Of the more than 12,000 species and subspecies of extant reptiles, about 100 have re-entered the ocean. Among them are seven species of sea turtles and about 80 species and subspecies of sea snakes, as well as a few other species that are occasionally or regularly found in brackish waters, including various other snakes, the saltwater crocodile, and the marine iguana of the Galapagos Islands. The largest group of marine reptiles, the sea snakes, occur in the tropical and subtropical waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans from the east coast of Africa to the Gulf of Panama. They inhabit shallow waters along coasts, around islands and coral reefs, river mouths and travel into rivers more than 150 km away from the open ocean. A single species has been found more than 1000 km up rivers. Some have also been found in lakes. The taxonomic status of the sea snakes is still under review and no general agreement exists at the moment. The effects of the exploitation on sea snakes have been investigated in the Philippines and Australia but are almost unknown from other areas. Investigations indicate that some populations are already extinct and others are in danger of extinction in various parts of Asia. All sea turtles are endangered except one. The marine iguana of the Galapagos Islands remains vulnerable due to its limited range. Brackish water snakes are closely associated with mangrove forests and as such are subject to deforestation and coastal development schemes that result in habitat loss. In addition, some are collected for their skins. While none of the coastal species are considered in danger of extinction at the present time, many are data deficient.
Introduction
Reptiles are the most diverse terrestrial vertebrates with about 12,000 described forms, including about 9,350 currently recognized species and about 3,000 subspecies [1].
About 260 million years ago reptiles evolved from aquatic amphibians and by the Jurassic (150–200 myr) modern reptiles had appeared. However, only a few reptile groups re-entered the oceans, primarily sea snakes (elapids related to cobras and kraits), and sea turtles. All major reptile groups, i.e. the snakes, lizards, turtles, and crocodiles, have at least a few members that enter marine habitats even though they may have never completely adapted to a life in the open sea. Here we give an overview of those reptiles that are found exclusively or at least occasionally in the oceans.
Sea Turtles
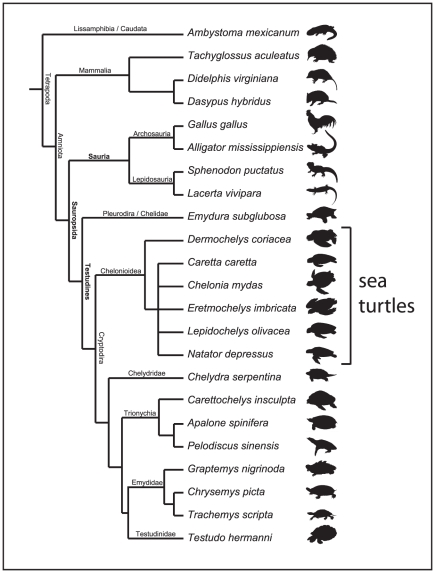
Sea turtles arose about 100 million years ago from terrestrial or fresh-water turtles ( Figure 1 ) [2]. Currently only 7 species are extant ( Table 1 ) although certain authors list Chelonia mydas agassizi as an eighth valid species (e.g. [3]). Sea turtles are found primarily along tropical coasts ( Figure 2 ). However, some are also well-known for their long journeys across the oceans. Most species nest along the coasts of Central and South America or in the Caribbean, although some species occasionally travel as far north as Scandinavia.
Figure 1. Phylogeny of sea turtles.
(A) Phylogenetic relationships of amniotes with the position of sea turtles relative to other vertebrates. Modified after [124].
Table 1. All species of sea turtles.
| Species | Common name | IUCN Red List status* |
| Caretta caretta | Loggerhead | Endangered |
| Chelonia mydas | Green Turtle | Endangered |
| Dermochelys coriacea | Leatherback | Critically Endangered |
| Eretmochelys imbricata | Hawksbill | Critically Endangered |
| Lepidochelys kempii | Atlantic Ridley | Critically Endangered |
| Lepidochelys olivacea | Pacific Ridley | Vulnerable |
| Natator depressus | Flatback Turtle | ? (data deficient) |
*IUCN Red List data from http://www.iucnredlist.org/.
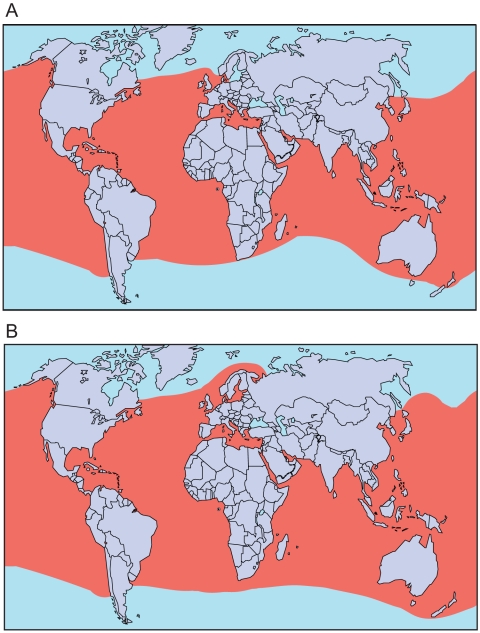
Figure 2. Distribution of sea turtles.
(A) Cheloniidae. (B) Dermochelyidae. From [125]. Detailed maps for individual species can be found in [126].
Like many other reptiles, most if not all sea turtles seem to use temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD). TSD has been demonstrated for loggerhead (Caretta caretta), green (Chelonia mydas), leatherback (Dermochelys coriacea) and olive ridley (Lepidochelys olivacea) turtles [4]. Since TSD is often sensitive to small changes in temperature, global warming may eventually affect sex ratios in these species and, together with their general vulnerabilities (see below), have a dramatic effect on their reproductive rate and thus long-term survival.
Migration
Usually, sea turtles travel the seas on their own. However, during the nesting season they head towards their home beaches and may form large groups of turtles traveling together, even if they maintain distances of up to several hundred meters between individuals. The ability of sea turtles to find their original nesting sites has spurred considerable interest. Only recently it has been shown that sea turtles use geomagnetic sensing to orient themselves [5], [6]. While sea turtles appear to return to a certain geographic region, they not necessarily return to a specific. However, Kemp's Ridley does nest on only one location in Mexico, so it is especially endangered. It remains unclear though how precise other turtles are in returning [5], [7], [8].
Conservation
Most sea turtles are endangered or even critically endangered. The Olive Ridley Turtle (Lepidochelys olivacea) is vulnerable and for the Flatback Turtle (Natator depressus) there is simply not enough data, although in previous years it had been classified as “vulnerable” too. The IUCN Red List says about the Green Turtle (Chelonia mydas):
“Analysis of historic and recent published accounts indicate extensive subpopulation declines in all major ocean basins over the last three generations as a result of overexploitation of eggs and adult females at nesting beaches, juveniles and adults in foraging areas, and, to a lesser extent, incidental mortality relating to marine fisheries and degradation of marine and nesting habitats. Analyses of subpopulation changes at 32 Index Sites distributed globally show a 48% to 67% decline in the number of mature females nesting annually over the last 3 generations.” [9]
Similar statements are true for all sea turtles: overexploitation and the destruction of nesting sites cause concern for these species, as tropical beaches are also in high demand for touristic reasons and easily exploited by locals.
Other Turtles Living in Brackish Environments
Of the more than 300 species of turtles only seven are truly marine while about 50 species are fully terrestrial, belonging to the family of tortoises, the Testudinidae. The majority of the remaining species, and most of the world's turtles, are aquatic or semi-aquatic freshwater species. However, a few are associated with estuarine and other brackish water habitats in an environment that is neither marine nor fresh water ( Table 2 ).
