Abstract
The title compound, C16H12BClN2, is one in a series of diazaborinanes, derived from 1,8-diaminonaphthalene, featuring substitution at the 1, 2 and 3 positions in the nitrogen-boron heterocycle. The structure deviates from planarity, the torsion angle subtended by the p-chlorophenyl ring relative to the nitrogen–boron heterocycle being −44-.3(3)°. The molecules form infinite chains with strong interactions between the vacant pz orbital of the B atom and the π-system of an adjacent molecule. The distance between the B atom and the 10-atom centroid of an adjacent naphthalene ring is 3.381 (4) Å. One N-H H atom is weakly hydrogen bonded to the Cl atom of an adjacent molecule. This combination of intermolecular interactions leads to the formation of an infinite two-dimensional network perpendicular to the c axis.
Related literature
For the synthesis of related compounds, see: Letsinger & Hamilton (1958 ▶); Pailer & Fenzl (1961 ▶); Kaupp et al. (2003 ▶); Slabber 2011 ▶. For single-crystal X-ray structures and luminescence studies of related compounds, see: Weber, et al. (2009 ▶).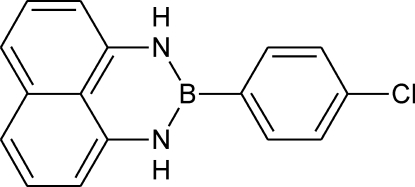
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H12BClN2
M r = 278.54
Monoclinic,
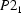
a = 4.7165 (2) Å
b = 10.2815 (4) Å
c = 13.5711 (6) Å
β = 96.555 (4)°
V = 653.79 (5) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.28 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.50 × 0.15 × 0.07 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur 2 CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2003 ▶) T min = 0.896, T max = 0.981
4902 measured reflections
2286 independent reflections
2011 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.027
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.039
wR(F 2) = 0.098
S = 1.00
2286 reflections
189 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 924 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.05 (7)
Data collection: CrysAlis CCD (Oxford Diffraction, 2008 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis CCD; data reduction: CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811025487/om2441sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811025487/om2441Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811025487/om2441Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2⋯Cli | 0.78 (2) | 2.93 (2) | 3.666 (2) | 158 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i) 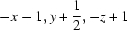 .
.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the University of KwaZulu-Natal and the National Research Foundation for their support and funding.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
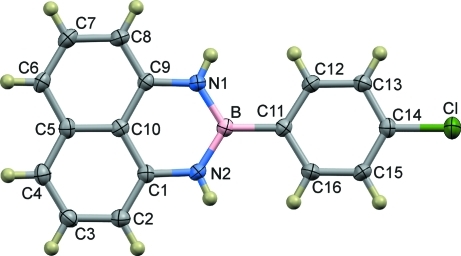
The structure of the title compound is nominally planar with a slight rotation of the p-chlorophenyl ring relative to the naphthalene rings and boron-nitrogen heterocycle. The N1—B—C11—C12 torsion angle is -4.3 (3)° (refer to Figure 1 for the atom numbering scheme). The orientation of the heterocycle relative to the diazaborolyl groups is critical, since as the rings approach co-planarity there is more effective overlap of the π-systems of the boron atom and the carbon atom to which it is attached. The bond lengths N1—B and N2—B are approximately equal, measuring 1.416 (3) and 1.405 (3) Å, respectively, while the B—C11 bond length is 1.568 (4) Å. The Cl—C14 bond length is 1.736 (2) Å. The N1—B—N2 bond angle is 115.6 (2)°, the N1—B—C11 and N2—B—C11 bond angles are equal, both measuring 122.2 (2)°. These bond length and angles are comparable to those of previously reported diazaborolyl systems (Weber et al., 2009).
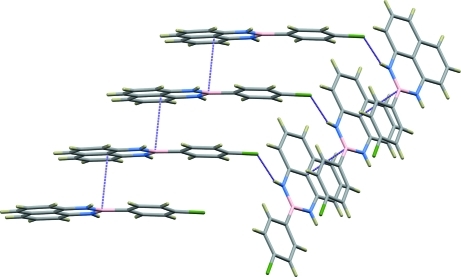
Examination of the title compound showed that there is a short contact between the boron atom and the naphthalene rings of an adjacent molecule. The distance from the boron atom to the 10-atom naphthalene centroid is 3.381 (4) Å. These B-π interaction link the molecules, forming infinite, one-dimensional chains. Adjacent one dimensional chains are then weakly hydrogen-bonded together by a N-H hydrogen atom and the chlorine atom of the adjacent molecule. These hydrogen bonds are likely to be very weak as they are only nominally shorter than the sum of the van der Waals radii (0.022 Å shorter) (Table 1). The combination of intermolecular interactions results in the formation of infinite, two-dimensional sheets (Figure 2). The two-dimensional sheet runs perpendicular to the c axis.
