Abstract
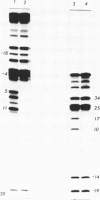
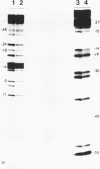
Hedamycin forms a stable complex with DNA and introduces alkali labile linkages in the DNA. These labile linkages are located at deoxyguanosine residues and are cleaved by the treatment used for breakage at bases alkylated by dimethyl sulfate. The reaction of hedamycin with all G residues in the chain is not uniform, and certain positions, particularily those in TG tracts, are especially reactive. The reaction of hedamycin with DNA can be inhibited by ethidium bromide, suggesting that intercalation is important in positioning the reactive group of hedamycin near to the base which is modified. The low amount of hedamycin needed to produce observable breakage, its specificity for reaction with DNA and its ability to react with DNA under mild conditions make it suitable for use as a probe of protein-DNA complexes. This was shown by the ability of lac repressor and RNA polymerase to block reaction of hedamycin with the DNA of the lac regulatory region.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradner W. T., Heinemann B., Gourevitch A. Hedamycin, a new antitumor antibiotic. II. Biological properties. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1966;6:613–618. doi: 10.1128/AAC.6.5.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuVernay V. H., Jr, Pachter J. A., Crooke S. T. DNA binding studies on several new anthracycline antitumor antibiotics II. The importance of the carbomethoxy-group as position-10 of the class II anthracycline molecule. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;16(2):623–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jernigan H. M., Jr, Irvin J. L., White J. R. Binding of hedamycin to deoxyribonucleic acid and chromatin of testis and liver. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 3;17(20):4232–4239. doi: 10.1021/bi00613a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzawa Y., Oki T., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Structure-activity relationships of anthracyclines relative to cytotoxicity and effects on macromolecular synthesis in L1210 leukemia cells. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1981 Dec;34(12):1596–1607. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.34.1596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mong S., Strong J. E., Crooke S. T. Interaction of covalently closed circular PM-2 DNA and hedamycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 14;88(1):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91721-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuss M. E., James T. L., Apple M. A., Kollman P. A. An NMR study of the interaction of daunomycin with dinucleotides and dinucleoside phosphates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 26;609(1):136–147. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pigram W. J., Fuller W., Hamilton L. D. Stereochemistry of intercalation: interaction of daunomycin with DNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 5;235(53):17–19. doi: 10.1038/newbio235017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. R., Bennett G. N. Characterization of the beta-lactamase promoter of pBR322. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 11;9(11):2517–2533. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.11.2517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Crook K. E., Jr, Bush J. A. Hedamycin, a new antitumor antibiotic. I. Production, isolation, and characterization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1966;6:606–612. doi: 10.1128/AAC.6.5.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B. The chemical effects of nucleic acid alkylation and their relation to mutagenesis and carcinogenesis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1975;15(0):219–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha B. K. Binding specificity of chemically and enzymatically activated anthracycline anticancer agents to nucleic acids. Chem Biol Interact. 1980 Apr;30(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(80)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. pBR322 restriction map derived from the DNA sequence: accurate DNA size markers up to 4361 nucleotide pairs long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2721–2728. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yielding K. L., Yielding L. W. Photoaffinity labeling of DNA. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;346:368–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb22108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]