Table 2. Turtles in brackish waters.
| Genus | number of all species | brackish species |
| Malaclemys | 1 | 1 |
| Batagur | 6 | 3 |
| Carettochelys | 1 | 1 |
| Pelochelys | 3 | 1 |
Included among the species that spend a portion or all of the year in estuarine habitats are the mangrove terrapins (Batagur affinis and B. baska) of south-east Asia and India, as well as the pig-nosed turtles (Carettochelys sp.) in southern New Guinea. Painted terrapins (Batagur borneoensis) of south-east Asia characteristically spend an even greater portion of their life cycle in estuarine and brackish waters, even laying their eggs on oceanfront beaches in the same areas as sea turtles. A few additional species of turtles, such as the giant softshell (Pelochelys cantori) of Asia, will enter estuarine brackish waters and even into full saltwater habitats temporarily, but the majority of their range includes freshwater habitats.
The only exclusively brackish water turtle in the world is the diamondback terrapin (Malaclemys terrapin, Figure 3 ), which is endemic to tidal creeks and salt marshes as well as the brackish portions of estuaries of the Atlantic and Gulf coasts in the United States, from Cape Cod to Texas. Diamondback terrapins in Florida are found in mangrove swamps. Two species of Batagur in Asia and the painted terrapin in Malaysia also occupy mangrove swamps. All of the species found in mangrove swamps also inhabit other brackish waters of coastal areas and most are associated to some degree with river estuaries, and the Asian species commonly enter freshwater systems as well. None of the turtle species in South America, Africa, or Europe has an affinity for brackish water conditions characteristic of the species noted above. However, many species of freshwater turtles that live in coastal areas around the world are known to enter brackish waters on occasion. The diamondback terrapin has a functional salt gland and can live indefinitely in fresh water or sea water. Other estuarine turtles have not been reported to have well developed salt glands comparable to those in the diamondback terrapin.
Figure 3. Malaclemys terrapin.
This species is the only terrestrial turtle with significant adaptions to coastal habitats. Photo courtesy of J.D. Willson, by permission.
All turtle species that are brackish water inhabitants face severe conservation threats in all or part of their range because of the numerous environmental impacts on coastal systems throughout the world. Habitat degradation from pollution, sediment runoff, and other consequences of overdevelopment as well as mortality as targeted commercial species or as bycatch from the fisheries industry take an increasingly greater toll on these species.
Marine Crocodiles
None of the currently 23 species of crocodile is truly marine (Crocodylus raninus has been revalidated as 24th species only recently but this has not been universally accepted). However, at least one species, the Saltwater or “Estuary” Crocodile (Crocodylus porosus) is regularly found in brackish waters [10] of south-east Asia and Australia ( Figure 4 ). Other crocodiles have been found in tidal waters, such as Crocodylus johnstoni or C. acutus, but C. porosus is the only one that does show some adaptations to salt water [11], [12].
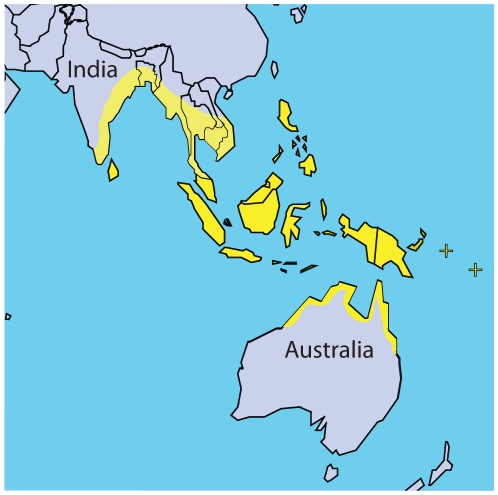
Figure 4. Distribution of the saltwater crocodile, Crocodylus porosus.
The range is shown in yellow. “+” symbols represent the Pacific islands that are also inhabited by this species, including the Solomon islands and Vanuatu. Adapted from http://www.flmnh.ufl.edu/cnhc/cst_cpor_dh_map.htm.
The saltwater crocodile is the largest living crocodile and thus the largest living reptile, reaching a total length of more than 6 meters [13]. The species seems to be most closely related to C. siamensis which is not particularly associated with brackish waters [14].
The saltwater crocodile has a high tolerance for salinity, being found in brackish water around coastal areas and in rivers. However, it is also present in freshwater rivers and swamps. Movement between different habitats occurs between the dry and wet season, and as a result of social status: juveniles are raised in freshwater areas, but eventually sub-adult crocodiles are usually forced out of these areas (used for breeding by dominant, territorial adults), into more marginal and saline areas. Subordinate animals unable to establish a territory in a tidal river system are either killed or forced out into the sea where they move around the coast in search of another river system. In recent years in northern Australia, saltwater crocodile populations in some areas have recovered to such an extent that increasing numbers are being forced further upstream into marginal habitat.
Crocodiles use their lingual salt glands to secrete excess salt ions [15]. The morphology of these salt-secreting glands is highly conserved [16]. These tissues are typified by their abundance of ion pumps, responsible for the maintenance of cellular electrochemical gradients through the movement of Na+ and K+ ions against their osmotic gradients. Crocodylus porosus possesses lingual salt glands which function to remove excess Na+ and Cl– ions accumulated as a consequence of living in a marine environment [15], [17]. However, other crocodiles, such as the Nile crocodile, seem to have similar glands, even though they may be not as active or efficient as those in the saltwater crocodile [18]. Some authors have suggested that such adaptations to sea water are evidence for a marine evolutionary origin of crocodiles [18].
Sea Snakes
Besides the sea turtles, the sea snakes are the reptiles that are best adapted to marine environments. The most typical feature of a sea snake is the vertically flattened paddle-like tail, which is not found in any other terrestrial or aquatic snakes ( Figure 5 ). Sea snakes occur in the tropical and subtropical waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans from the east coast of Africa to the Gulf of Panama ( Figure 6 ). However, two specimens of Pelamis platurus reported from Namibia indicate that the species may be extending its range into the Atlantic Ocean [19]. Most species are concentrated in the Indo-Malayan Archipelago, South China Sea, Indonesia and the Australian region [20]–[29]. Sea snakes inhabit shallow waters along coasts and around islands, river mouths and up rivers for more than 150 km and they have also been found in lakes in Thailand, Cambodia, the Philippines and Rennell Island in the Solomon archipelago [27], [30]–[33]. However, information on precise geographical distribution and abundance for each species is still lacking.
Figure 5. A typical sea snake, Hydrophis belcheri.
Note the flattened tail as an adaptation to swimming in the open sea.
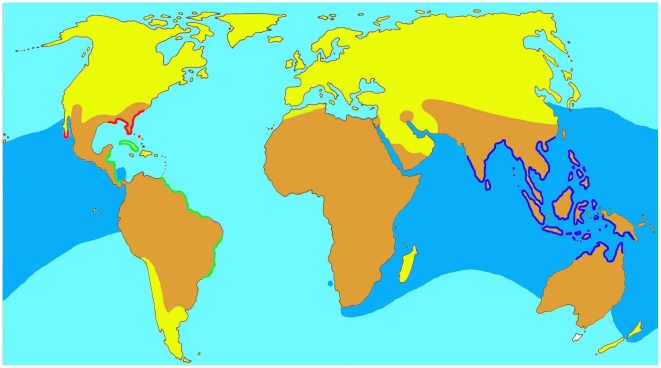
Figure 6. Distribution of marine snakes.
Terrestrial distribution represents terrestrial elapids (brown), marine distribution represents sea snakes, i.e. the subfamily Hydrophiinae of the Elapidae (blue). Dark blue: homalopsid snakes along the Asian and Australian coasts. Red: North-American Natricidae, green: neotropical Dipsadidae.
Notably, a few sea snakes are actually freshwater species, such as Hydrophis semperi, H. sibauensis, H. obscurus, and L. crockeri. However, all evidence indicates that these species have radiated into freshwaters independently from saltwater species [34].
