Abstract
The formation of cluster roots by plants represents a highly efficient strategy for acquisition of sparingly available phosphate. This particular root type is characterized by a densely branched structure and high exudation of organic acids and protons, which are likely to influence the resident bacterial community. Until now, the identity of the bacterial populations living in cluster roots has not been investigated. We applied cultivation-dependent and cultivation-independent methods to characterize the dominant bacterial genera inhabiting the growing cluster roots of white lupin. We observed a high relative abundance of Burkholderia species (up to 58% of all isolated strains and 44% of all retrieved 16S rRNA sequences) and a significant enrichment with increasing cluster root age. Most of the sequences retrieved clustered together with known plant- or fungus-associated Burkholderia species, while only one of 98 sequences was affiliated with the Burkholderia cepacia complex. In vitro assays revealed that Burkholderia strains were much more tolerant to low pH than non-Burkholderia strains. Moreover, many strains produced large amounts of siderophores and were able to utilize citrate and oxalate as carbon sources. These features seem to represent important traits for the successful colonization and maintenance of Burkholderia species in white lupin cluster roots.
INTRODUCTION
To access sparingly available nutrients such as phosphate, plants have evolved several strategies, e.g., mycorrhizal association and cluster root formation. Cluster roots are very densely branched root structures with a particular excretion physiology (20, 21, 25). They occur in many species of the Proteaceae family and occasionally in the Mimosaceae, Casuarinaceae, or Fabaceae (7). White lupin is the only cluster-rooted species of agricultural importance and has thus been extensively studied (9, 17, 26, 32, 33, 41, 42). In white lupin, cluster root development follows a well-defined pattern: at the juvenile stage, cluster roots secrete small amounts of malate; at the mature stage, high quantities of citrate and protons are excreted, leading to drastic rhizosphere acidification; and at the senescent stage, organic acid excretion decreases. Besides citrate and malate, oxalate and fumarate have also been reported to be exuded by soil-grown lupin plants (6, 41). The close vicinity of growing cluster roots constitutes a highly selective environment, owing to rapid changes in pH and carbon availability. The abundance of bacteria, as well as richness and diversity, has been shown to decrease temporarily in mature cluster roots (40). However, the identity of the populations repressed or enriched during cluster root development has yet to be elucidated. We analyzed the bacterial communities living in the direct vicinity of cluster roots (root surface and inner tissues) by sequencing isolated strains and clone libraries constructed from root-extracted DNA. We then tested relevant physiological properties of isolates to better understand which metabolic abilities might enable bacteria to efficiently colonize this highly selective and rapidly changing environment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant material, growing conditions, and sampling.
Plants were grown as described in reference 40. Briefly, white lupin seeds (Lupinus albus cv. Amiga) were germinated in 0.2 mM CaCl2 and transferred after 4 days to 4 microcosms (1 plant per microcosm) containing 800 g of tyndallized sandy substrate (origin, Nigeria; pH [H2O] 5.7; grain size, 0.1 to 1 mm; 91.8% sand, 7.5% silt, and 0.7% clay). Microcosms were inoculated with a soil suspension (0.5%, vol/vol) from a field in Piemonte (northern Italy) where white lupins had been grown for 20 years. The resulting substrate showed very low phosphate levels (about 0.25 mg · g−1, present mostly as inorganic P). To avoid iron and nitrogen deficiency, both nutrients were supplemented during biweekly watering, and the plants did not form nodules. Plants were grown for 5 weeks in a climate chamber at 22°C and 65% relative humidity with a light period of 16 h at 200 μmol m−2 s−1. Prior to harvesting, cluster root stages were determined using a pH indicator agar overlay method (40). The roots were washed from their adhering rhizosphere soil in sodium phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 7) (SPB). Cluster roots belonging to the same developmental stage within each plant and between the four replicate plants were pooled to obtain sufficient and representative material for each stage. Fingerprinting analyses previously performed on the same samples showed that the variability between cluster roots from the four different replicate plants was very low (40).
Identification and physiological characterization of isolates.
