Abstract
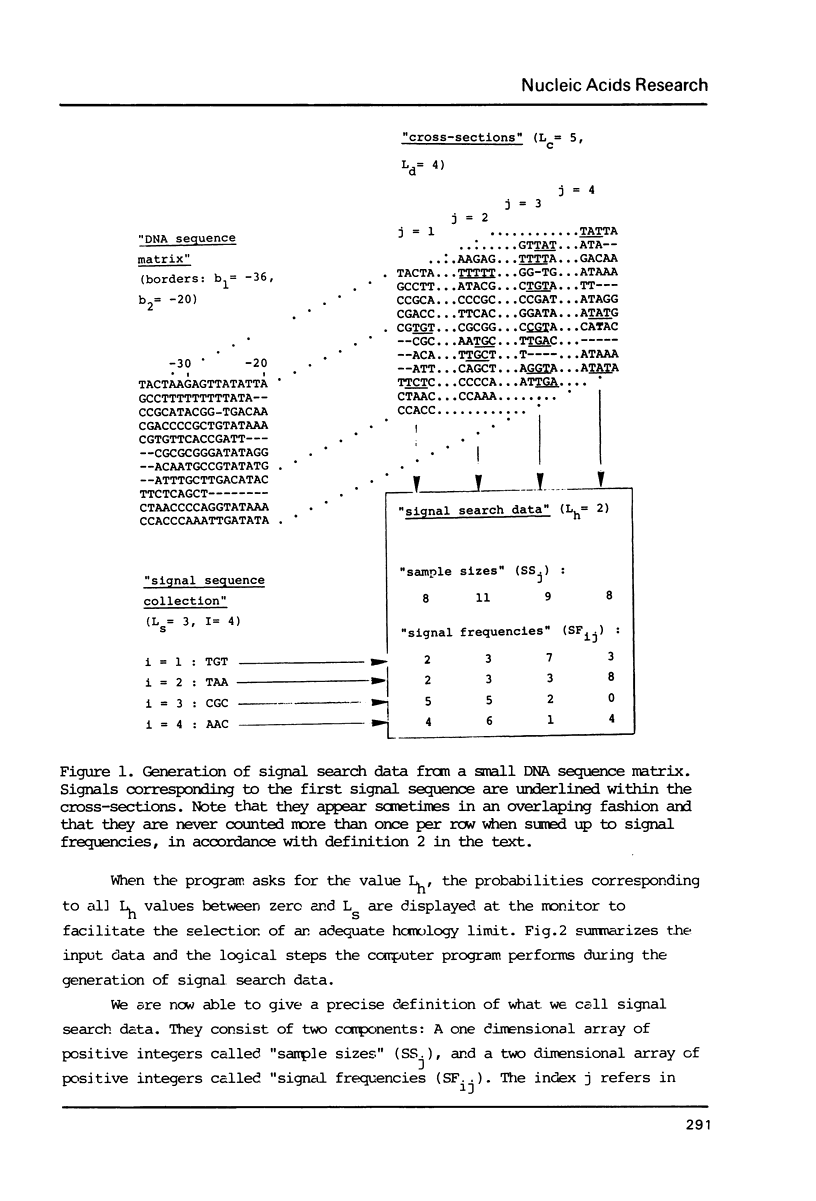
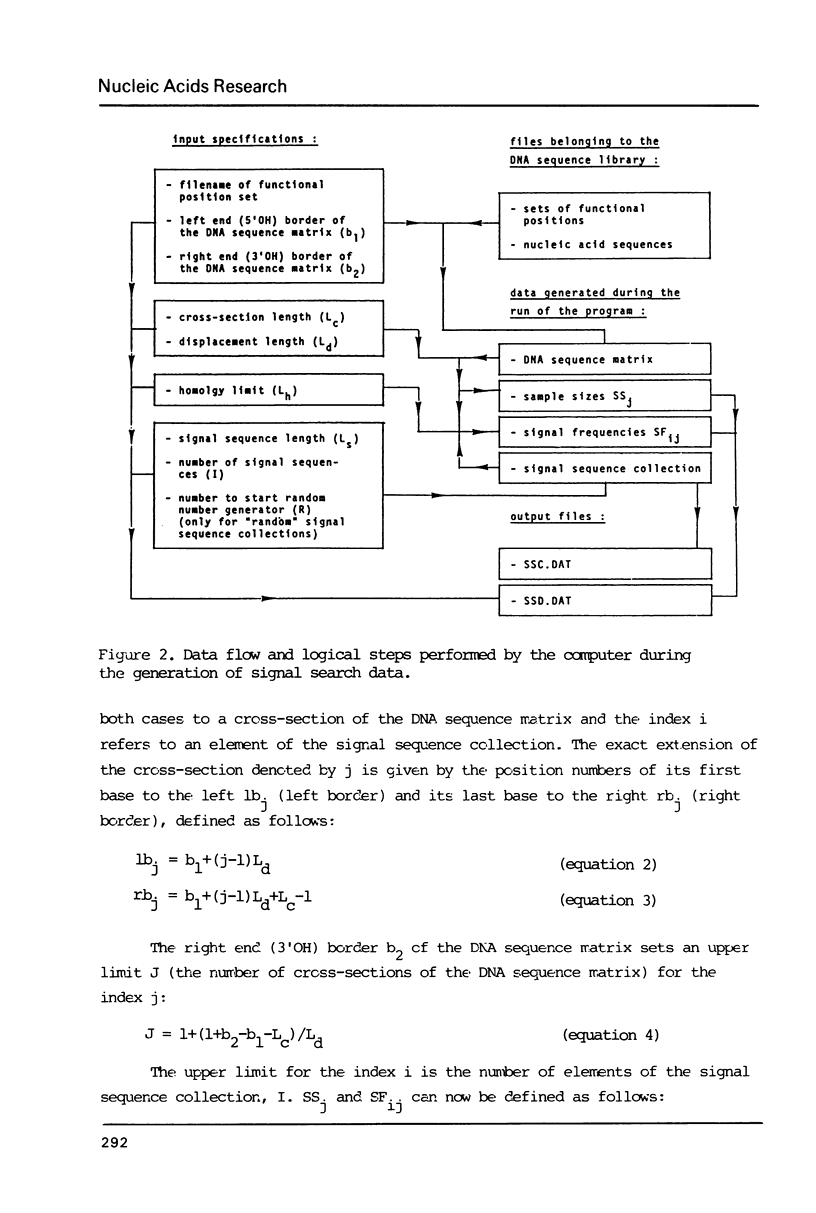
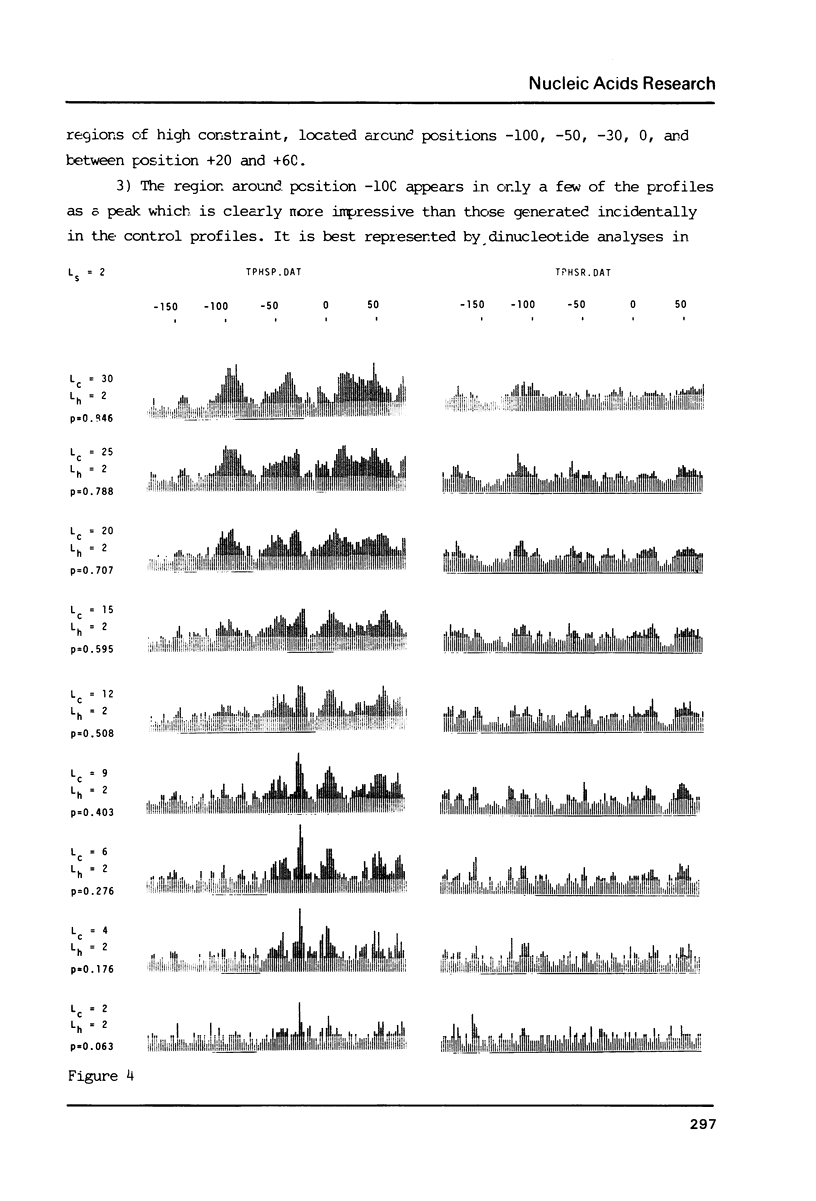
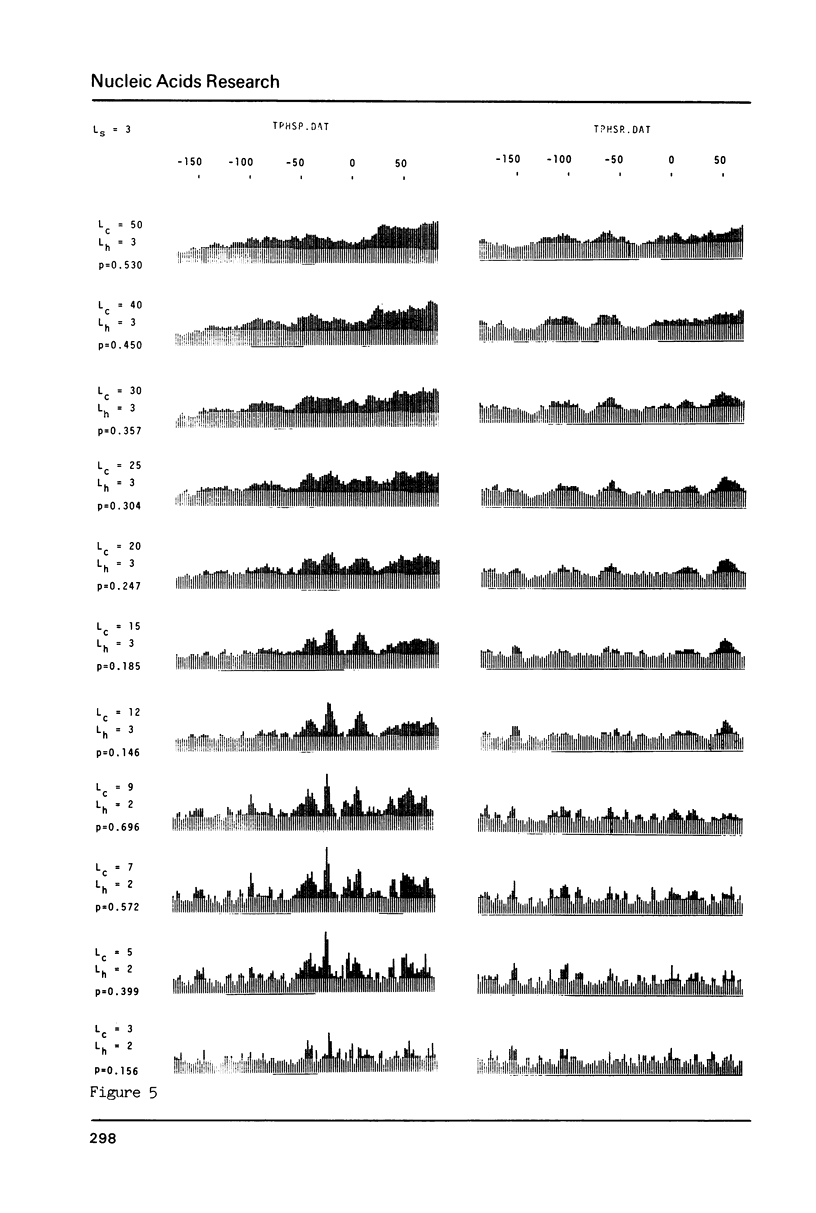
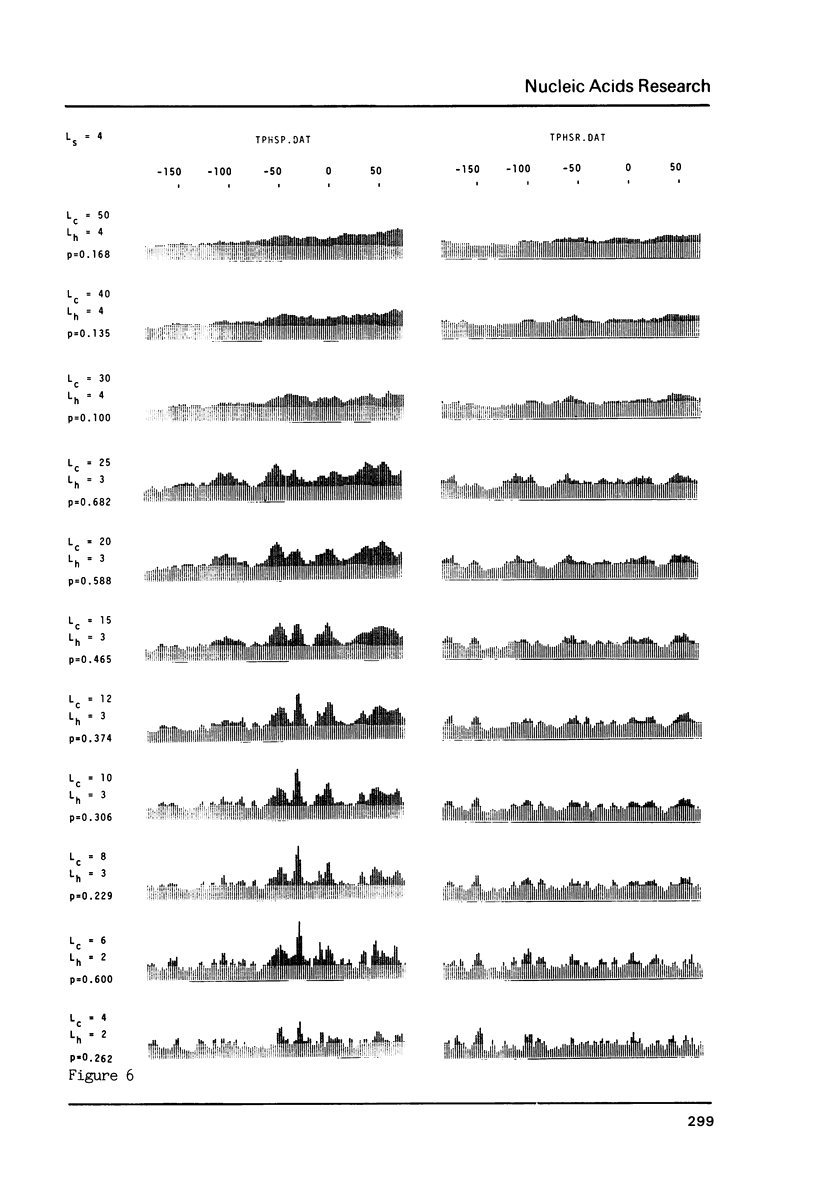
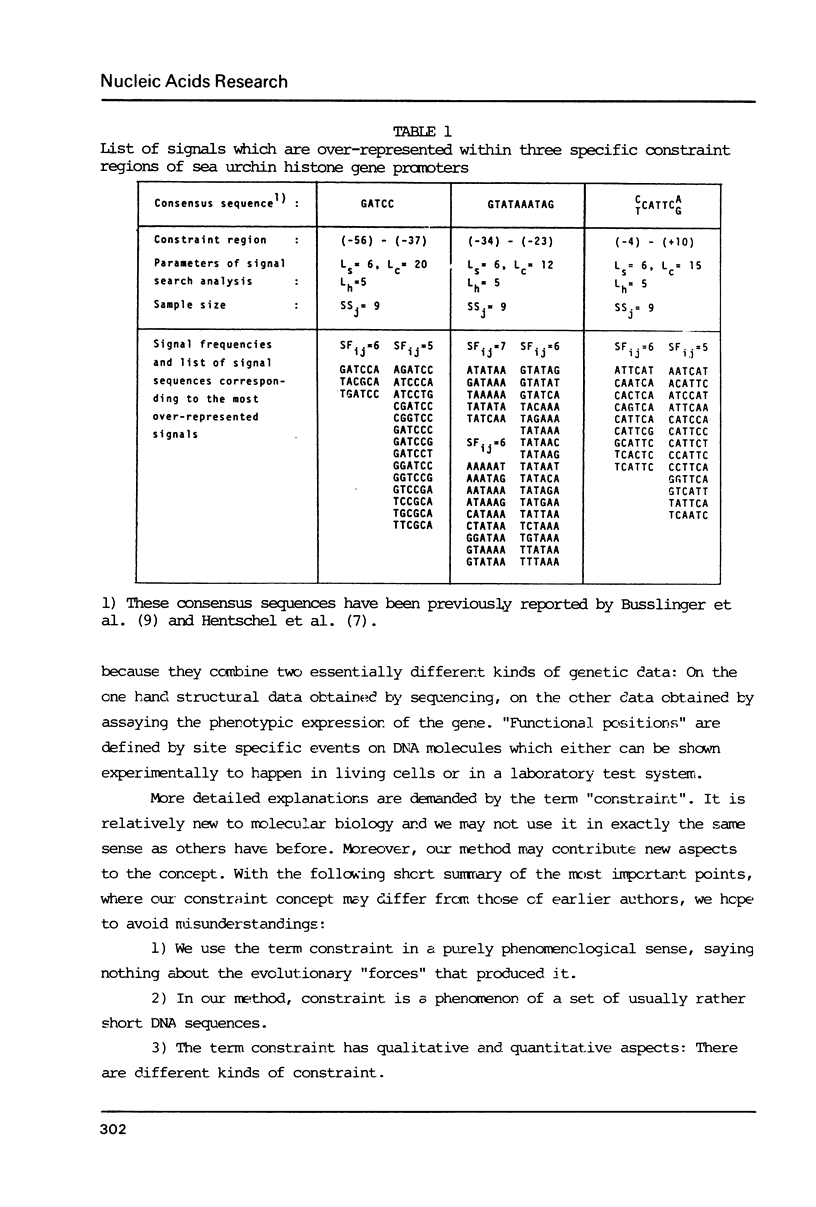
The generation of "signal search data" represents a general method of describing the common properties of a set of DNA sequences presumed to be functionally analogous. Besides the detailed description of this method we present two computer programs which use signal search data as input data: One that processes them to a "constraint