Sea snake bite
Sea snake bite is the cause of human fatalities. The typical victim is a fisherman handling gape nets or down nets, sorting fish (and sea snakes) on board a trawling boat or dragging a net by wading in muddy coastal waters or in river-mouths. Some sea snakes are gentle, inoffensive creatures that bite only under provocation, but other species are much more aggressive (e.g. Aipysurus laevis, Astrotia stokesii, Enhydrina schistosa, Hydrophis elegans, H. macdowelli, H. major, H. ornatus and H. ocellatus) [35]–[39]. As a general rule all sea snakes must be handled with great caution: however, it is worth mentioning that when sea snakes do bite, they do not always inject much or any of their venom, so that only trivial severity of poisoning will be recognizable [39].
Taxonomy
The taxonomic status of the sea snakes is still under review and no general agreement exists at the moment. Traditionally sea snakes have been regarded as belonging to one family, Hydrophiidae, with Laticauda as the most primitive genus [27].
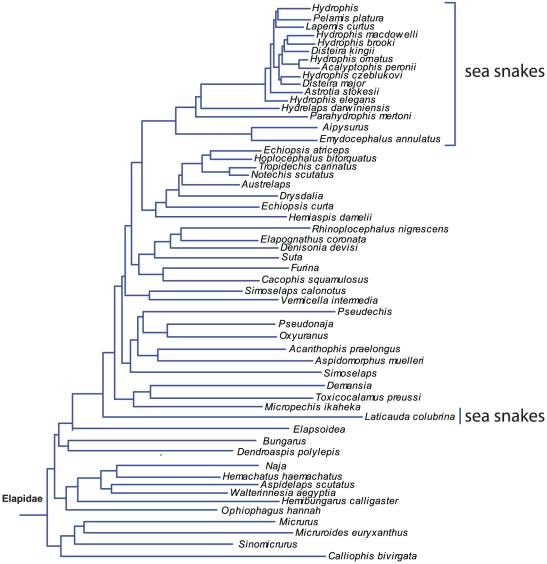
However, more recent results support the position that Laticaudinae and Hydrophiinae (true sea snakes) have evolved from different terrestrial elapids [34], [40]–[44] ( Figure 7 ). The combined morphological and molecular results by Scanlon and Lee [44] support that sea kraits (Laticauda) and Solomon Islands elapids are basal to the remaining Australian terrestrial elapids and true sea snakes (Hydrophiinae). The Australian Elapids and true sea snakes include three main lineages: a large-bodied oviparous lineage, a small-bodied oviparous lineage, and a viviparous lineage which also includes the true sea snakes. The results by Castoe et al. indicate that Laticauda is closest to some Asiatic elapids [45]. However, these authors suggest to interpret these results cautiously because of long branch attraction. Sanders et al. [40] indicate that Laticauda is the sister group to all other hydrophiines (oxyuranines), which is also consistent with a classic morphological feature: all oxyuranines have reduced the choanal process of the palatine and lost the lateral process, permitting novel jaw movements [40], [46].
Figure 7. Sea snakes and their relationship to other Elapid snake genera.
Note that the the “true” sea snakes (Hydrophiinae and Laticaudinae) are not closely related but nest within the terrestrial elapids. Generic names represent multiple species. The relationships among the many species of Hydrophis have not been resolved (see text for details). Modified after [127].
Some results indicate that true sea snakes (Hydrophiinae) can be separated into two totally different groups, indicating that sea snakes perhaps have evolved three times from terrestrial elapids [34], [47], [48]. However, this hypothesis is not supported by other recent results [40], [43], [44] and the latest molecular evidence suggests that the true sea snakes (Hydrophiinae) are a very young monophyletic group, perhaps only 8–13 Myr old [49] ( Figure 7 ).
On the genus level at least three completely different taxonomic hypotheses exist, resulting in much confusion in both scientific and non-scientific publications. The most thorough work on sea snakes is by Smith, 1926, whose taxonomy has been used by most authors during the past 85 years. In 1972 McDowell, based on a few specimens from selected species, suggested separating the genus Hydrophis into 3 different subgenera based on morphological data. McDowell also changed some genera using the same arguments, which were not based on a phylogenetic analysis, but more on morphological similarity [50]. Kharin has suggested raising some of McDowells' species groups to genus level [23], [51]–[56], however, Kharin also did not produce any phylogenetic analysis for these groups. Recently, Wells [57] suggested changing the nomenclature in the Australian sea snake species also without any phylogenetic analysis, thus creating new problems for the layman to use valid generic names for the groups. A couple of papers using phylogenetic methods do not support the hypothesis by McDowell (1972) [43], [58], [59], [60]. Because of sea snakes' extremely venomous bite it is important to have correct taxonomic assignments and thus correct names because physicians often apply anti-venoms based on the species of snake. As long as no thorough phylogenetic analysis is available for the group, we suggest using Smith's [27] classification, with a few corrections that have been generally accepted [20]–[22], [29], [34].
Identifying sea snakes to species level is very difficult; especially the genus Hydrophis shows great intraspecific variation making it difficult to use only external characters for their identification. The ∼70 species recognized here follow Golay et al. [61] and David & Ineich [21] with a few new species added or resurrected [32], [62], [63]. A complete species list can be found in [1] when searching for the two subfamilies, Hydrophiinae and Laticaudinae, respectively.
At a higher taxonomic level sea snakes are the closest relatives of terrestrial elapids, which include some of the most venomous snakes in the world (e.g. brown snakes, taipan, death adder, cobra, krait, mambas) [40], [43]. Sea snakes or aquatic elapids and terrestrial elapids are collectively known as proteroglyphous snakes because of the position of the poison-fangs in the frontal part of the upper jaw (maxillary bone) [64].
Feeding and breeding biology
Most sea snake species feed on fish that are close to the bottom or sedentary; a few prefer fish eggs (Aipysurus eydouxii, and the genus Emydocephalus; some specimens of A. fuscus also contained fish eggs) and at least Aipysurus laevis, Enhydrina schistosa and Lapemis curtus have been found with crustaceans and mollusks in their stomachs [58], [65]–[73]. The Laticauda group feed mostly on eels burrowed in sand at the bottom of the sea and in reef crevices [66], [72], [73]. Using sea snakes to capture undescribed eel species has been shown to be very effective because the eels are extremely secretive in their habits giving no chance to collect them using traditional methods [73].
All sea snakes produce living young (viviparous) except for the genus Laticauda which is egg laying (oviparous) [20], [74]. The annual reproductive cycles are synchronous between males and females and they reproduce every second year with a clutch size that increases with the size of the female [71], [75]–[83].
By-catch and commercial use of sea snakes
Sea snakes are not only of interest because of their poison, but also in connection with the commercial exploitation of reptile skin, organs and meat. Some species are accessible in great numbers (e.g. Laticauda spp., Lapemis spp. and some Hydrophis spp.) and are not protected by CITES (Washington convention).
Since at least 1934 sea snake meat and skins have been used commercially in the Philippines [84], but also in Australia. In Japan, Taiwan, Thailand and Vietnam sea snakes have been collected commercially [38], [85]–[89]. Local protection of sea snakes has been necessary to stop over-exploitation in the Philippines. In Australia commercial sea snake fisheries and by-catch have been investigated during the past 15 years [77], [90]–[97]. However, most sea snake fisheries in the Indian Ocean and in the Pacific are not reported in the literature and are beyond control of the local governments.
