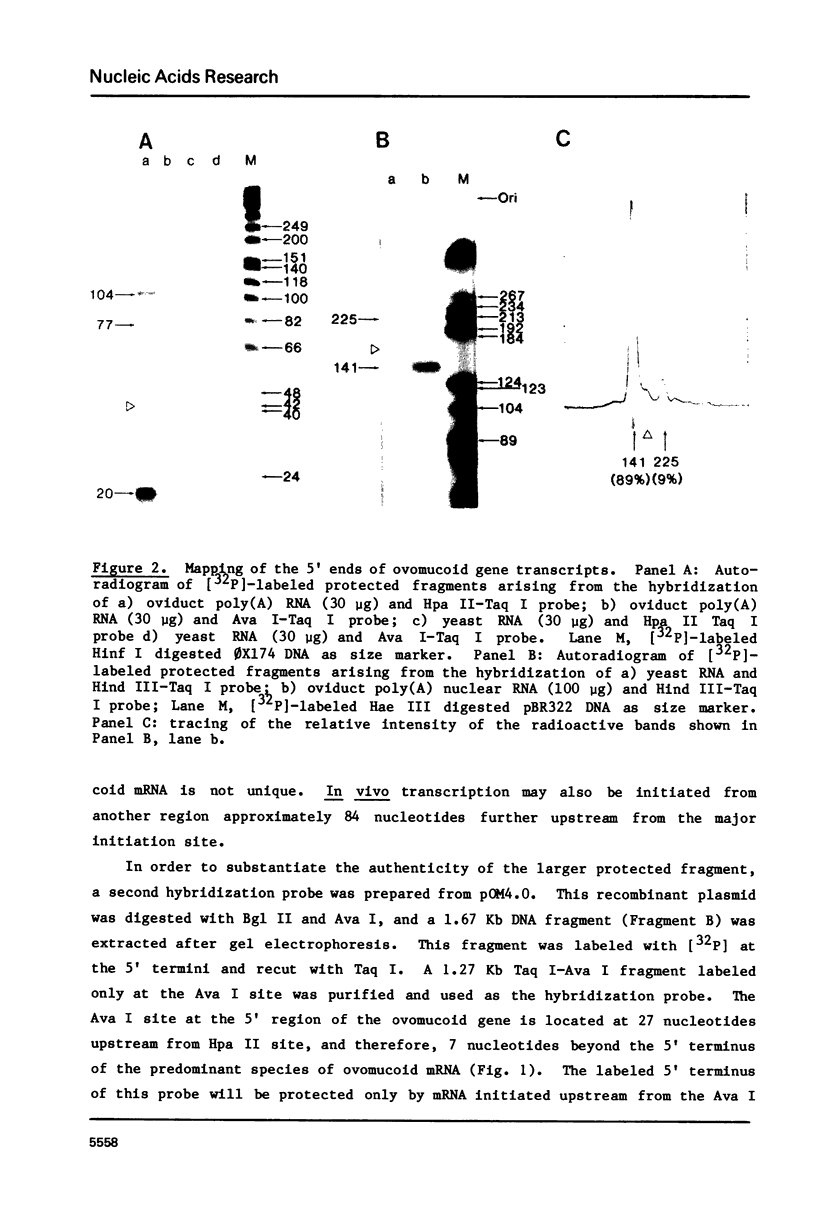
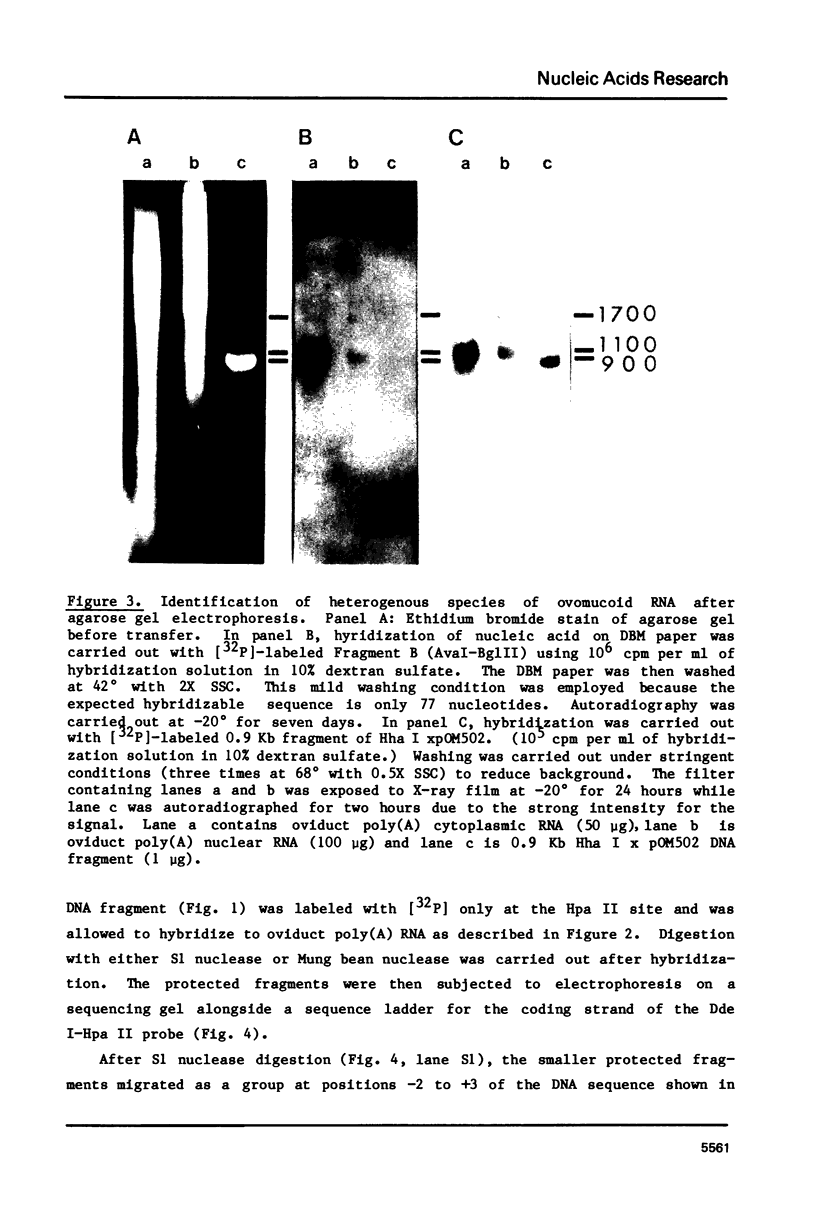
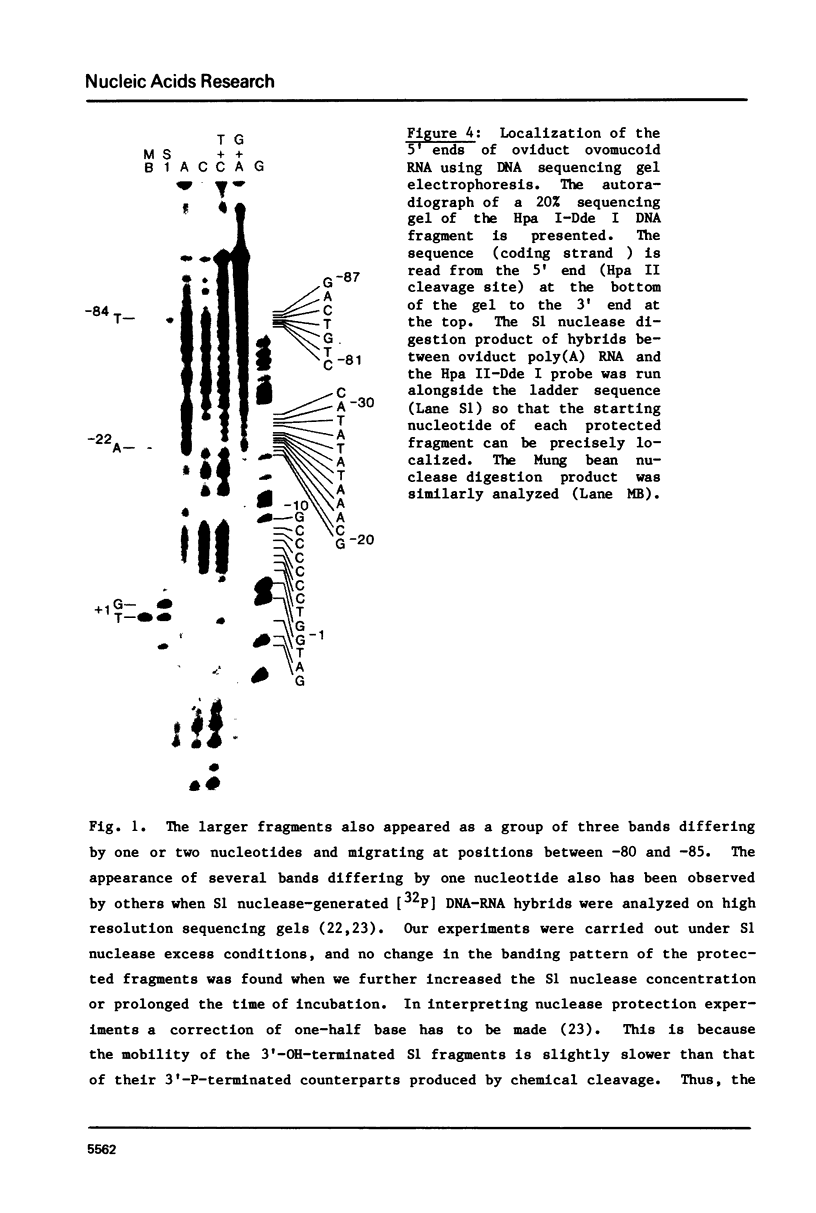
We have identified the 5' termini of ovomucoid RNA transcripts isolated from estrogen stimulated chick oviduct by S1-nuclease mapping. Most of the ovomucoid RNA molecules (88-89%) are initiated at a predominant region which is positioned at about 30 basepairs downstream from a "TATATAT" sequence. However, there is at least one additional initiation region which accounts for 9% of the ovomucoid RNA transcripts. It is located at approximately 80 basepairs further upstream (5') from the major initiation region. DNA sequence data reveal that an AT-rich sequence resembling the "TATA" box is also present 30 nucleotides before this minor region. Our finding provides additional insight into the molecular mechanism involved in the transcription initiation of eucaryotic genes, and indicates that in vivo synthesis of mRNA may not require an absolute site for initiation of transcription.
Full text
PDF


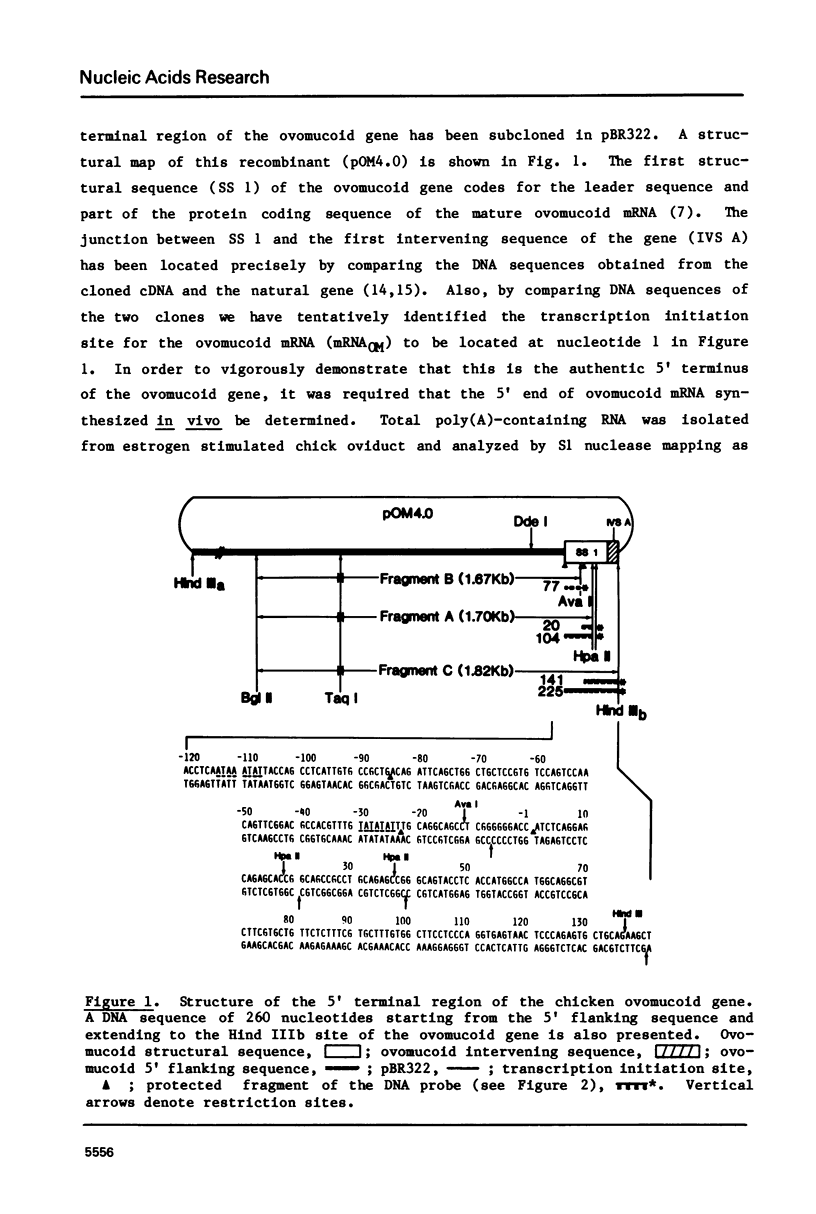








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani D., Kahana C., Mukamel A., Groner Y. Sequence heterogeneity at the 5' termini of late simian virus 40 19S and 16S mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3078–3082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall J. F., Stein J. P., Kristo P., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Primary sequence of ovomucoid messenger RNA as determined from cloned complementary DNA. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):480–487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Steroid hormone regulation of specific gene expression. Vitam Horm. 1978;36:259–295. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60986-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Tyndall C., Kamen R. Sequences at the capped 5'-ends of polyoma virus late region mRNAs: an example of extreme terminal heterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6305–6322. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodgson J. B., Wells R. D. Action of single-strand specific nucleases on model DNA heteroduplexes of defined size and sequence. Biochemistry. 1977 May 31;16(11):2374–2379. doi: 10.1021/bi00630a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faye G., Leung D. W., Tatchell K., Hall B. D., Smith M. Deletion mapping of sequences essential for in vivo transcription of the iso-1-cytochrome c gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Heterogeneity and 5'-terminal structures of the late RNAs of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):813–846. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grez M., Land H., Giesecke K., Schütz G., Jung A., Sippel A. E. Multiple mRNAs are generated from the chicken lysozyme gene. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groner Y., Carmi P., Aloni Y. Capping structures of simian virus 40 19S and 16S mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Nov;4(11):3959–3968. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.11.3959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Bovey R., Young R. A. Tissue-specific expression of mouse-alpha-amylase genes: nucleotide sequence of isoenzyme mRNAs from pancreas and salivary gland. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C., Irminger J. C., Bucher P., Birnstiel M. L. Sea urchin histone mRNA termini are located in gene regions downstream from putative regulatory sequences. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):147–151. doi: 10.1038/285147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N. E., Groner B., Sippel A. E., Nguyen-Huu M. C., Schütz G. mRNA complexity and egg white protein mRNA content in mature and hormone-withdrawn oviduct. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):923–932. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90303-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E. C., Stein J. P., Catterall J. F., Woo S. L., Mace M. L., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Molecular structure and flanking nucleotide sequences of the natural chicken ovomucoid gene. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90135-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek L. T., Eschenfeldt W. H., Munns T. W., Rhoads R. E. Heterogeneity of the 5' terminus of hen ovalbumin messenger ribonucleic acid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1657–1673. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McReynolds L., O'Malley B. W., Nisbet A. D., Fothergill J. E., Givol D., Fields S., Robertson M., Brownlee G. G. Sequence of chicken ovalbumin mRNA. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):723–728. doi: 10.1038/273723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Birnstiel M. L. The putative promoter of a Xenopus laevis ribosomal gene is reduplicated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 24;6(12):3733–3743. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.12.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Regulation of protein synthesis in chick oviduct. I. Independent regulation of ovalbumin, conalbumin, ovomucoid, and lysozyme induction. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6450–6461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Nordstrom J. L., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Transcription of structural and intervening sequences in the ovalbumin gene and identification of potential ovalbumin mRNA precursors. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):671–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Tosi M., Pittet A. C., Fabiani L., Wellauer P. K. Tissue-specific expression of mouse alpha-amylase genes. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 5;142(1):93–116. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. P., Catterall J. F., Kristo P., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Ovomucoid intervening sequences specify functional domains and generate protein polymorphism. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90431-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. P., Catterall J. F., Woo S. L., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Molecular cloning of ovomucoid gene sequences from partially purified ovomucoid messenger RNA. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5763–5772. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Roop D. R., Tsai M. J., Stein J. P., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Effect of estrogen on gene expression in the chick oviduct. Regulation of the ovomucoid gene. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5773–5780. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Specific 5' flanking sequences are required for faithful initiation of in vitro transcription of the ovalbumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):879–883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B. Transcription and RNA processing by the DNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):491–499. doi: 10.1038/287491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]