profile" and another one which lists over-represented "signals" of potential functional relevance. To illustrate the possibilities of our method we have analysed a set of transcription initiation sites of sea urchin histone genes.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Busslinger M., Portmann R., Irminger J. C., Birnstiel M. L. Ubiquitous and gene-specific regulatory 5' sequences in a sea urchin histone DNA clone coding for histone protein variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):957–977. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Rusconi S., Birnstiel M. L. An unusual evolutionary behaviour of a sea urchin histone gene cluster. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):27–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01119.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson S. G., Smith H. O., Schaffner W., Gross K. W., Birnstiel M. L. Integration of eukaryotic genes for 5S RNA and histone proteins into a phage lambda receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2617–2632. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C., Irminger J. C., Bucher P., Birnstiel M. L. Sea urchin histone mRNA termini are located in gene regions downstream from putative regulatory sequences. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):147–151. doi: 10.1038/285147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Chang A. C., Houseman D., Cohen S. N. Isolation of histone genes from unfractionated sea urchin DNA by subculture cloning in E. coli. Nature. 1975 Jun 12;255(5509):533–538. doi: 10.1038/255533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Maizel J. Comparative analysis of nucleic acid sequences by their general constraints. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2723–2739. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L., Ehrenfeucht A. Use of the 'Perceptron' algorithm to distinguish translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2997–3011. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Levy S., Kedes L. H. Leader sequences of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus histone mRNAs start at a unique heptanucleotide common to all five histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1265–1269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



