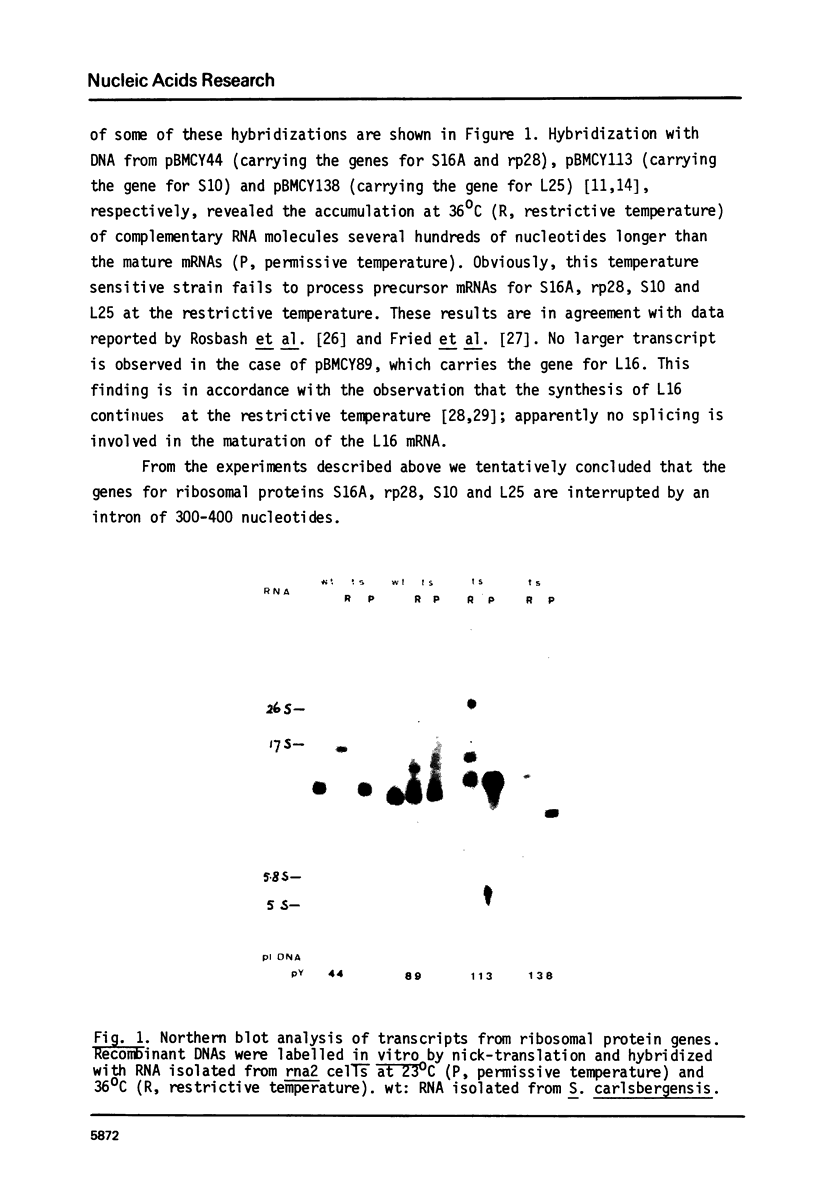
Abstract
From previous studies on cloned yeast ribosomal protein genes we obtained evidence that a large number of them contain an intron [Bollen et al. (1982) Gene 18, 29-38]. In the temperature-sensitive rna2-mutant transcription of these genes leads to the accumulation of precursor RNAs at the restrictive temperature. These precursor mRNAs are several hundreds of nucleotides longer than the respective mature mRNAs. The split character of one of these ribosomal protein genes, viz. the gene coding for the major phosphorylated small-subunit protein S10, was further established by sequence analysis. The intervening sequence interrupts the coding sequence after the second codon and has a length of 352 nucleotides. Genomic Southern hybridizations with a DNA fragment carrying part of the S10-gene revealed that this gene is duplicated on the yeast genome. The molecular weight of S10 as deduced from the sequence analysis was estimated to be 31462 dal. Comparison of the N-terminal aminoacid sequence of the yeast ribosomal protein S10 with that of ribosomal protein S6 from rat liver revealed a striking homology between both proteins. Moreover, at the C-terminal end of the yeast ribosomal protein the sequence Arg-Ala-Ser-Ser-Leu-Lys is present which is very similar to the phosphorylation site of the rat liver protein S6.