Experimental
To a solution of 1,8-diaminonaphthalene in toluene (4.11 mmol in 50 ml, 0.82M) (Letsinger & Hamilton, 1958; Slabber, 2011) was added the 3-chlorophenylboronic acid (4.11 mmol) in one portion. The round-bottomed flask was equipped with a Dean and Stark trap, and the solution was stirred and heated to reflux for 3 h. The solvent was removed in vacuo and column chromatography of the crude solid using silica gel as the stationary phase and eluting with CH2Cl2 yielded pale green crystalline material upon evaporation of the eluent with a yield of 66%. Recrystallization of the material from dichloromethane yielded crystals suitable for single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis were grown.
Refinement
The positions of all hydrogen atoms were calculated using the standard riding model of SHELXL97. with C—H(aromatic) distances of 0.93 Å and Uiso = 1.2 Ueq. The only exception is the NH hydrogen atoms which were located in the difference Fourier map and allowed to refine isotropically.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Thermal ellipsoid plot of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinane (50% probability surfaces). Hydrogen atoms have been rendered as spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
Two-dimensional network of the title compound perpendicular to the c axis. The network is supported by B···π interactions and hydrogen bonds between the terminal chlorine atom and the N-H hydrogen, as indicated.
Crystal data
| C16H12BClN2 | F(000) = 288 |
| Mr = 278.54 | Dx = 1.415 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2yb | Cell parameters from 2982 reflections |
| a = 4.7165 (2) Å | θ = 3.6–32.0° |
| b = 10.2815 (4) Å | µ = 0.28 mm−1 |
| c = 13.5711 (6) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 96.555 (4)° | Plate, colourless |
| V = 653.79 (5) Å3 | 0.50 × 0.15 × 0.07 mm |
| Z = 2 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur 2 CCD diffractometer | 2286 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2011 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.027 |
| Detector resolution: 8.4190 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.1°, θmin = 3.6° |
| ω scans | h = −5→5 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2003) | k = −12→11 |
| Tmin = 0.896, Tmax = 0.981 | l = −16→16 |
| 4902 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.098 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0669P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.00 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2286 reflections | Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3 |
| 189 parameters | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 924 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.05 (7) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl | −1.03675 (12) | 0.41269 (9) | 0.42497 (4) | 0.0546 (2) | |
| N1 | −0.1813 (4) | 0.7869 (2) | 0.15026 (15) | 0.0391 (4) | |
| H1 | −0.257 (5) | 0.732 (3) | 0.1114 (18) | 0.048 (8)* | |
| N2 | −0.1196 (4) | 0.9013 (2) | 0.30427 (13) | 0.0398 (4) | |
| H2 | −0.134 (5) | 0.911 (3) | 0.3607 (17) | 0.047 (7)* | |
| C1 | 0.0738 (5) | 0.9863 (2) | 0.26954 (16) | 0.0362 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.2031 (5) | 1.0847 (2) | 0.32771 (18) | 0.0462 (6) | |
| H2A | 0.1624 | 1.0952 | 0.3927 | 0.055* | |
| C3 | 0.3950 (6) | 1.1682 (2) | 0.28863 (19) | 0.0498 (6) | |
| H3 | 0.4782 | 1.2354 | 0.3278 | 0.060* | |
| C4 | 0.4629 (5) | 1.1536 (2) | 0.19447 (19) | 0.0479 (6) | |
| H4 | 0.5938 | 1.2097 | 0.1706 | 0.057* | |
| C5 | 0.3366 (5) | 1.0540 (2) | 0.13264 (16) | 0.0387 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.4036 (5) | 1.0340 (2) | 0.03481 (17) | 0.0447 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.5346 | 1.0879 | 0.0087 | 0.054* | |
| C7 | 0.2761 (5) | 0.9356 (3) | −0.02132 (16) | 0.0489 (6) | |
| H7 | 0.3219 | 0.9238 | −0.0856 | 0.059* | |
| C8 | 0.0804 (5) | 0.8527 (2) | 0.01465 (17) | 0.0463 (6) | |
| H8 | −0.0039 | 0.7867 | −0.0254 | 0.056* | |
| C9 | 0.0105 (4) | 0.8681 (2) | 0.11029 (16) | 0.0359 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.1391 (4) | 0.9690 (2) | 0.17085 (16) | 0.0350 (5) | |
| C11 | −0.4634 (5) | 0.7024 (2) | 0.29241 (16) | 0.0358 (5) | |
| C12 | −0.6037 (5) | 0.6040 (2) | 0.23650 (17) | 0.0440 (6) | |
| H11 | −0.5771 | 0.5972 | 0.1698 | 0.053* | |
| C13 | −0.7810 (5) | 0.5156 (2) | 0.27541 (17) | 0.0455 (6) | |
| H12 | −0.8725 | 0.4510 | 0.2357 | 0.055* | |
| C14 | −0.8199 (4) | 0.5247 (2) | 0.37392 (17) | 0.0389 (5) | |
| C15 | −0.6900 (5) | 0.6218 (3) | 0.43220 (17) | 0.0471 (6) | |
| H14 | −0.7205 | 0.6287 | 0.4985 | 0.057* | |
| C16 | −0.5137 (5) | 0.7092 (3) | 0.39146 (17) | 0.0485 (6) | |
| H15 | −0.4260 | 0.7746 | 0.4314 | 0.058* | |