Species distribution and density
Many of the more than 60 species of sea snakes have a broad distribution in both the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean ( Figure 6 ). Species such as Acalyptophis peronii, Aipysurus eydouxii, Astrotia stokesii, Enhydrina schistosa, Lapemis curtus, Laticauda colubrina, L. laticaudata and many Hydrophis species have been collected in both the Asian and the Australian region [21], [22], [26], [27], [63], [98] and are abundant in these areas. Other species are much less well known and some species are only collected from very restricted areas and therefore much more vulnerable for change in the environments. One of the rarest species is Hydrophis parviceps which is known from only two specimens collected in a very limited area in the southern Vietnamese part of the South China Sea [99], [100]. Hydrophis sibauensis is a recently described species which has been collected more than 150 km into rivers of Borneo and is only known from 3 specimens [32]. This is also the case for another recently described species, Hydrophis laboutei which is only known from two specimens collected at Chesterfield Reefs (New Caledonia) [62]. Other species with a limited distribution are therefore highly vulnerable to all kinds of environmental changes, including Aipysurus fuscus, A. apraefrontalis and A. foliosquama which have only been collected in the north west part of Australian coral reefs. Recent surveys indicate that there has been a drastic decline of specimens in this areas over the last 10–15 years ([101] and pers.comm. Michael Guinea). Hydrophis semperi and Laticauda crockeri, both species only known from Lake Taal in the Philippines and Lake Te-Nggano in Rennell Island, respectively [30], [33], also represent species that have a very restricted distribution and therefore are highly vulnerable to changes in the environment.
Our own (ARR) investigations in the Gulf of Thailand and part of Borneo indicated that the sea snake fauna in this area has also declined. In the Gulf of Thailand, especially populations of species going up rivers have disappeared (e.g. Hydrophis torquatus and H. klossi), but also in Borneo the number of specimens collected previously in great numbers inside river mouths appears to have declined. Trawl fisheries in the Andaman Sea (e.g. around Phuket, Thailand) also got fewer specimens and the fishermen also mention that the size of sea snakes they got in former times was much larger than the ones they get now. A small survey in Cambodia (ARR) in the year 2000/2001 indicated similar results to those found for Borneo and Thailand.
Conservation: What can we do to help the sea snakes to survive?
The main threat to sea snakes is the cultural indifference to conservation issues by locals and, as a consequence, their commercial exploitation. Only raising awareness may reduce this kind of threat. Another problem in trying to help the sea snakes to survive is the very limited knowledge on their biology, especially in Asia. It is very important to get much more information on the biology in formulating management plans. For the moment we still miss information on breeding cycles, by-catch and mortality, growth rates, population density, sexual maturity and taxonomy in most areas. The effects of the exploitation or/and by-catch on the sea snakes are almost unknown except from the Philippines and Australia [93], [95], [96]. Some populations may already be in danger of extinction. The only way to have a sustainable yield is by monitoring and controlling by-catch and commercial catch of sea snakes, giving local governments a chance to intervene before a catastrophic collapse of local populations occur. However, to limit exploitation of the most common species sustainable and to protect the endangered ones, we need to have much more biological focus on the group.
One cause for the disappearance of sea snake species from rivers is at least in part due to the great problems with the ongoing pollution in many rivers in both Asia and Australia. Also the information on breeding areas for most sea snake species is unknown, but there is no doubt that also habitat destructions (eg. mangrove clearings and water crafts) have a negative influence on sea snake populations.
A first step in sea snake conservation is to distinguish the many species from each other, which is not an easy task, and with the global decline of taxonomists it may be more important to focus initially on the entire group. The next step is to get more knowledge of sea snake biology and then to focus on the by-catch and management plan to protect the endangered species and harvest only the more common ones. Concerning the more global problems of pollution and habitat degradation, we have to put more pressure on politicians and hope that they will come up with solutions for the benefit of both humans and sea snakes.
Other Snakes Found in Marine and Brackish Environments
Evolution is continually tinkering with snake populations that live in coastal areas adjacent to brackish and salt water environments. Besides the true sea snakes, many terrestrial and arboreal species have learned to exploit marine resources by foraging in the intertidal zone at low tide or from the branches of mangroves, while some freshwater species have adapted to life in brackish water, sometimes enter the ocean, or live there permanently ( Figure 8 , Table 3 ).
Figure 8. Several families of snakes have independently adapted to saltwater.
Families with species that live in brackish or marine environments are shown in red.
Table 3. Non-elapid snakes that use brackish water.
| Genus | Total species | Species in brackish or marine water |
| Acrochordus | 3 | all (3) |
| Agkistrodon | 4 | 1 |
| Bitia | 1 | all (1) |
| Cantoria | 1 | all (1) |
| Cerberus | 3 | 2+ |
| Crotaphopeltis | 6 | 1 |
| Djokoiskandarus | 1 | all (1) |
| Enhydris | 24 | 1 |
| Farancia | 2 | all (2) |
| Fordonia | 1 | all (1) |
| Gerarda | 1 | all (1) |
| Grayia | 4 | 1 |
| Helicops | 15 | 2+ |
| Hydrops | 3 | 1 |
| Liophis | 39 | 2+ |
| Myron | 3 | all (3) |
| Natrix | 4 | 3+ |
| Nerodia | 10 | 4+ |
| Regina | 4 | 1 |
| Stegonotus | 9 | 2+ |
| Storeria | 4 | 1 |
| Thamnophis | 31 | 2 |
| Tretanorhinus | 4 | 2 |
The list does not include arboreal and terrestrial species that use mangrove forests or terrestrial species that occasionally enter water, or forage in the intertidal zone. A “+” indicates there are probably more species in this genus that use brackish water.
All three living species of the ancient Acrochordidae use a combination of aquatic environments ranging from freshwater to sea water, and have probably been living in coastal ocean habitats for most of their 90.7 million year history [102]. Acrochordids, particularly Acrochordus granulatus have some of the most specialized morphology and physiology for life in saltwater, including the greatest capacity to store oxygen found in any vertebrate [103]. These are low metabolism snakes, feeding and reproducing infrequently and incapable of active swimming for more than a few minutes [104]. Acrochordus arafurae females ambush prey in deep water while males actively search for prey in shallow water [105]. They have a constriction-like behavior for holding prey between body loops during ingestion, and enlarged keels on their scales aid in holding slippery fish. Additionally each scale contains a mechanoreceptor that may be used to locate fish in turbid water [106].
The Asian and Australasian Homalopsidae, ironically sometimes called the “freshwater snakes,” have species that live in coastal habitats such as mangrove forests and salt marshes. Homalopsids inhabit life zones that range from the fossorial Brachyorrhos albus and the semi-terrestrial Enhydris plumbea, to Erpeton tentaculatus that is all but incapable of leaving their freshwater habitats, to species inhabiting coastal marine environments (Bitia hydroides, Cantoria violacea, Myron sp., Fordonia leucobalia, Enhydris bennettii). The most widespread and successful brackish water homalopsids are the bockadams (Cerberus sp) which are distributed from the vicinity of Mumbai, India in the east to Palau, Micronesia in the west, and range southward into the Indonesian Archipelago, New Guinea, and northern Australia ( Figure 6 ). Like some of the Hydrophis and Laticauda, the Lake Buhi Bockadam (Cerberus microlepis) is a freshwater species, derived from its nearby salt water dwelling relative, Cerberus rynchops in the Philippines ( Figure 9 ). While most of the aquatic homalopids are piscivorous, three species, all members of the same clade specialize in feeding on crustaceans (Cantoria violacea, Fordonia leucobalia, and Gerarda prevostiana) in near shore habitats [107]–[109].
Figure 9. A homalopsid snake (Cerberus rynchops).
See text for details.
An assemblage of mangrove homalopsids studied in Singapore [110] was dominated by the piscivorous Asian Bockadam, Cerberus rynchops (73% of total snakes), while the other species were crustacean specialists and less common. Gerard's Mud Snake, Gerarda prevostiana (16% of the total snakes) feeds exclusively on recently-molted crabs; while the Crab-eating Snake, Fordonia leucobalia, (10% of total snakes) specializes in feeding on hard-shell crustaceans. The most uncommon Singapore homalopsid was Cantor's Mud Snake, Cantoria violacea, (2% of total snakes) and it too has a specialized diet, feeding on Alpheus snapping shrimp (Decapoda, Alpheidae). The crustacean-eaters were often observed in association with mud lobster mounds constructed by Thalassina anomala (Decapoda: Thalassinidae). The snakes were nocturnal and active throughout the night. Gerard's Mud Snake increased activity during spring tides, but the other species did not. Three male Crab-eating snakes were tracked using radiotelemetry: they rarely moved and when they did it was for short distances (1.8 to 14.0 m). As might be expected for tropical aquatic snakes, the body temperatures were very stable (26.3–29.0°C) and consistently higher than the microhabitat temperatures. Two of the radio tracked crab-eating Snakes made extensive use of mud lobster mounds.
