Abstract
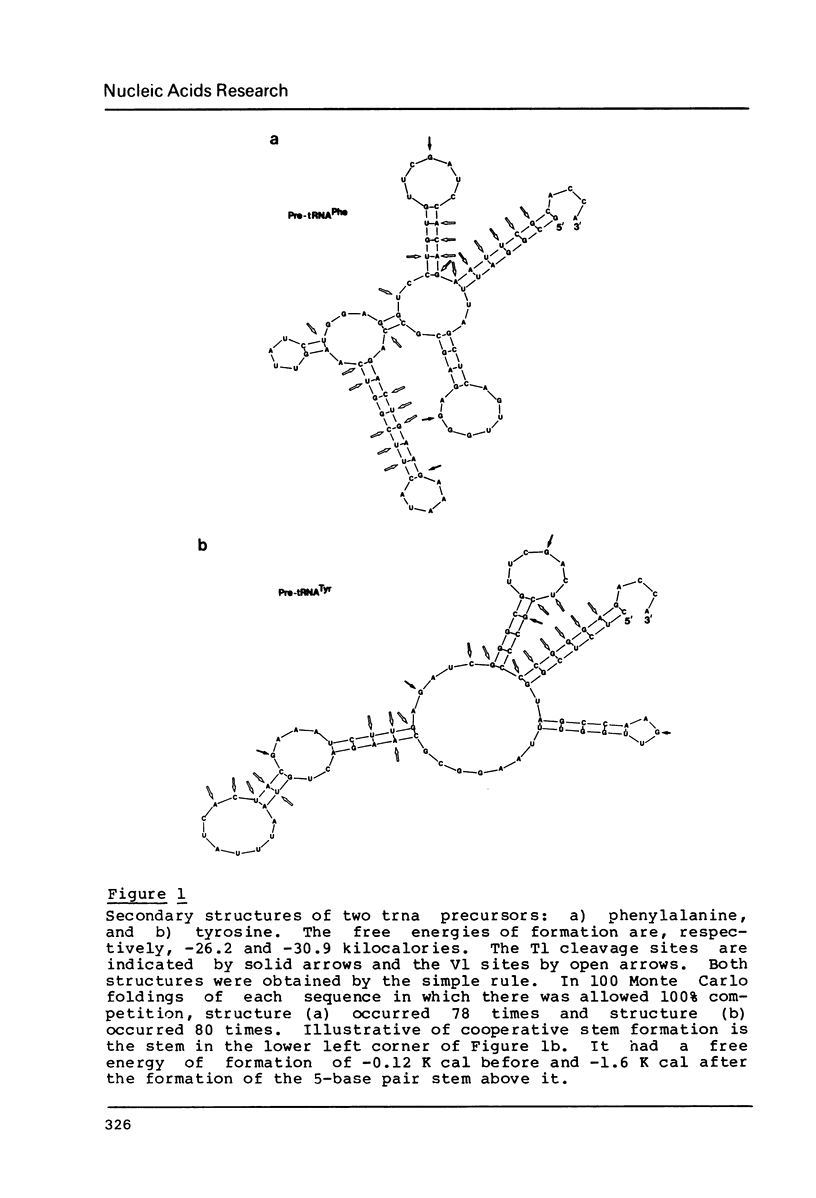
The folding of single-stranded RNA into its secondary structure is postulated to be equivalent to the simple rule that the next double-helical region (stem) to form is the one with the largest equilibrium constant. The rule is tested and shown to give results consistent with the enzyme cleavage data of several sequences. Computational time complexity is of order NxN for a sequence of N bases. A modification of the rule provides for the probabilistic choice of the next stem among those having an equilibrium constant within a specified range of the largest. Populations of competing structures are thus generated for detecting common characteristics and for assessing the applicability of the simple rule.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dumas J. P., Ninio J. Efficient algorithms for folding and comparing nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):197–206. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRESCO J. R., ALBERTS B. M., DOTY P. Some molecular details of the secondary structure of ribonucleic acid. Nature. 1960 Oct 8;188:98–101. doi: 10.1038/188098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W. Globin mRNA sequences: analysis of base pairing and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):985–1002. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studnicka G. M., Rahn G. M., Cummings I. W., Salser W. A. Computer method for predicting the secondary structure of single-stranded RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3365–3387. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



