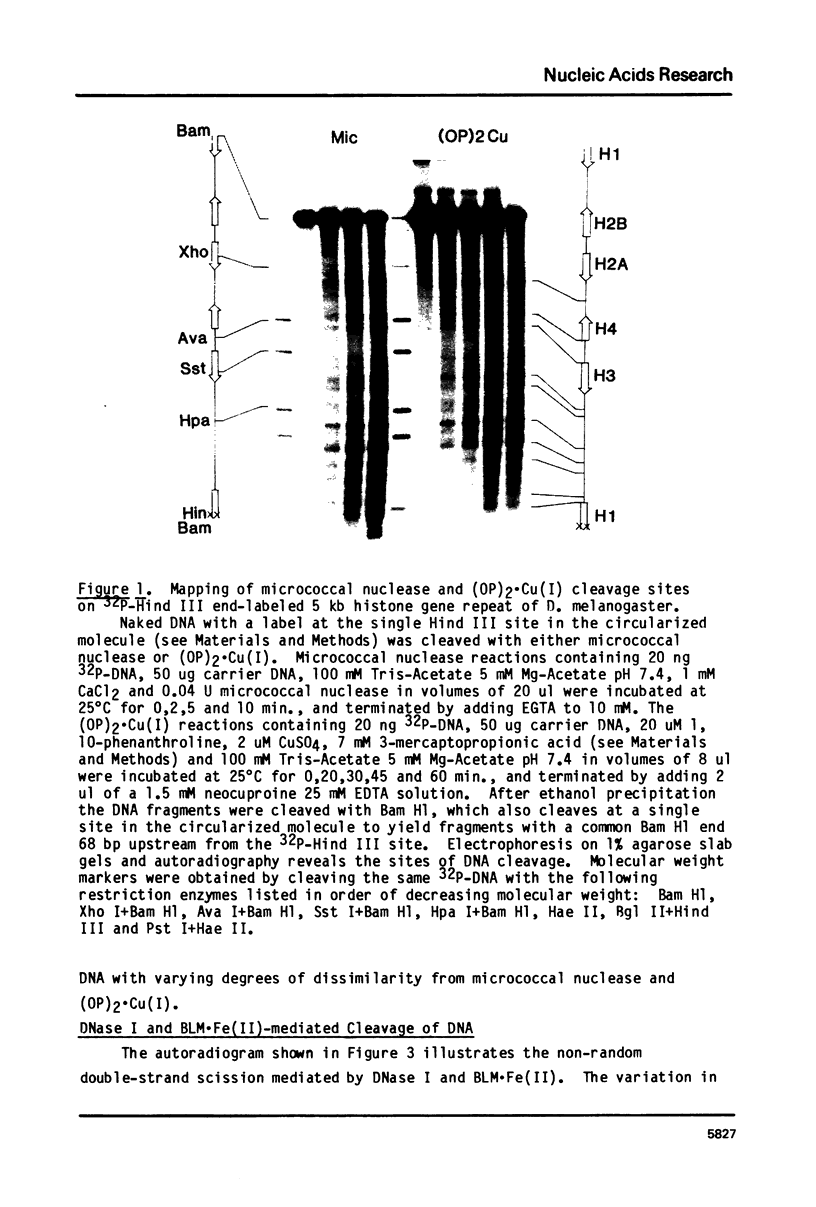
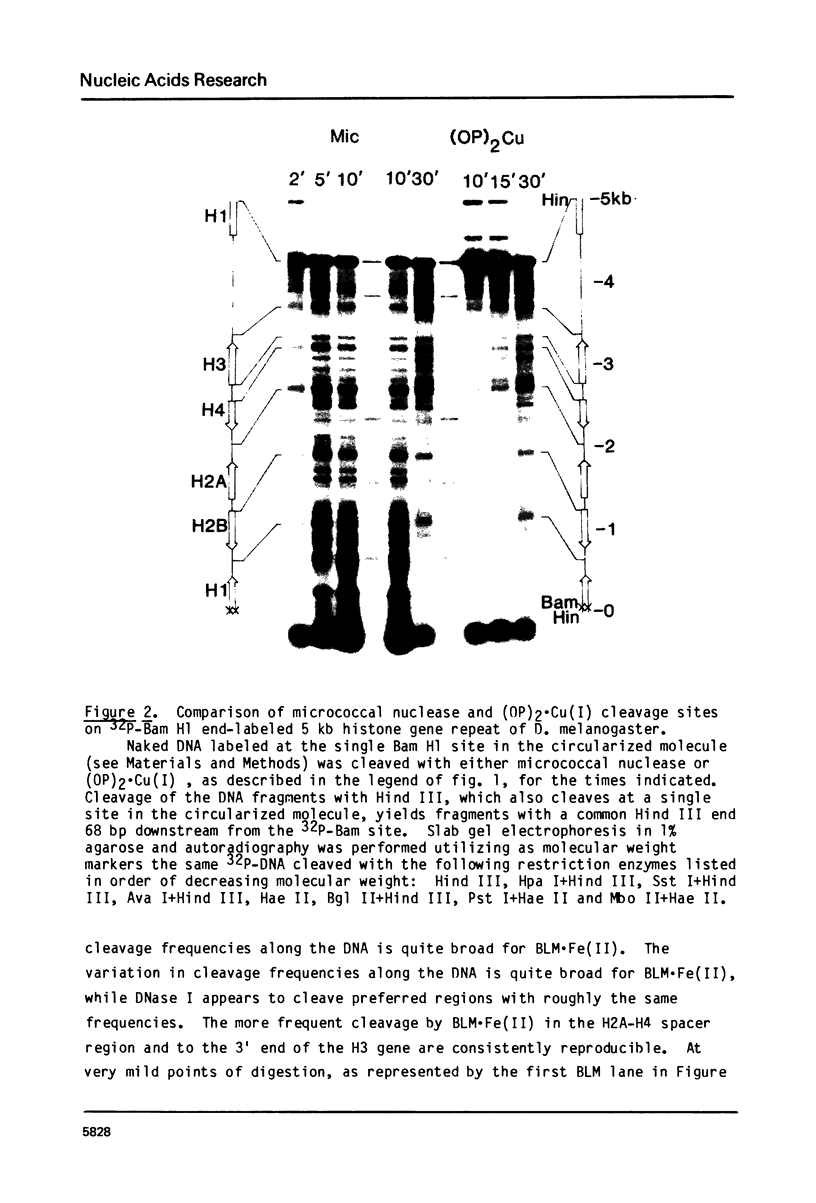
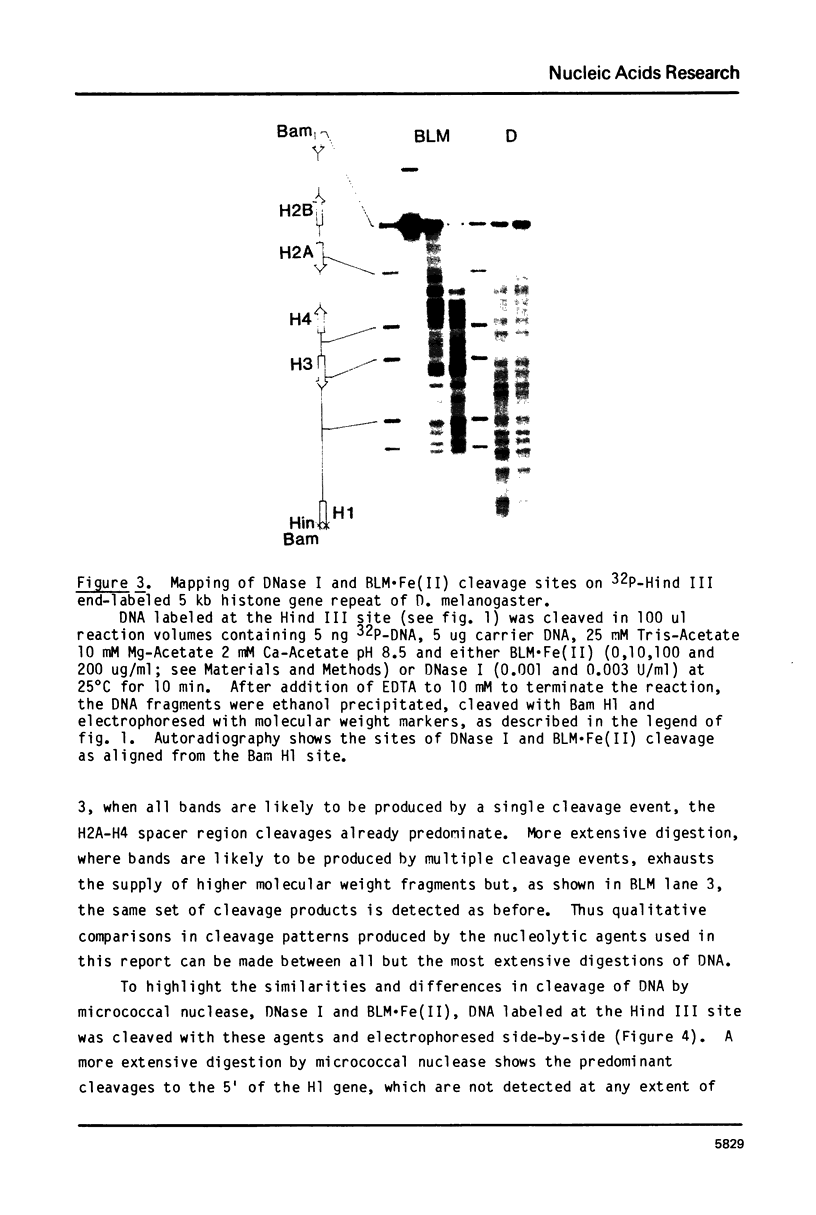
Abstract
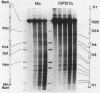
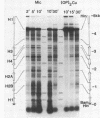
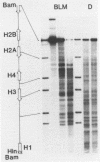
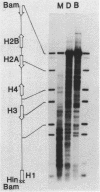
We have examined the DNA cleavage specificity of a 1,10-phenanthroline-cuprous complex and find this agent to recognize the same sites and cleave with the same relative preferences as micrococcal nuclease. In contrast, DNase I and bleomycin-ferrous complex cleave the same 5000 bp D. melanogaster histone gene DNA with different specificities, although some of the sites appear to be recognized and cleaved by all four reagents. Our results suggest that the reagents used probably detect discrete conformational perturbations along the DNA double helix.
Full text
PDF



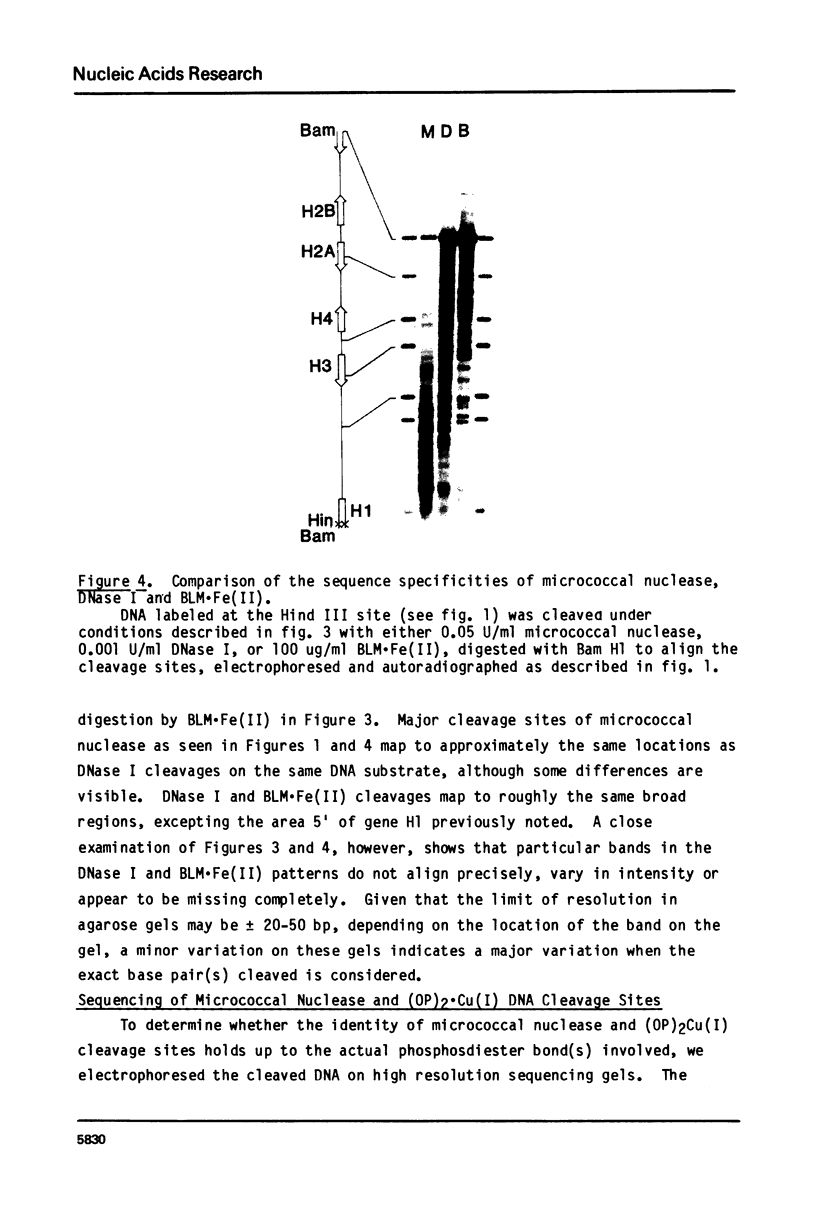
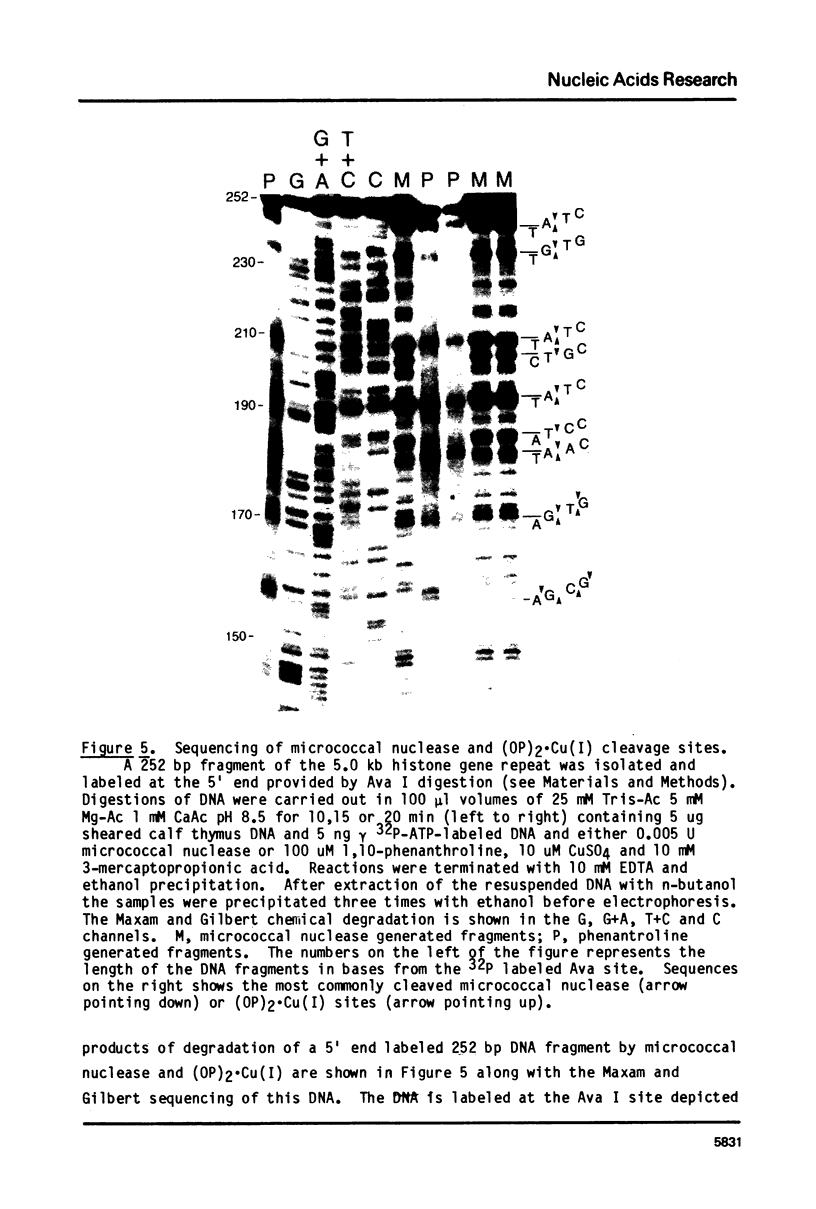