For each cluster root stage, tissue- and surface-inhabiting bacteria were isolated as described earlier (40). Briefly, serial dilutions of the washed root samples were performed in SPB and plated on Angle medium (1). Thirty to 80 colonies per cluster root stage were randomly picked, checked for purity, and stored in 25% glycerol at −80°C until further analysis. For strain identification, the entire 16S rRNA gene was amplified from strains isolated from roots of each stage (n = 34 to 52), using the universal bacterial primers 5F and 1545R (18). PCR products were purified and sequenced from both ends using an ABI3730 automated sequencer. The sequences were manually checked for quality, assembled, trimmed, and aligned using BioEdit (http://www.mbio.ncsu.edu/bioedit/bioedit.html). The sequences were subjected to Blast searches against the NCBI database (see Table S1 in the supplemental material for blast hits). To test the ability of isolates to grow on various C sources, strains were grown on AB minimal medium plates (pH 7) (16) supplemented with 400 μl of a 25,000× concentrated solution of micronutrients (40) and amended with 25 mM either citrate, malate, or fumarate as a carbon source. The AB medium containing oxalate was prepared in a double layer, the lower of which contained AB medium without a carbon source and the upper of which contained 0.7% Ca-oxalate and 1.2% agar. A transparent halo around the colonies was indicative of oxalotrophy. P solubilization, siderophore production, and auxin production were performed as described in reference 40. Acid tolerance was assessed as described in reference 39. The presence of acdS (encoding 1-aminocyclopropane 1-carboxylic acid [ACC] deaminase) in Burkholderia strains was checked using the newly designed primers acdS F (5′CGCAAGCTCGAATAYCTG) and acdS R (5′GTGCATCGAYTTGCCYTC) spanning 744 bp of the gene, from position 157 to 900 of Burkholderia vietnamiensis strain LMG 6999 (EU886310.1). The presence of the nifH gene (encoding nitrogenase) was tested using the PolyF/PolyR primer pair (30).
Cloning and sequencing of 16S rRNA genes from root-extracted DNA.
Cluster root DNA was extracted as described previously (40). The entire 16S rRNA gene was amplified using the primer set described above and cloned into pCR2.1 (Invitrogen). Clones were checked for inserts of plant origin (giving positive amplification with plastid-specific primers [14]), and clones containing an insert of bacterial origin were sequenced as described above. Sequences were checked for quality, manually assembled, and subjected to Blast searches as described above (see Table S2 in the supplemental material for blast hits). Construction of the phylogenetic tree was performed using the ARB software package (http://www.arb-home.de/). Sequences were aligned using ARB's Fast Aligner tool, manually checked, and added to the database. Ralstonia pickettii AY268176 was chosen as an outgroup. Bootstrap analysis (n = 1,000) was performed.
Nucleotide sequence accession numbers.
The sequences determined in this study have been deposited in GenBank under accession numbers JN590279 to JN590738.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Burkholderia species are among the dominant bacterial groups of the cluster root community.
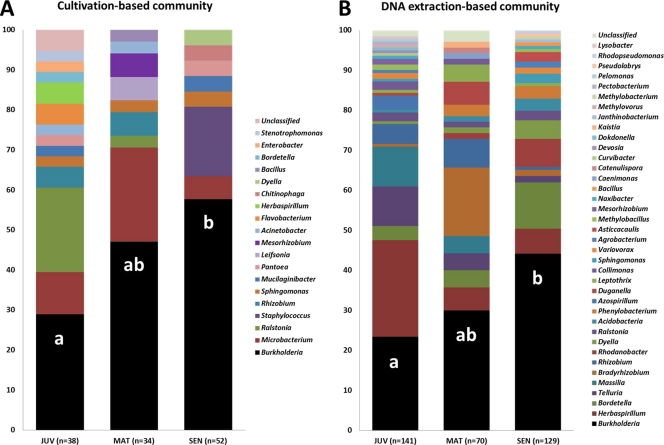
The 16S rRNA gene-based sequencing of strains isolated from inner tissues and surfaces of growing cluster roots revealed a high relative abundance of Burkholderia species, ranging from 29% of all isolates in juvenile cluster roots to 58% in senescent cluster roots (Fig. 1A). In order to assess whether the dominance of the Burkholderia genus was due to these organisms being more readily cultivable than other bacterial inhabitants of cluster roots, we constructed 16S rRNA-based clone libraries. While the relative abundance of Burkholderia spp. obtained with this cultivation-independent method was lower than that obtained with isolates (from 23% to 45%), the same pattern of enrichment of Burkholderia spp. with increasing cluster root age was observed (Fig. 