Full text
PDF


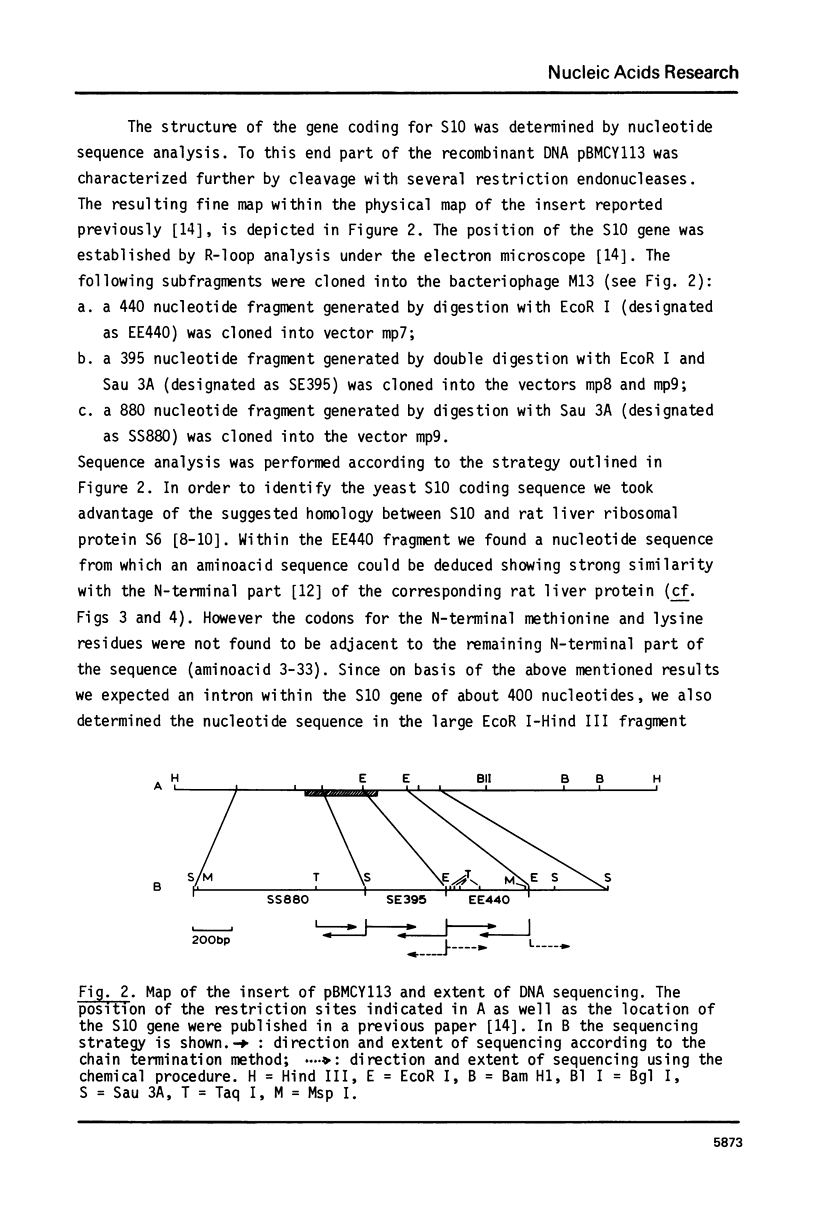





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen G. H., Cohen L. H., Mager W. H., Klaassen A. W., Planta R. J. Isolation of cloned ribosomal protein genes from the yeast Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Gene. 1981 Sep;14(4):279–287. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90160-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen G. H., Mager W. H., Jenneskens L. W., Planta R. J. Small-size mRNAs code for ribosomal proteins in yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;105(1):75–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04475.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen G. H., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. High resolution mini-two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of yeast ribosomal proteins. A standard nomenclature for yeast ribosomal proteins. Mol Biol Rep. 1981 Nov 30;8(1):37–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00798383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried H. M., Pearson N. J., Kim C. H., Warner J. R. The genes for fifteen ribosomal proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):10176–10183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorenstein C., Warner J. R. Coordinate regulation of the synthesis of eukaryotic ribosomal proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1547–1551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., McLaughlin C. S., Warner J. R. Identification of ten genes that control ribosome formation in yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;109(1):42–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00334045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert J., Pierre M., Loeb J. E. Phosphorylation in vitro and in vivo of ribosomal proteins from Saccharomyces cerevisia. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan 3;72(1):167–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalthoff H., Darmer D., Towbin H., Gordon J., Amons R., Möller W., Richter D. Ribosomal protein S6 from Xenopus laevis ovaries. Isolation, phosphorylation in vivo and cross-reaction with heterologous anti-S6 antibodies. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;122(3):439–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruiswijk T., de Hey J. T., Planta R. J. Modification of yeast ribosomal proteins. Phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 1;175(1):213–219. doi: 10.1042/bj1750213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey E. H., Bielka H., Gordon J., Lastick S. M., Lin A., Ogata K., Reboud J. P., Traugh J. A., Traut R. R., Warner J. R. Proposed uniform nomenclature for mammalian ribosomal proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 16;169(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00267538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Retèl J., Planta R. J. Nuclear satellite DNAs of yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 27;281(3):299–309. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90442-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosbash M., Harris P. K., Woolford J. L., Jr, Teem J. L. The effect of temperature-sensitive RNA mutants on the transcription products from cloned ribosomal protein genes of yeast. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):679–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Williams J. G. Quantitative analysis of specific labelled RNA'S using DNA covalently linked to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):195–203. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Madrid F., Reyes R., Conde P., Ballesta J. P. Acidic ribosomal proteins from eukaryotic cells. Effect on ribosomal functions. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):409–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidales F. J., Sanchez-Madrid F., Ballesta J. P. The acidic proteins of eukaryotic ribosomes. A comparative study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 27;656(1):28–35. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Gorenstein C. The ribosomal proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;20:45–60. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)62008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Gorenstein C. The synthesis of eucaryotic ribosomal proteins in vitro. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettenhall R. E., Cohen P. Isolation and characterisation of cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation sites from rat liver ribosomal protein S6. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 19;140(2):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80910-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettenhall R. E., Howlett G. J. Phosphorylation of a specific ribosomal protein during stimulation of thymocytes by concanavalin A and prostaglandin E1. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9317–9323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann-Liebold B., Geissler A. W., Lin A., Wool I. G. Sequence of the amino-terminal region of rat liver ribosomal proteins S4, S6, S8, L6, L7a, L18, L27, L30, L37, L37a, and L39. J Supramol Struct. 1979;12(4):425–433. doi: 10.1002/jss.400120403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinker S., Warner J. R. The ribosomal proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Phosphorylated and exchangeable proteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1799–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





