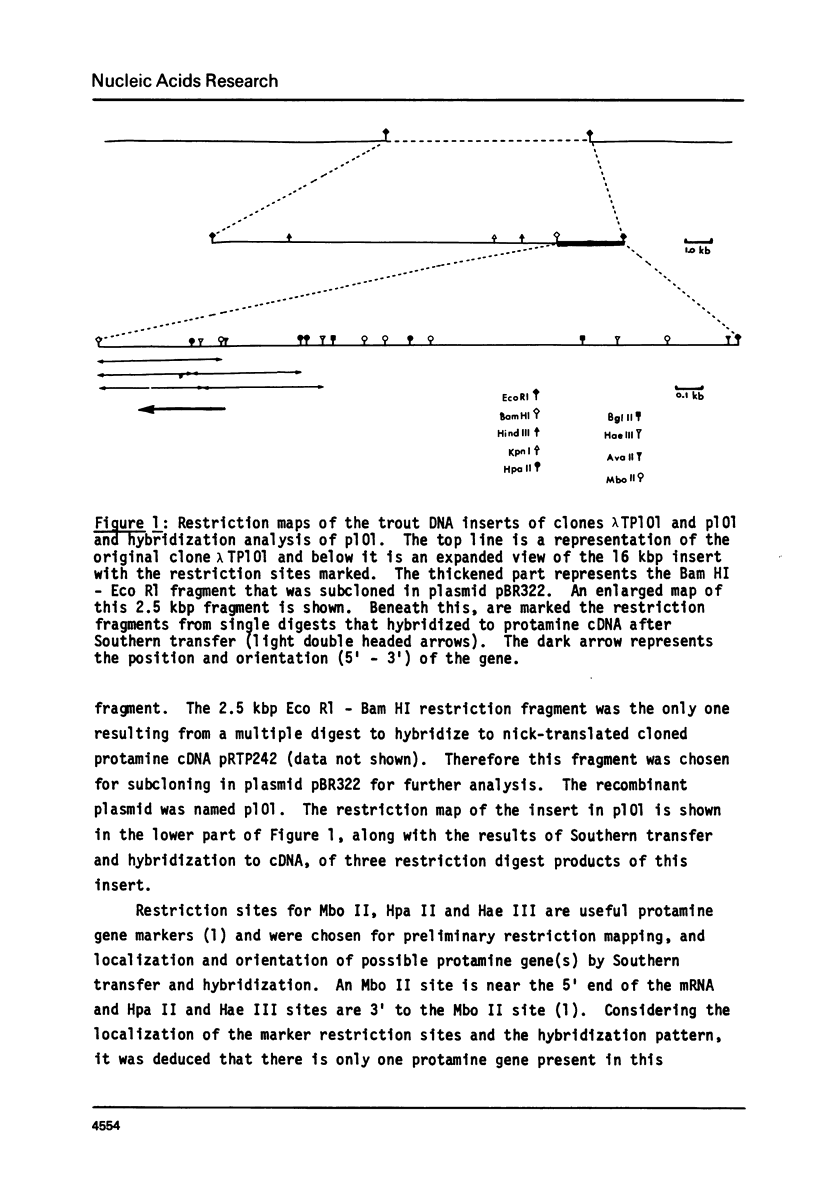
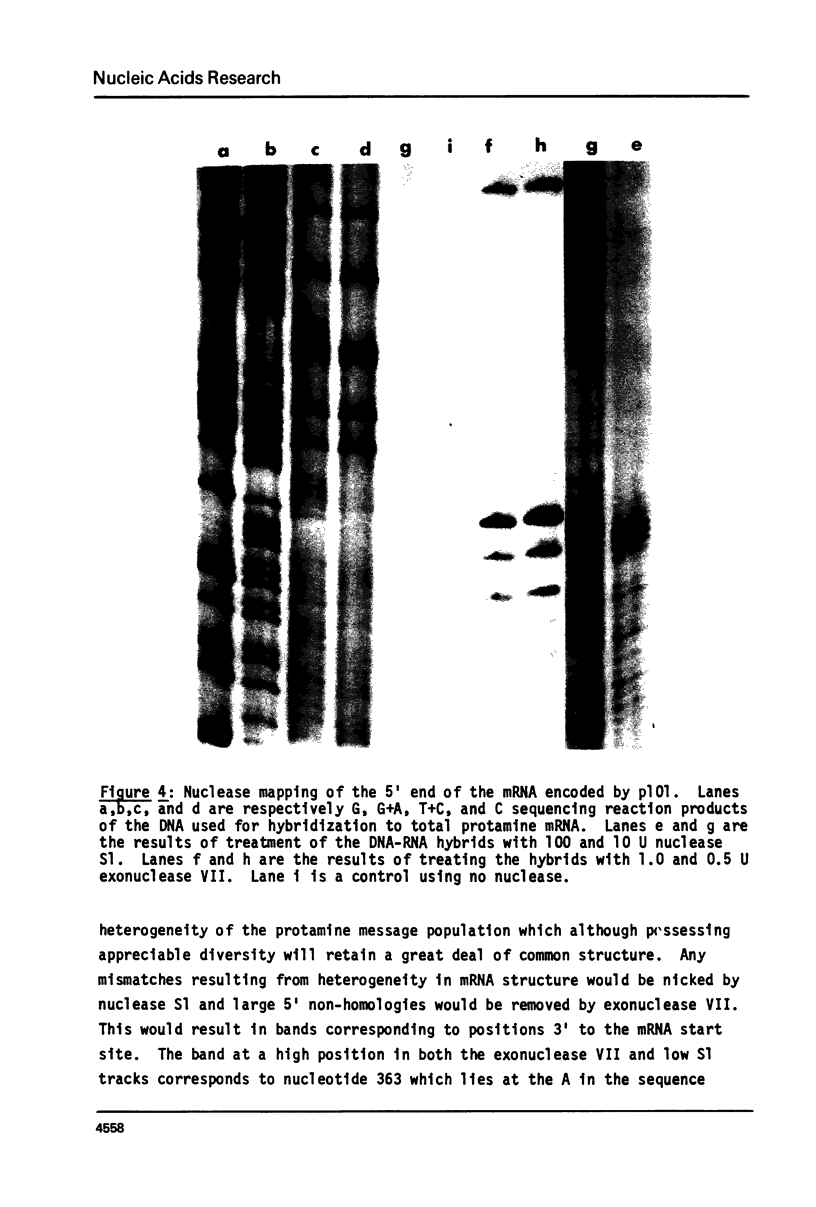
Abstract
We have isolated, using nick-translated cloned protamine cDNA's as probes, several genomic clones containing protamine gene sequences from a Charon 4A library of Eco R1 digested rainbow trout (Salmo gairdnerii) DNA. One clone was chosen for detailed study and the 2.5 kbp Bam HI-Eco R1 restriction fragment containing the gene was subcloned in the plasmid pBR322. A 920 bp Bg1 II - Bam HI restriction fragment contains a sequence coding for protamine component CII as well as regions 5' and 3' to the mRNA coding portion. Present in the region 5' to the mRNA coding sequence are the promoter associated signals "TATA" box and "CAAT" box. The 5' untranslated region of the mRNA whose length and sequence were not established from the cDNA clones (1) was determined by nuclease mapping and starts within a sequence similar to the "capping signal" found in other genes. The protamine gene for CII contains no introns, a situation common to most histone genes, but, unlike the histone genes does not occur close to other protamine genes in a "cluster".
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Portmann R., Irminger J. C., Birnstiel M. L. Ubiquitous and gene-specific regulatory 5' sequences in a sea urchin histone DNA clone coding for histone protein variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):957–977. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. L., Dixon G. H., Simoncsits A., Brownlee G. C. Sequences of large T1 ribonuclease-resistant oligoribonucleotides from protamine mRNA: the overall architecture of protamine mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2323–2345. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan M., Sugarman B. J., Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D. Chromosomal arrangement of the chicken beta-type globin genes. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):669–677. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedamu L., Dixon G. H. Heterogeneity of biologically active deadenylated protamine mRNA components isolated from rainbow trout testes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3661–3672. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedamu L., Iatrou K., Dixon G. H. A simple procedure for the isolation and purification of protamine messenger ribonucleic acid from trout testis. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):589–599. doi: 10.1042/bj1710589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedamu L., Wosnick M. A., Connor W., Watson D. C., Dixon G. H., Iatrou K. Molecular analysis of the protamine multi-gene family in rainbow trout testis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1463–1482. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R. Sequence divergence of rainbow trout protamine mRNAs; comparison of coding and non-coding nucleotide sequences in three protamine cDNA plasmids. Nature. 1979 Jun 28;279(5716):809–811. doi: 10.1038/279809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Kingsbury D. T., Helinski D. R. Stimulation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid replication and catabolite repression of the plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):577–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.577-591.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Mechanism of mRNA recognition by eukaryotic ribosomes during initiation of protein synthesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:81–123. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louie A. J., Dixon G. H. Trout testis cells. II. Synthesis and phosphorylation of histones and protamines in different cell types. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 10;247(17):5498–5505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marushige K., Dixon G. H. Developmental changes in chromosomal composition and template activity during spermatogenesis in trout testis. Dev Biol. 1969 Apr;19(4):397–414. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(69)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Taniguchi T. Structure of a chromosomal gene for human interferon beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5305–5309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Muramatsu M. Number and frequency of protamine genes in rainbow trout testis. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 12;17(25):5510–5515. doi: 10.1021/bi00618a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Saito T., Muramatsu M. Closely related mRNA sequences of protamines in rainbow trout testis. J Biochem. 1981 Jun;89(6):1863–1868. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Berk A. J., Berget S. M. Transcription maps of adenovirus. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):750–768. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Speculations on RNA splicing. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. J., Sharp J. A., Summers W. C. Nucleotide sequence of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1441–1445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dongen W., de Laaf L., Zaal R., Moorman A., Destrée O. The organization of the histone genes in the genome of Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2297–2311. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]