1B). Interestingly, besides Burkholderia, the four next most abundant genera in clone libraries (Fig. 1B) (i.e., Herbaspirillum, Bordetella, Telluria, and Massilia) all belonged to the order Burkholderiales, with the exception of Bradyrhizobium. Together with other, less abundant sequences, Burkholderiales represented about 70% of all retrieved sequences. These observations are in line with previous studies on endophytes which showed a large majority of Burkholderiales in cucumber seedlings (13, 27) and in Medicago sativa mycorrhizal roots (28). Furthermore, stable-isotope probing (SIP)-based studies revealed that within the Agrostis stolonifera root endophytic community, Burkholderiales were among the most active in taking up plant-derived carbon (35), corroborating earlier findings for the rice rhizosphere (23). Remarkably, Burkholderia was the only genus which significantly increased its relative abundance as cluster roots aged. This suggests adaptation to the growing cluster root environment and a capacity to survive the dramatic changes in carbon availability and pH (changing within a few days from pH 6 in juvenile roots to pH 4 in mature roots and to pH 7 in senescent roots) (26).
Fig. 1.
Major bacterial populations detected in growing cluster roots of white lupin (L. albus L.) by 16S rRNA sequencing of isolates (A) and clone libraries constructed from root-extracted DNA (B). JUV, juvenile cluster roots; MAT, mature cluster roots; SEN, senescent cluster roots. All but a few sequences (3 for isolates and 4 for clones) could be assigned with high confidence (≥97% for isolates and ≥94% for clones) to known genera. The relative abundance of each genus is shown as a percentage. The relative abundance of isolates or clones belonging to the genus Burkholderia was compared between root stages using the chi-square test. Different letters within the columns indicate statistically different values (P < 0.05).
Shifts in the Burkholderia populations from juvenile to senescent cluster roots.
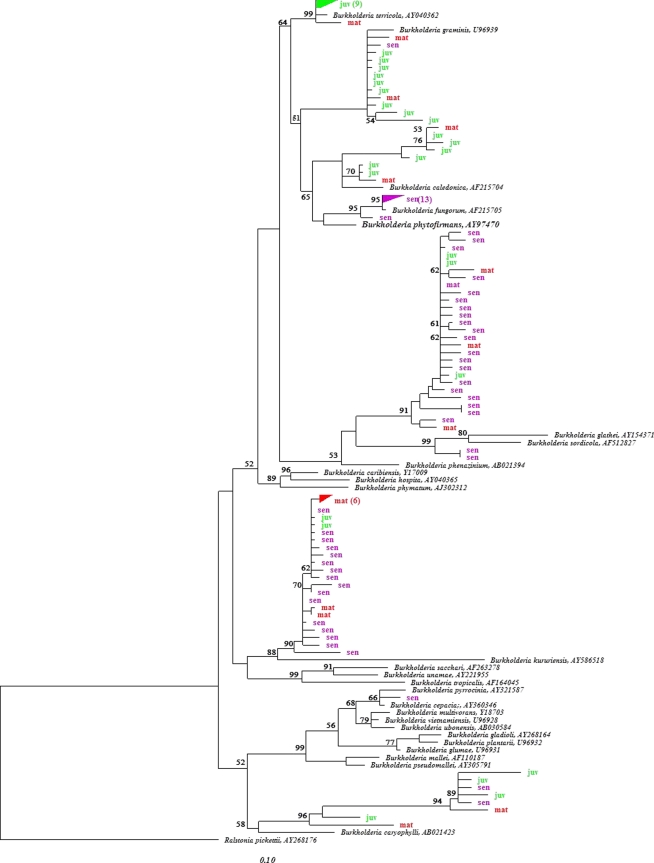
To investigate the intrageneric diversity of Burkholderia populations and their putative shifts along growing roots, sequences affiliated with the genus Burkholderia (>94%) were compared with their closest known relatives by neighbor-joining analysis (Fig. 2). Only one of the 98 Burkholderia sequences was indicative of a member of the Burkholderia cepacia complex. The B. cepacia complex consists of 17 closely related species, which are frequently found in natural habitats but can behave as opportunistic pathogens and have thus been extensively studied (5, 36). Few sequences from all three cluster root stages clustered with B. caryophylli, which is pathogenic to Dianthus caryophylli (3), although members of this species have also been shown to promote wheat growth in pot experiments (31). All other sequences clustered with plant- or fungus-associated Burkholderia species. Interestingly, there was a shift in the Burkholderia populations as cluster roots aged from juvenile to senescent: while many sequences retrieved from juvenile roots clustered with B. terricola, B. graminis, and B. caledonica, most of the sequences retrieved from senescent roots were associated with B. fungorum, B. glathei, B. sordidicola, and B. kururiensis. Although little is yet known about the natural habitat of B. terricola, B. graminis, and B. caledonica, they have been reported to be distantly or closely associated with plants (2, 4, 8, 12, 37). In contrast, B. fungorum, B. glathei, and B. sordidicola have been described as fungus-associated Burkholderia spp. (10, 19, 22, 38). This shift toward fungus-associated species as roots progress from the juvenile to the senescent stage might be linked to the rapid decay of senescent roots, which constitute an ideal niche for organic matter-degrading fungi. Burkholderia sequences retrieved from mature roots were phylogenetically diverse, despite the extremely selective environment (low pH and large amounts of citrate). Most sequences were closely related to B. kururiensis, a species first isolated from a polluted aquifer (43) and later observed to fix nitrogen and promote rice growth (24). However, other sequences retrieved from the mature stage were also found in phylogenetic clusters harboring sequences from juvenile and senescent origins. Based on this analysis, it appears that Burkholderia populations from mature cluster roots represent a transition state between juvenile and senescent stages, hosting both remnants of the past and pioneers of the future.