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryan P. N., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Nucleosome arrangement on tRNA genes of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90387-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A. D., Haseltine W. A. Sequence specific cleavage of DNA by the antitumor antibiotics neocarzinostatin and bleomycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3608–3612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of chromatin. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Altenburger W. Sequence specific cleavage of DNA by micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2643–2658. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacian D. L., Spiegelman S. Use of micrococcal nuclease to monitor hybridization reactions with DNA. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):534–540. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90221-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene M. A., Elgin S. C. Micrococcal nuclease as a probe of DNA sequence organization and chromatin structure. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Jack A., Viswamitra M. A., Kennard O., Shakked Z., Steitz T. A. A hypothesis on a specific sequence-dependent conformation of DNA and its relation to the binding of the lac-repressor protein. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Lutter L. C. The helical periodicity of DNA on the nucleosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4267–4283. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Structure of chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:931–954. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. The inverted repeat as a recognizable structural feature in supercoiled DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis C., Schedl P., Samal B., Worcel A. Chromatin structure of the 5S RNA genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):387–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90349-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall L. E., Graham D. R., Reich K. A., Sigman D. S. Cleavage of deoxyribonucleic acid by the 1,10-phenanthroline-cuprous complex. Hydrogen peroxide requirement and primary and secondary structure specificity. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 20;20(2):244–250. doi: 10.1021/bi00505a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musich P. R., Brown F. L., Maio J. J. Nucleosome phasing and micrococcal nuclease cleavage of African green monkey component alpha DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):118–122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Cruciform structures in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):466–470. doi: 10.1038/289466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T. T., Riordan J. M., Glickson J. D. Models of bleomycin interactions with poly(deoxyadenylylthymidylic acid). Fluorescence and proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies of cationic thiazole amides related to bleomycin A2. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 16;21(4):805–816. doi: 10.1021/bi00533a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samal B., Worcel A., Louis C., Schedl P. Chromatin structure of the histone genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):401–409. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigman D. S., Graham D. R., D'Aurora V., Stern A. M. Oxygen-dependent cleavage of DNA by the 1,10-phenanthroline . cuprous complex. Inhibition of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12269–12272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita M., Kappen L. S., Grollman A. P., Eisenberg M., Goldberg I. H. Strand scission of deoxyribonucleic acid by neocarzinostatin, auromomycin, and bleomycin: studies on base release and nucleotide sequence specificity. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 22;20(26):7599–7606. doi: 10.1021/bi00529a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]