Abstract
We describe a new method of comparing sequences, based on the Needleman-Wunsch sequence alignment algorithm, which can detect similarities that are interrupted by insertions or deletions in either sequence. The sequences are compared by calculating for each pair of residues a score which represents the best local alignment bringing those residues into correspondence; smooth localisation is achieved by reducing the contribution of distant parts of the alignment path by a factor which decreases exponentially with their distance from the point in question. The calculated values are used to draw a line graph in which regions of local similarity are shown by diagonal lines. Examples are shown of the application of the method to nucleic acid and amino acid sequences.
Full text
PDF


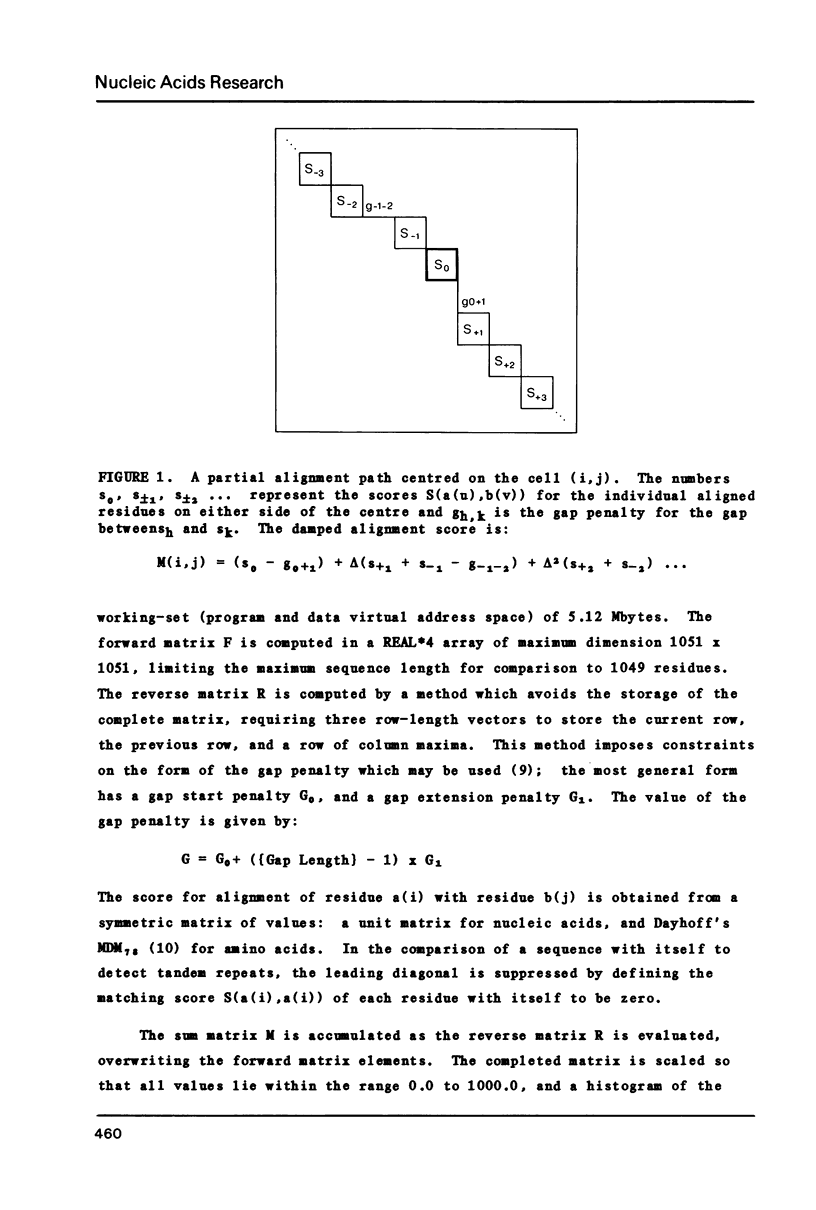




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bock S. C., Wion K. L., Vehar G. A., Lawn R. M. Cloning and expression of the cDNA for human antithrombin III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8113–8125. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W., Jeppsson J. O., Laurell C. B., Brennan S. O., Owen M. C., Vaughan L., Boswell D. R. Structure and variation of human alpha 1-antitrypsin. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):329–334. doi: 10.1038/298329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W., Jeppsson J. O., Vaughan L., Brennan S. O., Owen M. C., Boswell D. R. Human alpha 1-antitrypsin: carbohydrate attachment and sequence homology. FEBS Lett. 1981 Dec 7;135(2):301–303. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80805-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M. An improved method of testing for evolutionary homology. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80258-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M., Smith T. F. Optimal sequence alignments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1382–1386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goad W. B., Kanehisa M. I. Pattern recognition in nucleic acid sequences. I. A general method for finding local homologies and symmetries. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):247–263. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh O. An improved algorithm for matching biological sequences. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 15;162(3):705–708. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90398-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. Tests for comparing related amino-acid sequences. Cytochrome c and cytochrome c 551 . J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 28;61(2):409–424. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pech M., Streeck R. E., Zachau H. G. Patchwork structure of a bovine satellite DNA. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):883–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90140-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