Fig. 2.
16S rRNA-based neighbor-joining tree, showing the phylogenetic relationship of Burkholderia sequences retrieved from the inner and surface tissues of cluster roots with their closest phylogenetic relatives within the Burkholderia genus. juv, juvenile cluster roots; mat, mature cluster roots; sen, senescent cluster roots. Bootstrap values of higher than 50 are shown.
Relevant physiological properties for establishment and persistence of bacterial populations in growing cluster roots.
Cluster roots represent a very special environment for root-colonizing bacteria, and our observation that Burkholderia species constitute a major component of the community raises the question of the metabolic properties that may provide Burkholderia spp. a competitive advantage in this habitat. To address this issue, we performed physiological tests on isolates and compared Burkholderia isolates to non-Burkholderia isolates (Table 1). In view of the rapid and important acidification occurring in mature cluster roots, acid tolerance appears to be a prerequisite for persistence in cluster roots beyond the mature stage. Indeed, when acid tolerance of the isolates was tested, we observed that growth at low pH was significantly more frequent among Burkholderia isolates (with 77% of strains able to grow at pH 4) than among non-Burkholderia isolates (41%). Almost all isolates, irrespective of the identity and cluster root age, were able to use malate and fumarate as a sole C source (Table 1). However, utilization of citrate, the organic acid excreted in highest quantities by white lupin cluster roots, appeared to be more widespread in Burkholderia isolates (62%) than in non-Burkholderia isolates (25%). Finally, growth on oxalate was a property almost exclusive to Burkholderia isolates, with 93% of Burkholderia isolates able to grow on oxalate against only 2% of the non-Burkholderia isolates. To test for plant growth promotion properties, we assessed P solubilization, siderophore production (since cluster roots are also formed in response to iron starvation) (15), and synthesis of auxin (a hormone involved in cluster root formation [11]). A large proportion of isolates, both Burkholderia and non-Burkholderia, were able to solubilize inorganic P, which may reflect the low availability of this element in the direct vicinity of the root due to the plant's very efficient P acquisition. Siderophore production was widespread among Burkholderia isolates (80%) but less so among non-Burkholderia isolates (26%). Finally, auxin production was much more widespread among non-Burkholderia isolates than among Burkholderia isolates. This is not surprising, considering the facts that Burkholderia was isolated mostly from mature and senescent cluster roots and that auxin is required at the very early stage of cluster root development. In addition to the above-mentioned plant growth-promoting traits, ACC deaminase activity (which cleaves the ethylene precursor 1-aminocyclopropane 1-carboxylic acid [ACC], thereby reducing the levels of this stress hormone in plants) has been reported to be a widespread feature among plant-associated Burkholderia species (29). We therefore tested the Burkholderia isolates recovered from white lupin cluster roots for the presence of the ACC deaminase gene. A high proportion of the isolates (77%) possessed this gene, suggesting that they may play a role in plant stress alleviation. In contrast, the nifH gene could not be amplified from any of the isolates, which was not surprising given the fact that the plants were grown under nitrogen-sufficient conditions.
