Abstract
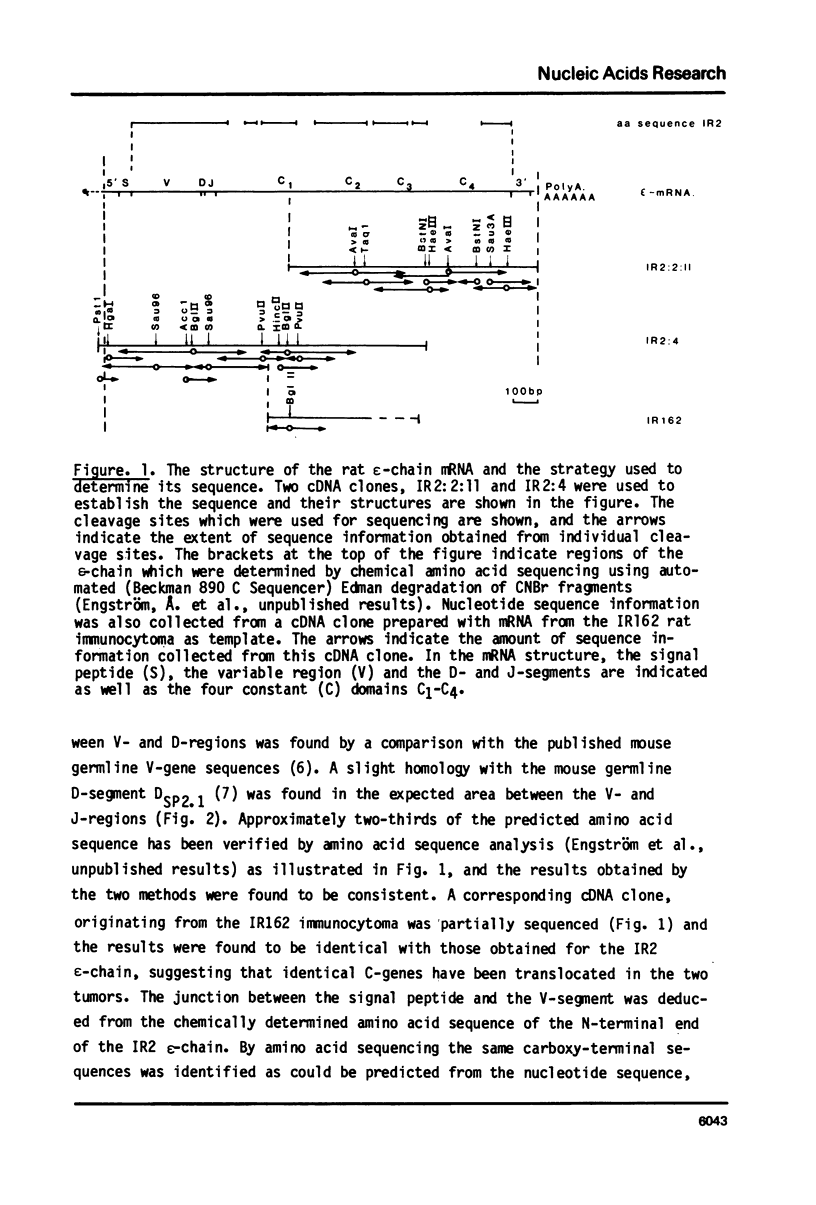
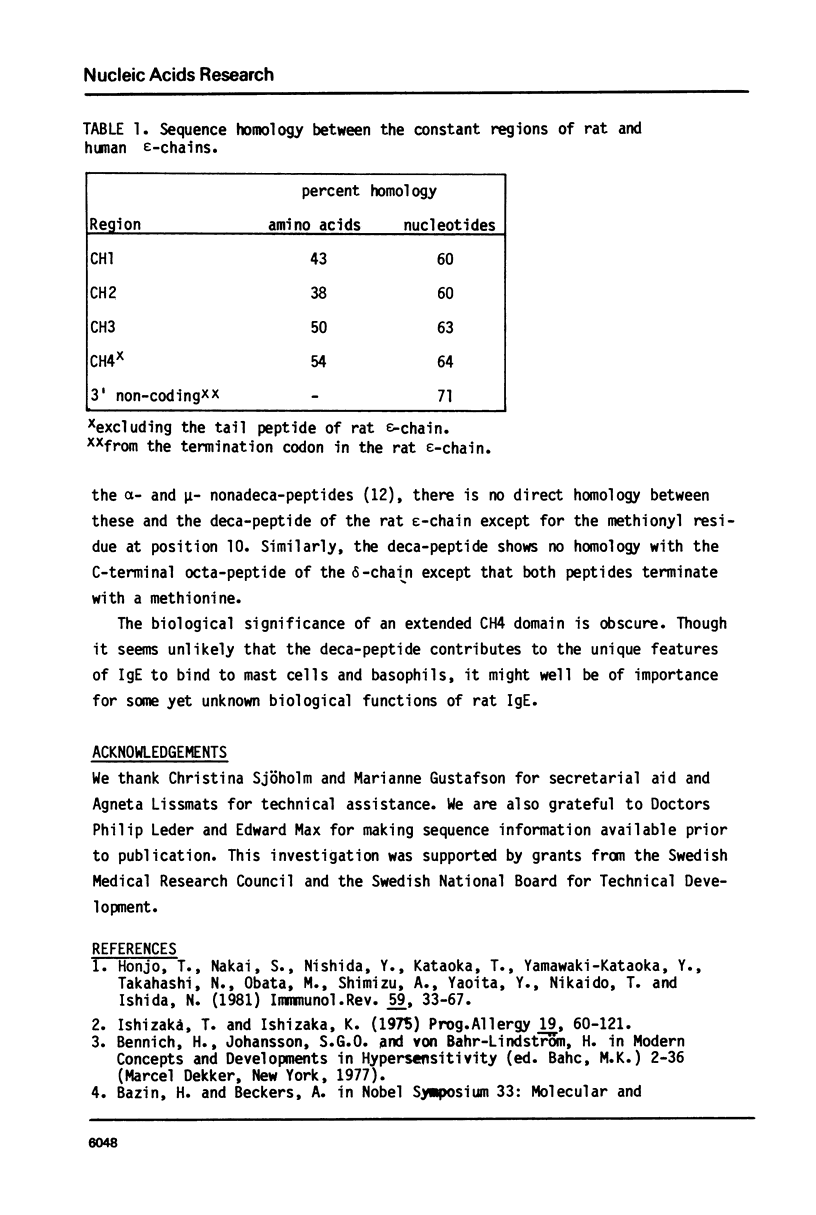
The nucleotide sequence of the rat epsilon-chain mRNA has been determined by sequencing cloned cDNA copies of the mRNA. The established sequence covers the coding region, the 3'-non coding region and most of the 5' non-coding region. A comparison with the nucleotide sequence of the human epsilon-chain constant region reveals that C3 and C4 are the most highly conserved domains. The rat epsilon-chain contains a C-terminal decapeptide which is not present in the human counterpart.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen J. B., Effron K., Rechavi G., Ben-Neriah Y., Zakut R., Givol D. Simple DNA sequences in homologous flanking regions near immunoglobulin VH genes: a role in gene interaction? Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 11;10(11):3353–3370. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.11.3353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman L., Pettersson U., Bennich H. Characterization and molecular cloning of the mRNA for the heavy (epsilon) chain of rat immunoglobulin E. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1264–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nakai S., Nishida Y., Kataoka T., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Takahashi N., Obata M., Shimizu A., Yaoita Y., Nikaido T. Rearrangements of immunoglobulin genes during differentiation and evolution. Immunol Rev. 1981;59:33–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K. Biology of immunoglobulin E. Molecular basis of reaginic hypersensitivity. Prog Allergy. 1975;19:60–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami T., Takahashi N., Honjo T. Complete nucleotide sequence of mouse immunoglobulin mu gene and comparison with other immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3933–3945. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa Y., von Boehmer H., Haas W., Sakano H., Trauneker A., Tonegawa S. Identification of D segments of immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes and their rearrangement in T lymphocytes. Nature. 1981 Apr 16;290(5807):565–570. doi: 10.1038/290565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. C., Putnam F. W. Primary structure of the Fc region of human immunoglobulin D: implications for evolutionary origin and biological function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):504–508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell N., Richards J. E., Tucker P. W., Blattner F. R. J genes for heavy chain immunoglobulins of mouse. Science. 1980 Sep 5;209(4461):1128–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.6250219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