Snakes of the family Natricidae (or subfamily Natricinae) make up about 30 genera and 210 species [1]. They occur in both hemispheres and in both temperate and tropical environments, but they appear to have originated in Asia, and dispersed into Europe, and North America. Many of these snakes are semi-aquatic and some inhabit brackish water. In North Africa and Europe at least three species use coastal habitats: the Viperine Snake, Natrix maura, the Grass Snake, N. natrix sicula, and the Dice Snake, N. tessellata [111]–[113]. North American brackish water natricids use mangrove and salt marsh habitats include the Mangrove Water Snake, Nerodia clarkii, in the southeastern USA, and the Baja Garter Snakes, Thamnophis valida. Both these species are piscivorous and like some freshwater natricids, Nerodia clarkii juveniles lure prey with their tongue [114]. The Salt Marsh Brown Snake, Storeria dekayi limnectes is less aquatic than the previous species, and it feeds on soft bodied invertebrates [115].
In the Neotropics, the family Dipsadidae (or subfamily Dipsadinae) has more than 92 genera and >700 species [1], a few of which use brackish and salt water habitats (Helicops, Hydrops, Liophis, and Tretanorhinus) to varying degrees. For the most part these snakes are poorly known and their brackish water habits are known only from anecdotal observations [116]. Similarly, at least two aquatic African snakes, of uncertain lineages (Grayia smythii and Crotaphopeltis hotamboeia) occur in the brackish water of mangrove forests as well as freshwater [117], [118].
There is another group of snakes that use marine resources that is worthy of note. These species forage in mangroves, salt marshes, and intertidal zone without actually spending much time in the water. The most specialized is perhaps the Burmese Vine Snake, Ahaetulla fronticincta (family Colubridae) which hunts gobies from branches over hanging the water [28]. The Southeast Asian Mangrove Pitviper, Cryptelytrops purpureomaculatus (Viperidae) also hunts from the mangrove branches but its diet is unknown. There are others, for the most part habitat generalists with populations in or adjacent to marine habitats and include Python molurus, Python reticulatus (Pythonidae), Ophiophagus hannah (Elapidae), and Boiga dendrophilia (Colubridae) – all medium to large snakes that forage for food in coastal habitats. Other snakes forage in the intertidal zone: Coluber anthonyi (Colubridae); Crotalus mitchelli and Crotalus muertensis (family Viperidae, subfamily Crotalinae).
Thus, of 34 lineages of snakes (families and subfamilies), four (Acrochordidae, Homalopsidae, Dipsadidae, and Elapidae) contain most of the species adapted for marine environments, while other clades have relatively few, or no, species adapted for the saline water. As more herpetologists investigate mangroves and salt marshes a more complete picture of brackish water snakes will emerge.
Marine Iguanas
Lizards are the most speciose and diverse group of reptiles, with almost 5,500 species (60% of all reptiles) [1]. Nevertheless, only a few species have ventured into the oceans. The marine iguanas of the Galapagos Islands are the most aquatic of the lizards, but bask and reproduce on land and are subject to terrestrial predators.
The Galapagos archipelago arose through volcanic activity 960 km off the coast of Ecuador. Lizards and other animals probably reached the island on rafts of vegetation washed down the rivers of western South America. The rafts may have included juveniles, adults, or eggs. The Humboldt and El Niño currents would allow for such rafting to originate from the western coast of South or Central America. Other species, such as rats, have been introduced by humans only about 100 years ago.
Besides seven species of smaller iguanids of the genus Microlophus four large species of iguanas inhabit the Galapagos islands [119]: three species of land iguanas (genus Conolophus) and the related marine iguanas (Amblyrhynchus cristatus). Because the land iguanas are endemic to only a few islands, they are threatened by predation of introduced mammals. However, recent measures to control and protect their habitats seem to have stabilized their populations. In addition to these anthropogenic factors, the archipelago is subject to strong seasonal and annual variations in environmental conditions, so that a combination of factors could turn out to be detrimental.
The marine iguana, Amblyrhynchus cristatus, and the land iguanas of the genus Conolophus are all about 1.2 m in length. Amblyrhynchus inhabits virtually all islands of the archipelago, given its ability to disperse to various islands. As a result, they are less prone to extinction.
Although land and marine iguanas are very different in appearance, they are closely related. In fact, several instances of hybridization between the two genera have been reported [120], [121]. Hence it is likely that they both evolved relatively recently from a land iguana that came from the South American mainland.
Marine iguanas feed exclusively on marine plants. While they spent a considerable time in the water foraging, they have not completely adapted to marine life. For instance, they still have to nest on land and also bask on land to reach their optimal body temperature which rapidly declines in the rather cool ocean water. Nevertheless, considerable selection pressure has resulted in several adaptations to their marine lifestyle such as a flattened tail and limited webbing of all four feet, supporting swimming. Powerful claws help them to hold on to rocks in the heavy sea. Marine iguanas also have reduced the number of heartbeats per minute from about 43 on land to 7 to 9 while diving, as do several other reptiles [122]. Finally, both Conolophus and Amblyrhynchus possess nasal salt glands, similar to those found in other reptiles that have high dietary salt intakes [122]. Interestingly, neither species has the capacity to produce hyperosmotic urine. Thus, the marine iguana has the highest known extracloacal excretion rate of Na, Cl, and K of any reptile [123].
Acknowledgments
Adam Britton kindly provided information on Crocodylus porosus and a distribution map. Ken Lohmann shared data on sea turtle migration. J.D. Willson kindly provided the photo of Malaclemys terrapin, and Ingmar Werneburg supplied Figure 1.
Footnotes
Competing Interests: While some of the data described here were collected, the Reptile Database was hosted by the J Craig Venter Institute (JCVI). The JCVI thought that the Reptile Database used the JCVI brand name without permission and fired the corresponding author (PU) as a consequence. However, PU does not believe that there was any conflict, just to indicate this fact.
Funding: Support for manuscript preparation was provided by the U.S. Department of Energy under Award Number DE-FC09-07SR22506 to the University of Georgia Research Foundation and Savannah River Ecology Laboratory (JWG). PU acknowledges support by the European Union for the Reptile Database under the Catalogue of Life (4D4Life) e-Infrastructure projects. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Uetz P. 2011;15 The Reptile Database, Available: http://www.reptile-database.org, Accessed 2011 Sep. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Naro-Maciel E, Le M, FitzSimmons NN, Amato G. Evolutionary relationships of marine turtles: A molecular phylogeny based on nuclear and mitochondrial genes. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2008;49:659–662. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2008.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Liner EA. Herpetological Circular: SSAR; 1994. Scientific and common names for the Amphibians and Reptiles of Mexico in English and Spanish. pp. 1–113. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Standora EA, Spotila JR. Temperature-dependent sex determination in sea turtles. Copeia 1985. 1985:711–722. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Putman NF, Endres CS, Lohmann CM, Lohmann KJ. Longitude perception and bicoordinate magnetic maps in sea turtles. Curr Biol. 2011;21:463–466. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lohmann KJ, Cain SD, Dodge SA, Lohmann CM. Regional magnetic fields as navigational markers for sea turtles. Science. 2001;294:364–366. doi: 10.1126/science.1064557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lohmann KJ. Sea turtles: navigating with magnetism. Curr Biol. 2007;17:R102–104. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lohmann KJ, Putman NF, Lohmann CM. Geomagnetic imprinting: A unifying hypothesis of long-distance natal homing in salmon and sea turtles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:19096–19101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801859105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Seminoff JA. IUCN Red List: Chelonia mydas. 2011.