Table 1.
Physiological properties of Burkholderia and non-Burkholderia strains isolated from the inner tissues and surfaces of white lupin cluster roots
| Physiological property | % of isolates (n > 55) |
Significancea | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Burkholderia | Non-Burkholderia | ||
| Growth at low pH | 77 | 41 | *** |
| Growth on: | |||
| Citrate | 62 | 25 | *** |
| Malate | 95 | 87 | ns |
| Fumarate | 96 | 84 | ns |
| Oxalate | 93 | 2 | *** |
| P solubilization | 62 | 67 | ns |
| Siderophore production | 80 | 26 | *** |
| Auxin production | 4 | 43 | *** |
Differences in the percentages of Burkholderia and non-Burkholderia isolates capable of growth in each assay were tested using the chi-square test. ***, significant difference (P < 0.001); ns, not significant.
The present work investigated the previously unknown bacterial community of cluster roots, a highly specialized root type which is characterized by very densely branched rootlets that excrete high levels of organic acids and protons. We observed a strong dominance of Burkholderia species in growing cluster roots of white lupin. Earlier analyses focusing on phytate-degrading bacteria in lupin root tissues also revealed a large proportion of Burkholderia spp. (mostly affiliated with the B. cepacia complex) within the phytate-degrading community (34). However, the authors did not mention the presence of cluster roots, suggesting that under their experimental conditions, the soil contained sufficient available P to repress cluster root formation. Our results show that Burkholderia spp. were enriched as cluster roots developed and represented 58% of isolates and 44% of all sequences retrieved from senescent cluster roots. In vitro physiological assays revealed that tolerance of low pH, siderophore production, and utilization of citrate and oxalate as growth substrates might play a significant role in the establishment and persistence of Burkholderia spp. in growing cluster roots. Further investigations are needed of whether Burkholderia species dominate the cluster root communities to the same extent in field-grown lupin plants and whether they are also found among the root communities of other cluster-rooted plants with a similar root excretion physiology (e.g., Banksia or Hakea species). Interestingly, several of the Burkholderia species found in this study to colonize lupin cluster roots were previously (and often only anecdotally) encountered in soil samples. Our data suggest that these species may not be true soil bacteria but may originate from decayed plant material.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Enrico Martinoia and Michel Aragno for fruitful discussions. We are grateful to Rita Baumgartner for technical help, to Kirsty Agnoli for English corrections, and to Gabriella Pessi for critical reading of the manuscript.
This work was partly financed by the Swiss National Science Foundation (project 31003A-130089).
Footnotes
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://aem.asm.org/.
Published ahead of print on 9 September 2011.
