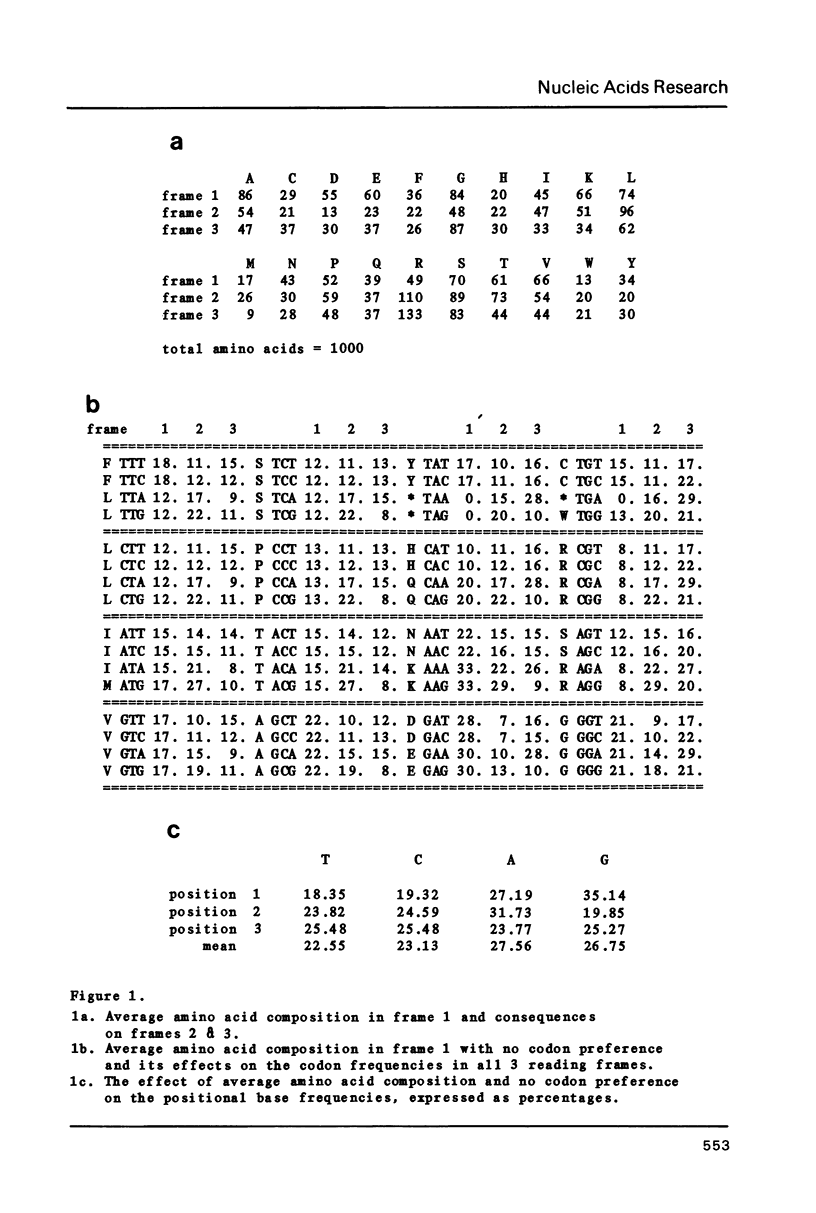
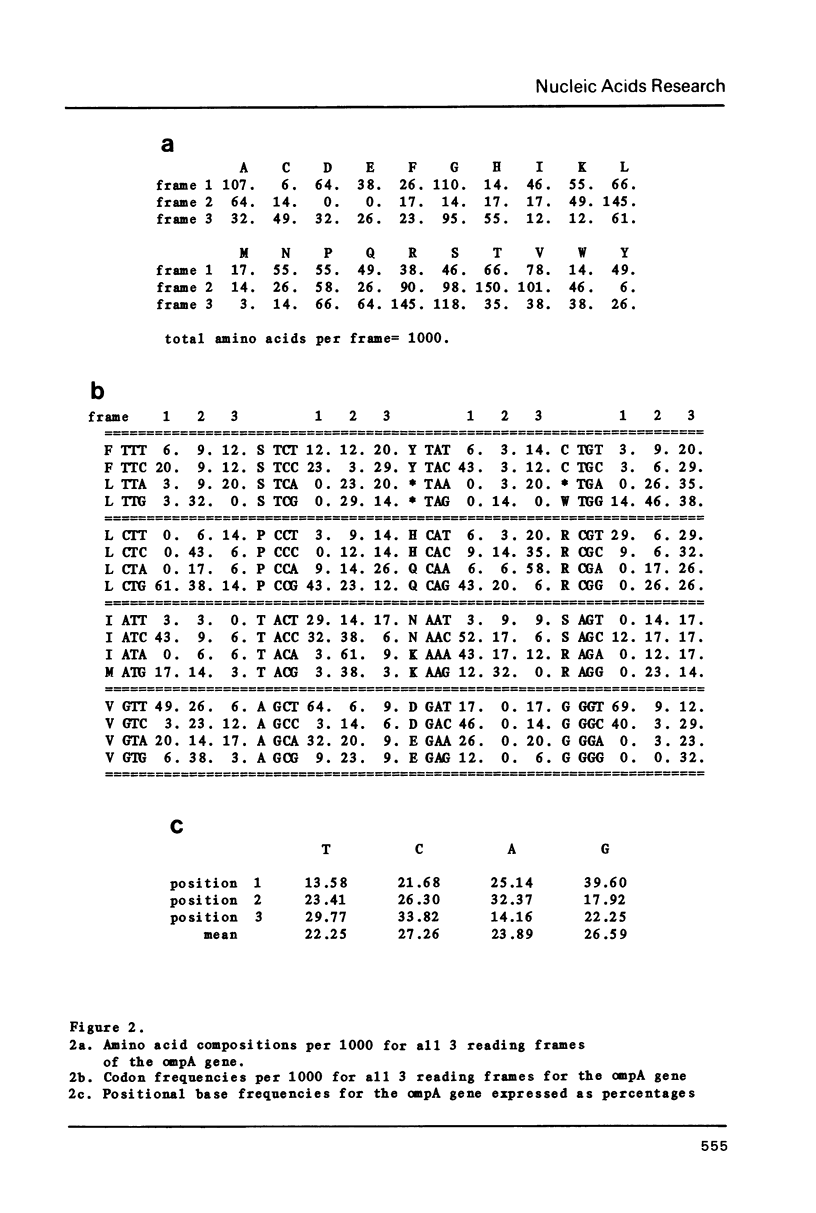
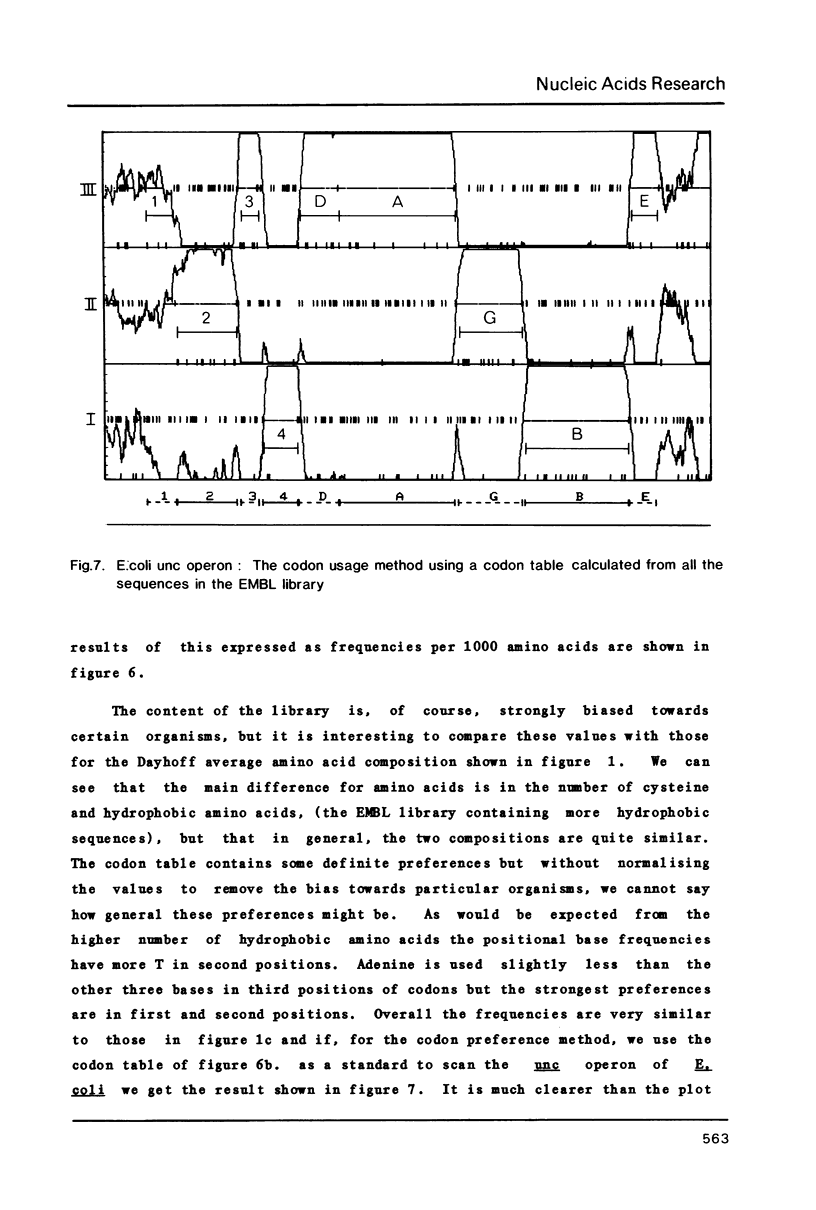
Abstract
Protein genes can be found either by searching the DNA sequence for signals such as ribosome binding sites or by looking for the effects that coding for a protein has on the coding sequence. This paper describes how these coding effects can be measured and used to detect protein coding regions.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck E., Bremer E. Nucleotide sequence of the gene ompA coding the outer membrane protein II of Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):3011–3027. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.3011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fickett J. W. Recognition of protein coding regions in DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5303–5318. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):389–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod A. R., Karn J., Brenner S. Molecular analysis of the unc-54 myosin heavy-chain gene of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1981 Jun 4;291(5814):386–390. doi: 10.1038/291386a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Hong G. F., Hill D. F., Petersen G. B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):729–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Gay N. J., Eberle A., Runswick M. J., Walker J. E. The atp operon: nucleotide sequence of the genes for the gamma, beta, and epsilon subunits of Escherichia coli ATP synthase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5287–5296. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R., McLachlan A. D. Codon preference and its use in identifying protein coding regions in long DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):141–156. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