- 10.Martin S. Global diversity of crocodiles (Crocodilia, Reptilia) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia. 2008;595:587–591. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dunson WA. Salinity relations of crocodiles in Florida Bay. Copeia 1982. 1982:374–385. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mazzotti J, Dunson WA. Adaptations of Crocodylus acutus and Alligator for life in saline water. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. 1984;79:641–646. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Montague JJ. A new size record for the saltwater crocodile (Crocodylus porosus). Herpetological Review. 1983;14:36–37. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Meganathan PR, Dubey B, Batzer MA, Ray DA, Haque I. Molecular phylogenetic analyses of genus Crocodylus (Eusuchia, Crocodylia, Crocodylidae) and the taxonomic position of Crocodylus porosus. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 2010;57:393–402. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2010.06.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Taplin LE, Grigg GC. Salt Glands in the Tongue of the Estuarine Crocodile Crocodylus porosus. Science. 1981;212:1045–1047. doi: 10.1126/science.212.4498.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kirschner LB. Comparison of vertebrate salt-excreting organs. Am J Physiol. 1980;238:R219–223. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1980.238.3.R219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cramp RL, Hudson NJ, Franklin CE. Activity, abundance, distribution and expression of Na+/K+-ATPase in the salt glands of Crocodylus porosus following chronic saltwater acclimation. J Exp Biol. 2010;213:1301–1308. doi: 10.1242/jeb.039305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Taplin LE, Loveridge JP. Nile crocodiles, Crocodylus niloticus, and estuarine crocodiles, Crocodylus porosus, show similar osmoregulatory responses on exposure to seawater. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1988;89:443–448. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(88)91054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Branch B. Sanibel Island, Florida: Ralph Curtis Books Publishing; 1998. Field guide to the snakes and other reptiles of southern Africa.399 [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cogger HG, Heatwole H. Laticauda frontalis (de Vis, 1905) and Laticauda saintgironsi n. sp. from Vanuatu and New Caledonia (Serpentes: Elapidae: Laticaudinae)–A new lineage of sea kraits? Records of the Australian Museum. 2006;58:245–256. [Google Scholar]
- 21.David P, Ineich I. Les Serpents venimeux du monde: systématique et répartition. Dumerilia(Paris) 1999;3:3–499. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Heatwole H, Busack S, Cogger HG. Geographic variation in sea kraits of the Laticauda colubrina complex (Serpentes: Elapidae: Hydrophiinae: Laticaudini). Herpetological Monographs. 2005;19:1–136. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kharin VE, Czeblukov VP. A revision of the sea snakes of subfamily Hydrophiinae. 1, tribe Disteirini nov. (Serpentes: Hydrophiidae). Russian Journal of Herpetology. 2009;16:183–202. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Minton SA. Geographic distribution of sea snakes. In: Dunson WA, editor. The Biology of Sea Snakes. Baltimor: London & tokyo; 1975. pp. 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nguyên VS, Ho TC, Nguyên QT. Frankfurt am Main: Edition Chimaira; 2009. Herpetofauna of Vietnam.768 [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rasmussen AR. Sea snakes. FAO species identification guide for fishery purposes//The living marine resources of the Western Central Pacific. 2000;6:3987–4008. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Smith MA. Monograph of the sea-snakes (Hydrophiidae): Printed by order of the Trustees of the British museum (Natural History) London 1926 [Google Scholar]
- 28.Smith MA. Reptilia and Amphibia London: Taylor & Francis; 1943. The fauna of British India Ceylon and Burma, including the whole of the Indo-Chinese sub-region. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cogger HG. Sea Snakes of Australia and New Guinea. In: Dunson WA, editor. The Biology of Sea Snakes. Baltimore London & Tokyo: University Park Press; 1975. pp. 59–139. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Alcala AC. Amphibians and Reptiles. Guide to Philippine flora and fauna. 1986;10:1–195. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ineich I. Geographic distribution. Hydrophis torquatus diadema. Herpetological Review. 1996;27:154. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rasmussen AR, Auliya M, Böhme W. A New Species of the Sea Snake Genus Hydrophis (Serpentes: Elapidae) from a River in West Kalimantan (Indonesia, Borneo). Herpetologica. 2001;57:23–32. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cogger HG, Heatwole H, Ishikawa Y, McCoy M, Tamiya N, et al. The Status and Natural History of the Rennell Island Sea Krait, Laticauda crockeri (Serpentes: Laticaudidae). Journal of Herpetology. 1987;21:255–266. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rasmussen AR. Systematics of sea snakes: A critical review. Symposium of the Zoological Society of London. 1997;70:15–30. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Guinea ML. Sea snakes of Fiji and Niue. In: Gopalakrishnakone P, editor. Sea Snake Toxinology. ed.: Singapore University Press; 1994. pp. 212–233. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Heatwole H, Cogger H. Fauna of Australia; 1994. Family Hydrophiidae. pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Toriba M. Sea snakes of Japan. In: Gopalakrishnakone P, editor. Sea Snake Toxinology. Singapore: Singapore University Press; 1994. pp. 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Warrell DA. Sea snake bites in the Asia-Pacific region. In: Gopalakrishnakone P, editor. Sea Snake Toxinology. Singapore: Singapore University Press; 1994. pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Reid HA. Sea snake venoms and toxins. In: Dunson WA, editor. The Biology of Sea Snakes. Baltimor: London & Tokyo; 1975. pp. 417–462. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sanders KL, Lee MSY, Leys R, Foster R, Keogh JS. Molecular phylogeny and divergence dates for Australasian elapids and sea snakes (Hydrophiinae): evidence from seven genes for rapid evolutionary radiations. Journal of Evolutionary Biology. 2008;21:682–695. doi: 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2008.01525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Keogh JS. Molecular phylogeny of elapid snakes and a consideration of their biogeographic history. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society. 1998;63:177–203. [Google Scholar]
- 42.McDowell SB. Aspidomorphus a genus of New Guinea snakes of the family Elapidae, with notes on related genera. Journal of Zoology. 1967;151:497–543. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lukoschek V, Keogh JS. Molecular phylogeny of sea snakes reveals a rapidly diverged adaptive radiation. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society. 2006;89:523–539. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Scanlon JD, Lee MSY. Phylogeny of Australasian venomous snakes (Colubroidea, Elapidae, Hydrophiinae) based on phenotypic and molecular evidence. Zoologica Scripta. 2004;33:335–366. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Castoe TA, Smith EN, Brown RM, Parkinson CL. Higher-level phylogeny of Asian and American coralsnakes, their placement within the Elapidae (Squamata), and the systematic affinities of the enigmatic Asian coralsnake Hemibungarus calligaster (Wiegmann, 1834). Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 2007;151:809–831. [Google Scholar]