REFERENCES
- 1. Angle J. S., McGrath S. P., Chaney R. L. 1991. New culture medium containing ionic concentrations of nutrients similar to concentrations found in the soil solution. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57:3674–3676 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Balandreau J., et al. 2001. Burkholderia cepacia genomovar III is a common plant-associated bacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67:982–985 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Burkholder W. H. 1942. Three bacterial plant pathogens: Pseudomonas caryophylli sp n. Phytomonas alliicola sp.n., and Phytomonas manihotis (Arthaud-Berthet et Bondar) Viegas. Phytopathology 32:141–149 [Google Scholar]
- 4. Coenye T., et al. 2001. Burkholderia fungorum sp nov, and Burkholderia caledonica sp nov., two new species isolated from the environment, animals and human clinical samples. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51:1099–1107 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Coenye T., Vandamme P. 2003. Diversity and significance of Burkholderia species occupying diverse ecological niches. Environ. Microbiol. 5:719–729 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Dessureault-Rompre J., Nowack B., Schulin R., Luster J. 2007. Spatial and temporal variation in organic acid anion exudation and nutrient anion uptake in the rhizosphere of Lupinus albus L. Plant Soil 301:123–134 [Google Scholar]
- 7. Dinkelaker B., Hengeler C., Marschner H. 1995. Distribution and function of proteoid rests and other root clusters. Bot. Acta 108:183–200 [Google Scholar]
- 8. Garau G., Yates R. J., Deiana P., Howieson J. G. 2009. Novel strains of nodulating Burkholderia have a role in nitrogen fixation with papilionoid herbaceous legumes adapted to acid, infertile soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 41:125–134 [Google Scholar]
- 9. Gerke J., Romer W., Jungk A. 1994. The excretion of citric and malic-acid by proteoid roots of Lupinus-albus L.—effects on soil solution concentrations of phosphate, iron, and aluminum in the proteoid rhizosphere in samples of an oxisol and a luvisol. Z. Pflanzenernahrung Bodenkunde 157:289–294 [Google Scholar]
- 10. Gerrits G. P., Klaassen C., Coenye T., Vandamme P., Meis J. F. 2005. Burkholderia fungorum septicemia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 11:1115–1117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Gilbert G. A., Knight J. D., Vance C. P., Allan D. L. 2000. Proteoid root development of phosphorus deficient lupin is mimicked by auxin and phosphonate. Ann. Bot. (Lond.) 85:921–928 [Google Scholar]
- 12. Goris J., et al. 2002. Diversity of transconjugants that acquired plasmid pJP4 or pEMT1 after inoculation of a donor strain in the A- and B-horizon of an agricultural soil and description of Burkholderia hospita sp nov and Burkholderia terricola sp nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 25:340–352 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Green S. J., Michel F. C., Hadar Y., Minz D. 2007. Contrasting patterns of seed and root colonization by bacteria from the genus Chryseobacterium and from the family Oxalobacteraceae. ISME J. 1:291–299 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Green S. J., Minz D. 2005. Suicide polymerase endonuclease restriction, a novel technique for enhancing PCR amplification of minor DNA templates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71:4721–4727 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Hagstrom J., James W. M., Skene K. R. 2001. A comparison of structure, development and function in cluster roots of Lupinus albus L. under phosphate and iron stress. Plant Soil 232:81–90 [Google Scholar]
- 16. Hartmann I., et al. 2010. Genes involved in Cronobacter sakazakii biofilm formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76:2251–2261 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Johnson J. F., Allan D. L., Vance C. P. 1994. Phosphorus stress-induced proteoid roots show altered metabolism in Lupinus albus. Plant Physiol. 104:657–665 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Juretschko S., et al. 1998. Combined molecular and conventional analyses of nitrifying bacterium diversity in activated sludge: Nitrosococcus mobilis and Nitrospira-like bacteria as dominant populations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64:3042–3051 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Koele N., Turpault M. P., Hildebrand E. E., Uroz S., Frey-Klett P. 2009. Interactions between mycorrhizal fungi and mycorrhizosphere bacteria during mineral weathering: budget analysis and bacterial quantification. Soil Biol. Biochem. 41:1935–1942 [Google Scholar]
- 20. Lambers H., Shane M. W., Cramer M. D., Pearse S. J., Veneklaas E. J. 2006. Root structure and functioning for efficient acquisition of phosphorus: matching morphological and physiological traits. Ann. Bot. (Lond.) 98:693–713 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Lamont B. B. 2003. Structure, ecology and physiology of root clusters—a review. Plant Soil 248:1–19 [Google Scholar]
