Abstract
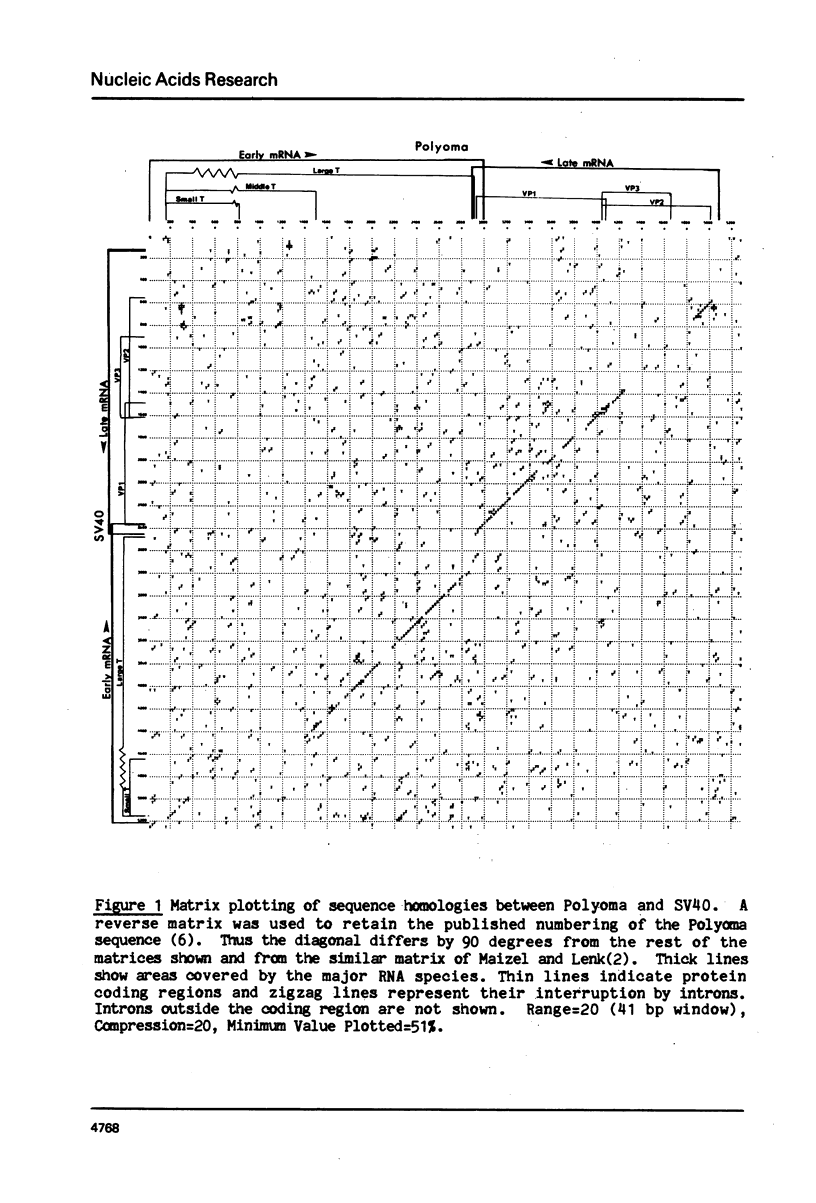
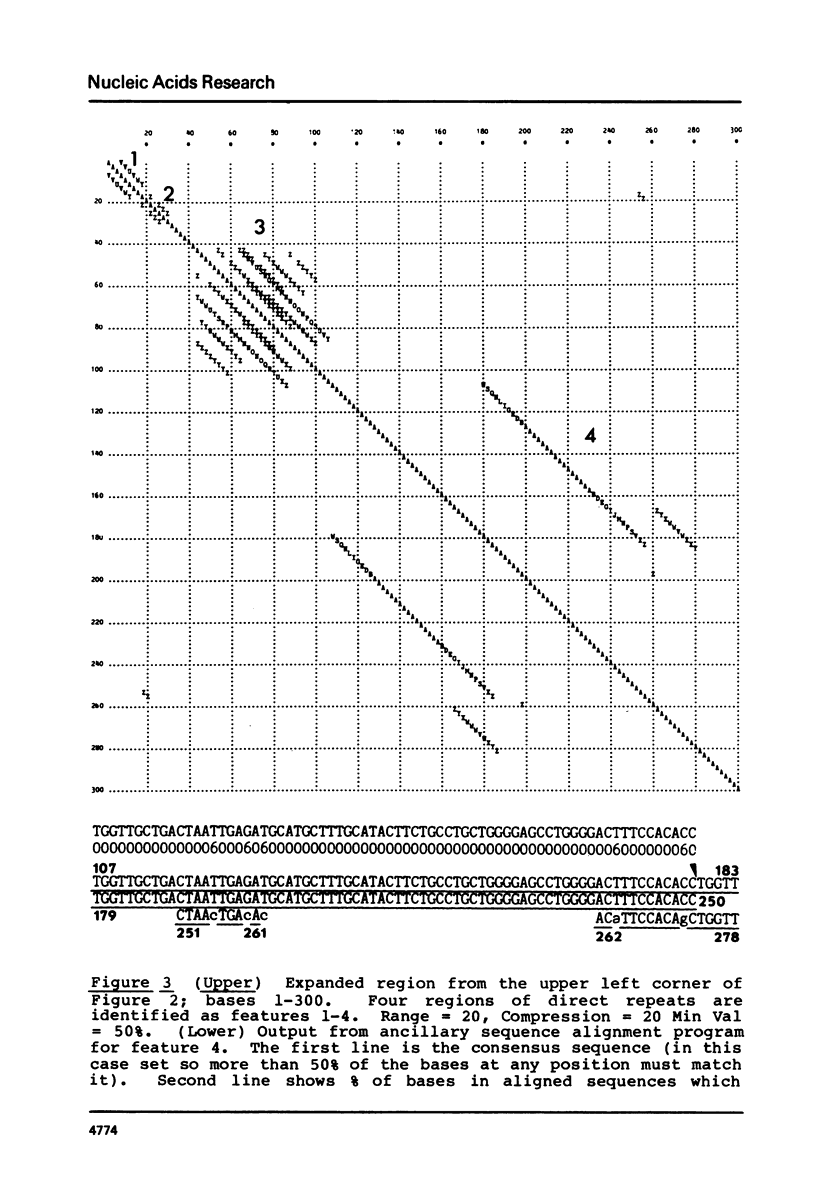
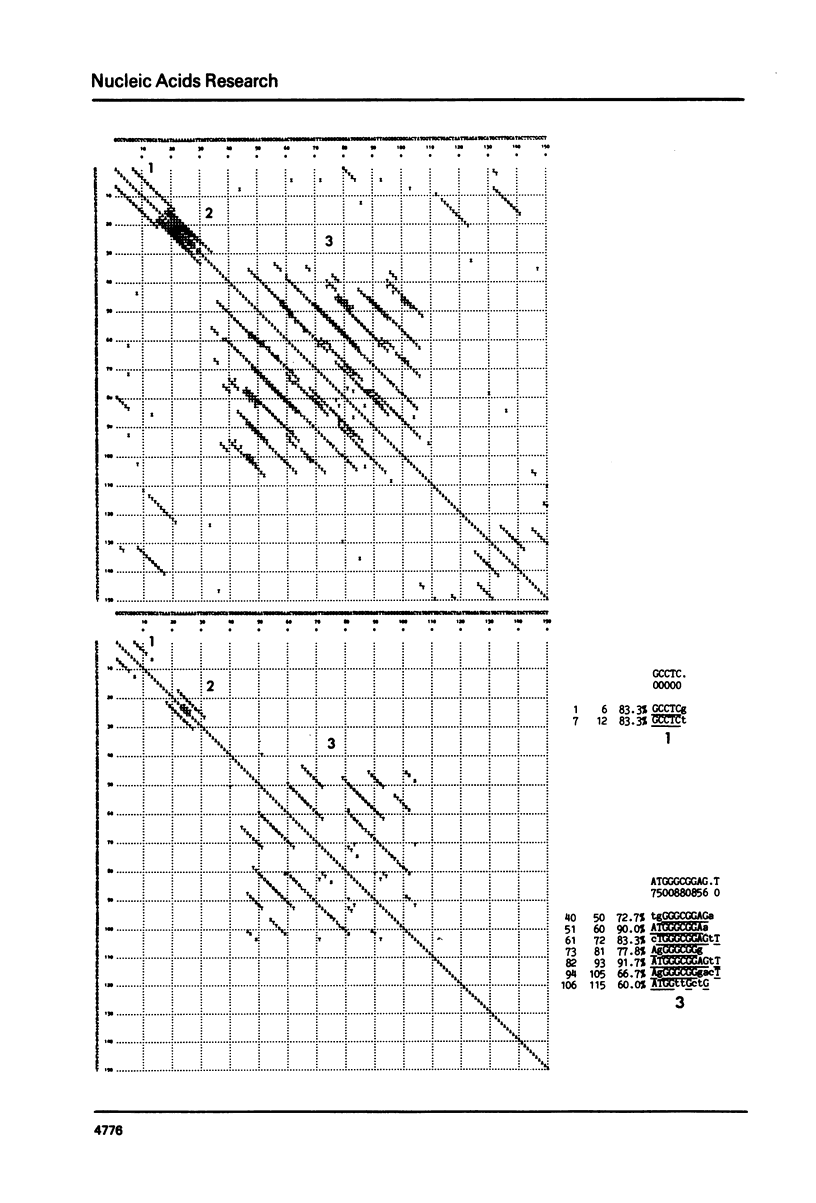
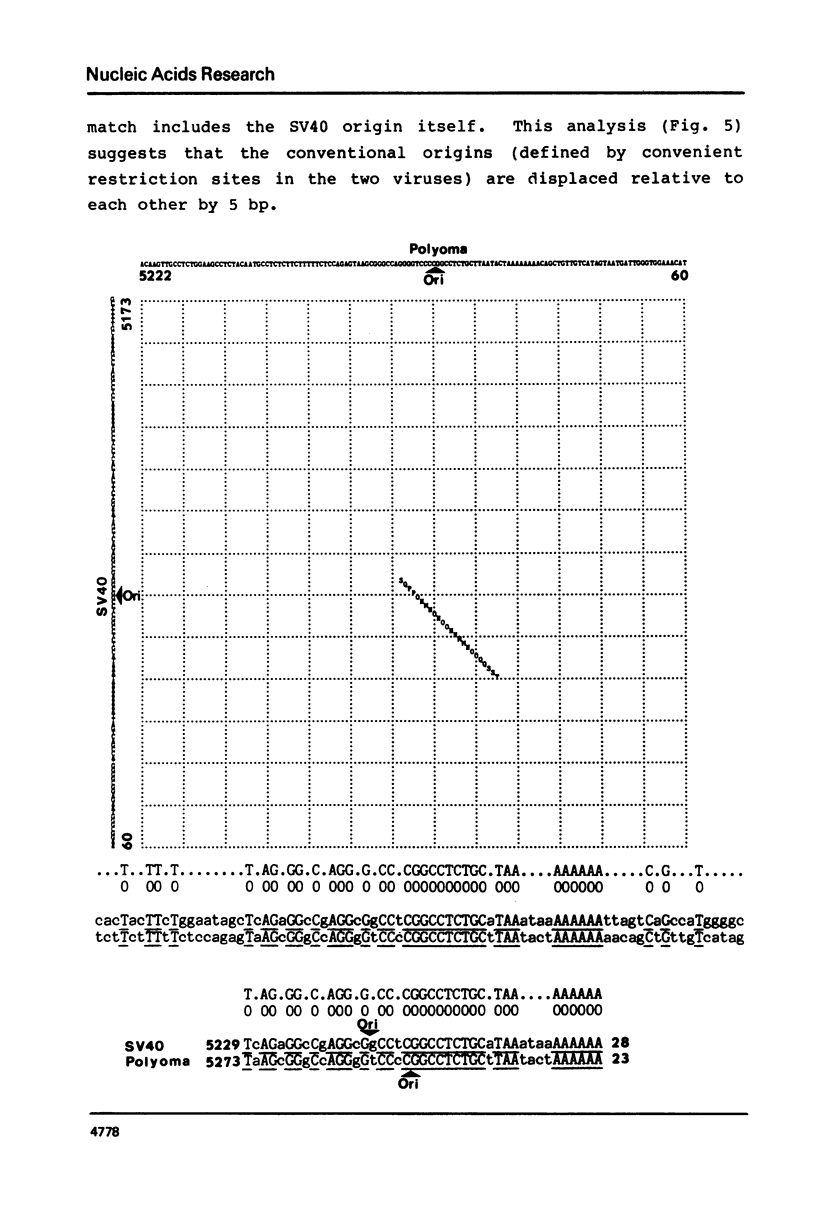
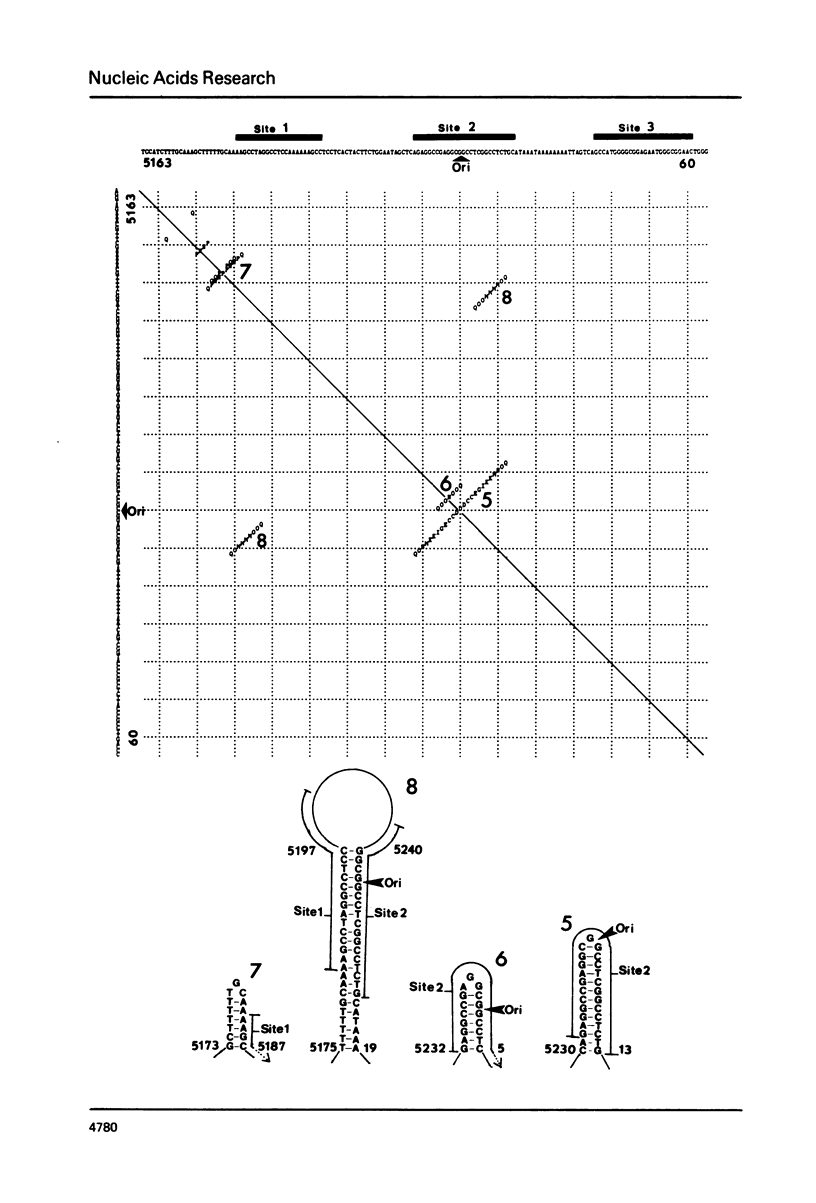
We present a new homology matrix program which owes its basic conception to the two-dimensional dot matrices previously described (1,2), but has important improvements and new features. It scores sequence homology over an adjustable range and plots the scores which are above an operator-determined filtration level. Its powerful noise-filtration system, capacity for compression without much loss of information, and speed of execution make this program a valuable tool in the analysis of homologies, internal direct repeats and reverse repeats, including palindromic sequences. The properties of the program are exemplified by analysis of SV40 and polyoma DNA sequences.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. Cloned human and mouse kappa immunoglobulin constant and J region genes conserve homology in functional segments. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkel D. A., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. The evolution and sequence comparison of two recently diverged mouse chromosomal beta--globin genes. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):865–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr, Lenk R. P. Enhanced graphic matrix analysis of nucleic acid and protein sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7665–7669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny J. Matrix program to analyze primary structure homology. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):127–131. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C. L., Korn L. J. Computer analysis of nucleic acids and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):595–609. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Walsh J. E., Griffin B. E. Coding potential and regulatory signals of the polyoma virus genome. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):445–453. doi: 10.1038/283445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Frelinger J. G., Fisher D., Hunkapiller T., Pereira D., Weissman S. M., Uehara H., Nathenson S., Hood L. Three cDNA clones encoding mouse transplantation antigens: homology to immunoglobulin genes. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90508-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. Protein-DNA interactions at the origin of simian virus 40 DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):655–661. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