- 46.McDowell SB. On the status and relationships of the Solomon Island elapid snakes. Zool J Linn Soc. 1970;161:145–190. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Voris HK. A phylogeny of the sea snakes (Hydrophiidae). Fieldiana Zoology. 1977;70:79–166. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rasmussen AR. Phylogenetic analysis of the "true" aquatic elapid snakes Hydrophiinae (sensu Smith et al. 1977) indicating two independent radiations into water. Steenstrupia. 2002;27:47–63. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sanders KL, Mumpuni, Lee MS. Uncoupling ecological innovation and speciation in sea snakes (Elapidae, Hydrophiinae, Hydrophiini). J Evol Biol. 2010;23:2685–2693. doi: 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2010.02131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.McDowell SB. The genera of sea-snakes of the Hydrophis group (Serpentes: Elapidae). Transactions of the Zoological Society of London. 1972;32:189–247. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kharin VE. A review of sea snakes of the group Hydrophis sensu lato (Serpentes, Hydrophiidae). S. the genus Leioselasma. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal. 1984;63:1535–1546. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kharin VE. A new sea snake species of the genus Disteira (Serpentes, Hydrophiidae) from the waters of the Malay Archipelago. Vestnik Zoologii 1989. 1989:29–32. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kharin VE. Review of sea snakes of the genus Hydrophis sensu stricto (Serpentes: Hydrophiidae). Russian Journal of Marine Biology. 2004;30:387–394. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kharin VE. On the Taxonomic Position of the Sea Snake Hydrophis caerulescens (Shaw, 1802) (Serpentes: Hydrophiidae). Russian Journal of Marine Biology. 2004;30:196–198. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kharin VE. A check-list of sea snakes (Serpentes: Laticaudidae, Hydrophiidae) of the World Ocean. TINRO. 2005;140:71–89. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kharin VE, CP V. A new revision of sea kraits of family Laticaudidae Cope, 1879 (Serpentes: Colubroidea) Russian Journal of Herpetology. 2006;13:227–241. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wells RW. Some Taxonomic and Nomenclatural Considerations on the Class Reptilia in Australia. The Sea Snakes of Australia. An Introduction to the Members of the Families Hydrophiidae and Laticaudidae in Australia, with a New Familial and Generic Arrangement. Australian Biodiversity Record. 2007;8:1325–2992. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Voris HK. The role of sea snakes (Hydrophiidae) in the trophic structure of coastal ocean communities. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of India. 1972;14:429–442. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Rasmussen AR. A cladistic analysis of Hydrophis subgenus Chitulia (McDowell, 1972) (Serpentes, Hydrophiidae). Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 1994;111:161–178. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Slowinski JB. The Interrelationships of Laticaudine Sea Snakes Based on the Amino Acid Sequences of Short-Chain Neurotoxins. Copeia 1989. 1989:783–788. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Golay P, Smith HM, Broadley DG, Dixon JR, McCarthy C, et al. Schweize: Herpetological Data Centre, Azemiops; 1993. Endoglyphs and other major venomous snakes of the world. A checklist. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Rasmussen AR, Ineich I. Sea snakes of New Caledonia and surrounding waters (Serpentes: Elapidae): first report on the occurrence of Lapemis curtus and description of a new species from the genus Hydrophis. Hamadryad. 2000;25:91–99. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Rasmussen AR, Gravlund P, van Nguyên C, Chanhome L. A resurrection of Hydrophis pachycercos Fischer 1855 (Serpentes: Elapidae) with a new neotype from Vietnamese waters. Hamadryad. 2007;31:288–298. [Google Scholar]
- 64.McCarthy CJ. Relationships of the laticaudine sea snakes (Serpentes: Elapidae: Laticaudinae). Bulletin of the British Museum Natural History (Zoology) 1986;50:127–161. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Volsøe H. The sea-snakes of the Iranian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. Danish Scientific Investigation in Iran. 1939;1:9–45. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Voris HK, Voris HH. Feeding Strategies in Marine Snakes: An Analysis of Evolutionary, Morphological, Behavioral and Ecological Relationships. American Zoologist. 1983;23:411–425. [Google Scholar]
- 67.McCosker JE. Feeding behavior of Indo-Australian Hydrophiidae. In: Dunson WA, editor. The Biology of Sea Snakes. London & Tokyo, Baltimore: 1975. pp. 217–232. [Google Scholar]
- 68.Rasmussen AR. An analysis of Hydrophis ornatus (Gray), H. lamberti Smith, and H. inornatus (Gray)(Hydrophiidae, Serpentes) based on samples from various localities, with remarks on feeding and breeding biology of H. ornatus. Amphibia-Reptilia. 1989;10:397–417. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Rasmussen AR. Rediscovery and redescription of Hydrophis bituberculatus Peters, 1872 (Serpentes: Hydrophidae). Herpetologica. 1992;48:85–97. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Rasmussen AR. The status of the Persian Gulf Sea Snake Hydrophis lapemoides (Gray, 1849)(Serpentes, Hydrophiidae). Bulletin of Natural History Museum (zoology), London. 1993;59:97–105. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Karthikeyan R, Balasubramanian T. Feeding and reproductive behavior of captive sea snakes Hydrophis cyanocinctus. Applied Herpetology. 2008;5:75–80. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Brischoux F, Bonnet X, Shine R. Conflicts between feeding and reproduction in amphibious snakes (sea kraits, Laticauda spp.). Austral Ecology 2010 [Google Scholar]
- 73.Ineich I, Bonnet X, Brischoux F, Kulbicki M, Seret B, et al. Anguilliform fishes and sea kraits: neglected predators in coral-reef ecosystems. Marine Biology. 2007;151:793–802. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Greer AE. Sydney New South Wales, Australia: Surrey Beatty and Sons; 1997. The biology and evolution of Australian snakes. [Google Scholar]
- 75.Bergman AM. The Breeding Habits of Sea Snakes. Copeia 1943. 1943:156–160. [Google Scholar]
- 76.Tu MC, Fong SC, Lue KY. Reproductive Biology of the Sea Snake, Laticauda semifasciata, in Taiwan. Journal of Herpetology. 1990;24:119–126. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Fry GC, Milton DA, Wassenberg TJ. The reproductive biology and diet of sea snake bycatch of prawn trawling in northern Australia: characteristics important for assessing the impacts on populations. Pacific conservation biology. 2001;7:55–73. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Gorman GC, Licht P, McCollum F. Annual Reproductive Patterns in Three Species of Marine Snakes from the Central Phillippines. Journal of Herpetology. 1981;15:335–354. [Google Scholar]
- 79.Lemen CA, Voris HK. A Comparison of Reproductive Strategies Among Marine Snakes. The Journal of Animal Ecology. 1981;50:89–101. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Masunaga G, Matsuura R, Yoshino T, Ota H. Reproductive biology of the viviparous sea snake Emydocephalus ijimae(Reptilia: Elapidae: Hydrophiinae) under a seasonal environment in the NorthernHemisphere. Herpetological journal. 2003;13:113–119. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Shine R. Review Paper. Reproductive Strategies in Snakes. Proceedings: Biological Sciences. 2003;270:995–1004. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2002.2307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Ward TM. Age structures and reproductive patterns of two species of sea snake, Lapemis hardwickii Grey (1836) and Hydrophis elegans (Grey 1842), incidentally captured by prawn trawlers in northern Australia. Marine and Freshwater Research. 2001;52:193–203. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Voris HK, Jayne BC. Growth, Reproduction and Population Structure of a Marine Snake, Enhydrina schistose (Hydrophiidae). Copeia 1979. 1979:307–318. [Google Scholar]
- 84.Punay EY. Commercial sea snake fisheries in the Philippines. In: Dunson WA, editor. The Biology of Sea Snakes. London & Tokyo, Baltimor: 1975. pp. 417–462. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Mao SH, Chen BY. Sea snakes of Taiwan. The National Science Council Special publication. 1980;4:1–64. [Google Scholar]
- 86.Heatwole H. Marine Snakes: Are They a Sustainable Resource? Wildlife Society Bulletin. 1997;25:766–772. [Google Scholar]