- 22. Lim Y. W., Baik K. S., Han S. K., Kim S. B., Bae K. S. 2003. Burkholderia sordidicola sp nov., isolated from the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete sordida. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 53:1631–1636 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Lu Y. H., Rosencrantz D., Liesack W., Conrad R. 2006. Structure and activity of bacterial community inhabiting rice roots and the rhizosphere. Environ. Microbiol. 8:1351–1360 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Mattos K. A., et al. 2008. Endophytic colonization of rice (Oryza sativa L.) by the diazotrophic bacterium Burkholderia kururiensis and its ability to enhance plant growth. Ann. Acad. Bras. Cie. 80:477–493 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Neumann G., Martinoia E. 2002. Cluster roots—an underground adaptation for survival in extreme environments. Trends Plant Sci. 7:162–167 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Neumann G., et al. 2000. Physiological aspects of cluster root function and development in phosphorus-deficient white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). Ann. Bot. (Lond.) 85:909–919 [Google Scholar]
- 27. Ofek M., Hadar Y., Minz D. 2009. Comparison of effects of compost amendment and of single-strain inoculation on root bacterial communities of young cucumber seedlings. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75:6441–6450 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Offre P., et al. 2007. Identification of bacterial groups preferentially associated with mycorrhizal roots of Medicago truncatula. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73:913–921 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Onofre-Lemus J., Hernandez-Lucas I., Girard L., Caballero-Mellado J. 2009. ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate) deaminase activity, a widespread trait in Burkholderia species, and its growth-promoting effect on tomato plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75:6581–6590 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Poly F., Monrozier L. J., Bally R. 2001. Improvement in the RFLP procedure for studying the diversity of nifH genes in communities of nitrogen fixers in soil. Res. Microbiol. 152:95–103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Shaharoona B., Jamro G. M., Zahir Z. A., Arshad M., Memon K. S. 2007. Effectiveness of various Pseudomonas spp. and Burkholderia caryophylli containing ACC-deaminase for improving growth and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 17:1300–1307 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Tomasi N., et al. 2009. Plasma membrane H+-ATPase-dependent citrate exudation from cluster roots of phosphate-deficient white lupin. Plant Cell Environ. 32:465–475 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Tomasi N., et al. 2008. Flavonoids of white lupin roots participate in phosphorus mobilization from soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 40:1971–1974 [Google Scholar]
- 34. Unno Y., Okubo K., Wasaki J., Shinano T., Osaki M. 2005. Plant growth promotion abilities and microscale bacterial dynamics in the rhizosphere of lupin analysed by phytate utilization ability. Environ. Microbiol. 7:396–404 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Vandenkoornhuyse P., et al. 2007. Active root-inhabiting microbes identified by rapid incorporation of plant-derived carbon into RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104:16970–16975 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Vial L., Chapalain A., Groleau M. C., Deziel E. 2011. The various lifestyles of the Burkholderia cepacia complex species: a tribute to adaptation. Environ. Microbiol. 13:1–12 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Viallard V., et al. 1998. Burkholderia graminis sp. nov., a rhizospheric Burkholderia species, and reassessment of Pseudomonas phenazinium, Pseudomonas pyrrocinia and Pseudomonas glathei as Burkholderia. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 48:549–563 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Warmink J. A., van Elsas J. D. 2009. Migratory response of soil bacteria to Lyophyllum sp. strain Karsten in soil microcosms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75:2820–2830 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Weisskopf L., et al. 2006. White lupin has developed a complex strategy to limit microbial degradation of secreted citrate required for phosphate acquisition. Plant Cell Environ. 29:919–927 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Weisskopf L., Fromin N., Tomasi N., Aragno M., Martinoia E. 2005. Secretion activity of white lupin's cluster roots influences bacterial abundance, function and community structure. Plant Soil 268:181–194 [Google Scholar]
- 41. Weisskopf L., et al. 2008. Spatio-temporal dynamics of bacterial communities associated with two plant species differing in organic acid secretion: a one-year microcosm study on lupin and wheat. Soil Biol. Biochem. 40:1772–1780 [Google Scholar]
- 42. Weisskopf L., et al. 2006. Isoflavonoid exudation from white lupin roots is influenced by phosphate supply, root type and cluster-root stage. New Phytol. 171:657–668 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Zhang H., et al. 2000. Burkholderia kururiensis sp nov., a trichloroethylene (TCE)-degrading bacterium isolated from an aquifer polluted with TCE. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50:743–749 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.