- 87.Bussarawit S, Rasmussen AR, Andersen M. A preliminary study on sea snakes from Phuket Habour Phuket Island, Thailand. Natural History Bulletin of the Siam Society. 1989;37:209–225. [Google Scholar]
- 88.Bacolod PT. The biology of some commercially important species of sea snakes (Hydrophiidae) in the Visayas Sea. The Philippine Scientist. 1990;27:61–88. [Google Scholar]
- 89.Ward TM. Sea snake by-catch of prawn trawlers on the northern Australian continental shelf. Marine and Freshwater Research. 1996;47:631–635. [Google Scholar]
- 90.Brewer D, Heales D, Milton D, Dell Q, Fry G, et al. The impact of turtle excluder devices and bycatch reduction devices on diverse tropical marine communities in Australia's northern prawn trawl fishery. Fisheries Research. 2006;81:176–188. [Google Scholar]
- 91.Brewer D, Rawlinson N, Eayrs S, Burridge C. An assessment of bycatch reduction devices in a tropical Australian prawn trawl fishery. Fisheries Research. 1998;36:195–215. [Google Scholar]
- 92.Tonks ML, Griffiths SP, Heales DS, Brewer DT, Dell Q. Species composition and temporal variation of prawn trawl bycatch in the Joseph Bonaparte Gulf, northwestern Australia. Fisheries Research. 2008;89:276–293. [Google Scholar]
- 93.Wassenberg TJ, Milton DA, Burridge CY. Survival rates of sea snakes caught by demersal trawlers in northern and eastern Australia. Biological Conservation. 2001;100:271–280. [Google Scholar]
- 94.Wassenberg TJ, Salini JP, Heatwole H, Kerr JD. Incidental capture of sea-snakes (Hydrophiidae) by prawn trawlers in the Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia . Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research. 1994;45:429–443. [Google Scholar]
- 95.Ward TM. Factors affecting the catch rates and relative abundance of sea snakes in the by-catch of trawlers targeting tiger and endeavour prawns on the northern Australian continental shelf. Marine and Freshwater Research. 2000;51:155–164. [Google Scholar]
- 96.Heales DS, Gregor R, Wakeford J, Wang YG, Yarrow J, et al. Tropical prawn trawl bycatch of fish and seasnakes reduced by Yarrow Fisheye Bycatch Reduction Device. Fisheries Research. 2008;89:76–83. [Google Scholar]
- 97.Lobo AS. The Bycatch problem. Resonance. 2007;12:60–70. [Google Scholar]
- 98.Rasmussen AR, Elmberg J, Gravlund P, Ineich I. Sea snakes (subfamilies Hydrophiinae and Laticaudinae) in Vietnam: a comprehensive checklist and an updated identification key. Zootaxa. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.3869.4.1. (In press) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Taylor EH. New and Rare Oriental Serpents. Copeia 1963. 1963:429–433. [Google Scholar]
- 100.Smith MA. The sea snakes (Hydrophiidae). Dana-Report. 1935;8:1–6. [Google Scholar]
- 101.Guinea ML, Whiting SD. Insights into the distribution and abundance of sea snakes at Ashmore Reef. The Beagle. 2005;1:199–206. [Google Scholar]
- 102.Vidal N RJ, Couloux A, Hedges SB. Snakes (Serpentes). Timetree of Life Chronology 2009 [Google Scholar]
- 103.Heatwole H. Malabar, FL: Krieger; 1999. Sea Snakes. vi, 148, 112 plates. p. [Google Scholar]
- 104.Shine R. Ecology of a low-energy specialist: food habits and reproductive biology of the Arafura Filesnake. Copeia 1986. 1986:424–437. [Google Scholar]
- 105.Vincent SE, Shine R, Brown GP. Does foraging mode influence sensory modalities for prey detection in male and female filesnakes, Acrochordus arafurae. Animal Behaviour. 2005;70:715–721. [Google Scholar]
- 106.Povel D, Van Der Kooij J. Scale Sensillae of the File Snake (Serpentes: Acrochordidae) and Some Other Aquatic and Burrowing Snakes. Netherlands Journal of Zoology. Netherlands Journal of Zoology. 1996;47:443–456. [Google Scholar]
- 107.Voris HK, Murphy JC. Prey and predators of homalopsine snakes. Journal of Natural History. 2002;36:1621–1632. [Google Scholar]
- 108.Alfaro ME, Karns DR, Voris HK, Abernathy E, Sellins SL. Phylogeny of Cerberus (Serpentes: Homalopsinae) and phylogeny of Cerberus rynchops: diversification of a coastal marine snake in Southeast Asia. Journal of Biogeography. 2004;31:1277–1292. [Google Scholar]
- 109.Murphy JC. Malabar: Krieger Publishin Company; 2007. Homalopsid Snakes, Evolution in the Mud.249 [Google Scholar]
- 110.Karns DR VH, Goodwin TG. Ecology of Oriental-Australian rear-fanged water snakes (Colubridae: Homalopsidae) in the Pasir Ris Park Mangrove Forest, Singapore. The Raffles Bulletin of Zoology. 2002;50:487–498. [Google Scholar]
- 111.Schleich HH, Kästle K, Kabisch K. Koenigstein: Koeltz Scientific Books; 1996. Amphibians and Reptiles of North Africa, Biology, Systematics, Field Guide. [Google Scholar]
- 112.Luiselli L, Angelici F, Di Vittorio M, Spinnato A, Politano E. Analysis of a herpetofaunal community from an altered marshy area in Sicily; with special remarks on habitat use (niche breadth and overlap), relative abundance of lizards and snakes, and the correlation between predator abundance and tail loss in lizards. Contributions to Zoology. 2005;74:41–49. [Google Scholar]
- 113.Sindaco R, Dora G, Razzetti E, F B. Atlas of Italian Amphibians and Reptiles. Societas Herpetologica Italica, Editzioni 2006 [Google Scholar]
- 114.Hansknecht KA, Burghardt GM. Stimulus Control of Lingual Predatory Luring and Related Foraging Tactics of Mangrove Saltmarsh Snakes (Nerodia clarkii compressicauda). Journal of Comparative Psychology. 2010;122:159–165. doi: 10.1037/a0019143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Anderson PK. Variation in Populations of Brown Snakes, Genus Storeria, Bordering the Gulf of Mexico. American Midland Naturalist. 1961;66:235–249. [Google Scholar]
- 116.Neill WT. The occurrence of amphibians and reptiles in saltwater areas, and a bibliography. Bulletin of Marine Science in the Gulf and Caribbean. 1957;8:1–97. [Google Scholar]
- 117.Kelly CMR, Barker NP, Villet MH, Broadley DG. Phylogeny, biogeography and classification of the snake superfamily Elapoidea: a rapid radiation in the late Eocene. . Cladistics. 2009;25:38–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1096-0031.2008.00237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Luiselli L, Akani GC. An investigation into the composition, complexity and functioning of snake communities in the mangroves of south-eastern Nigeria. . African Journal of Ecology. 2002;40:220–227. [Google Scholar]
- 119.Switak KH. The iguanas of the Galapagos Islands. Reptiles. 1996;4:12–30. [Google Scholar]
- 120.Lücker H, Feiler A. Beobachtungen einer Paarung zwischen Meerechsen-Männchen (Amblyrhynchus cristatus) und Landleguan-Weibchen (Conolophus subcristatus) auf Plaza-Sur/Galapagos-Inseln sowie Beobachtungen an einem adulten Gattungshybriden (Amblyrhynchus x Conolophus). Elaphe. 2002;10:49–54. [Google Scholar]
- 121.Rassmann K, Trillmich F, Tautz D. Hybridization between the Galapagos land and marine iguana (Conolophus subcristatus and Amblyrhynchus cristatus) on Plaza Sur. J Zool (London) 1997;242:729–739. [Google Scholar]
- 122.Higgins PJ. The Galapagos Iguanas: Models of Reptilian Differentiation. BioScience. 1978;28:512–515. [Google Scholar]
- 123.Dunson WA. Electrolyte excretion by the salt gland of the Galapagos marine iguana. Am J Physiol. 1969;216:995–1002. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.4.995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Werneburg I, Sanchez-Villagra MR. Timing of organogenesis support basal position of turtles in the amniote tree of life. BMC Evol Biol. 2009;9:82. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-9-82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Zug GR, Vitt LJ, Caldwell JP. London, San Diego: Academic Press; 2001. Herpetology. [Google Scholar]
- 126.McCord WP, Joseph-Ouni M. Sea turtles of the world. Reptilia (GB); 2003. Chelonian Illustrations #8. pp. 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- 127.Pyron RA, Burbrink FT, Colli GR, de Oca AN, Vitt LJ, et al. The phylogeny of advanced snakes (Colubroidea), with discovery of a new subfamily and comparison of support methods for likelihood trees. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2011;58:329–342. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2010.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]