| B | −0.2545 (5) | 0.7993 (3) | 0.24819 (18) | 0.0346 (5) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl | 0.0573 (3) | 0.0516 (3) | 0.0563 (3) | −0.0125 (3) | 0.0131 (2) | 0.0070 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0428 (10) | 0.0405 (11) | 0.0344 (10) | −0.0057 (9) | 0.0062 (8) | −0.0030 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0443 (9) | 0.0446 (11) | 0.0319 (9) | −0.0039 (9) | 0.0107 (7) | −0.0019 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0350 (10) | 0.0339 (12) | 0.0398 (11) | 0.0027 (9) | 0.0046 (9) | 0.0023 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0519 (14) | 0.0451 (14) | 0.0420 (13) | −0.0015 (11) | 0.0071 (11) | −0.0053 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0554 (15) | 0.0415 (15) | 0.0511 (16) | −0.0086 (11) | 0.0005 (12) | −0.0048 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0506 (14) | 0.0385 (14) | 0.0547 (15) | −0.0025 (11) | 0.0065 (11) | 0.0089 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0360 (11) | 0.0359 (12) | 0.0437 (12) | 0.0038 (9) | 0.0019 (9) | 0.0091 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0490 (13) | 0.0469 (13) | 0.0395 (13) | 0.0008 (11) | 0.0109 (10) | 0.0118 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0551 (13) | 0.0576 (18) | 0.0356 (11) | 0.0042 (11) | 0.0123 (10) | 0.0064 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0534 (14) | 0.0521 (14) | 0.0342 (12) | −0.0029 (11) | 0.0087 (10) | −0.0059 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0336 (10) | 0.0392 (12) | 0.0353 (11) | 0.0029 (8) | 0.0053 (8) | 0.0033 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0343 (10) | 0.0342 (11) | 0.0361 (11) | 0.0072 (9) | 0.0020 (9) | 0.0033 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0354 (11) | 0.0367 (12) | 0.0354 (11) | 0.0040 (9) | 0.0051 (8) | 0.0037 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0521 (14) | 0.0473 (15) | 0.0337 (12) | −0.0039 (11) | 0.0094 (11) | −0.0010 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0524 (13) | 0.0437 (14) | 0.0397 (13) | −0.0071 (11) | 0.0023 (10) | −0.0035 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0354 (11) | 0.0378 (12) | 0.0435 (13) | 0.0018 (9) | 0.0047 (9) | 0.0058 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0564 (14) | 0.0538 (15) | 0.0325 (12) | −0.0100 (12) | 0.0108 (10) | −0.0030 (11) |
| C16 | 0.0550 (15) | 0.0512 (15) | 0.0399 (13) | −0.0140 (12) | 0.0074 (11) | −0.0092 (12) |
| B | 0.0319 (11) | 0.0361 (13) | 0.0358 (12) | 0.0030 (10) | 0.0037 (9) | 0.0049 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl—C14 | 1.736 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C9 | 1.386 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.386 (3) |
| N1—B | 1.416 (3) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1 | 0.82 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.384 (3) |
| N2—C1 | 1.384 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| N2—B | 1.405 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.416 (3) |
| N2—H2 | 0.78 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.387 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.382 (3) | C11—C16 | 1.393 (3) |
| C1—C10 | 1.419 (3) | C11—B | 1.568 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.396 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.380 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C12—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.361 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.373 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C13—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.411 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.373 (3) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C15—C16 | 1.382 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.414 (3) | C15—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C10 | 1.418 (3) | C16—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.364 (3) | ||
| C9—N1—B | 123.6 (2) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.0 |
| C9—N1—H1 | 114.6 (17) | C8—C9—N1 | 122.3 (2) |
| B—N1—H1 | 121.7 (17) | C8—C9—C10 | 119.74 (19) |
| C1—N2—B | 124.20 (18) | N1—C9—C10 | 117.99 (18) |
| C1—N2—H2 | 113 (2) | C9—C10—C5 | 119.67 (19) |
| B—N2—H2 | 123 (2) | C9—C10—C1 | 120.99 (19) |
| C2—C1—N2 | 122.2 (2) | C5—C10—C1 | 119.3 (2) |
| C2—C1—C10 | 120.1 (2) | C12—C11—C16 | 116.2 (2) |
| N2—C1—C10 | 117.69 (19) | C12—C11—B | 122.39 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.8 (2) | C16—C11—B | 121.4 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 120.1 | C13—C12—C11 | 122.9 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 120.1 | C13—C12—H11 | 118.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.4 (2) | C11—C12—H11 | 118.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.3 | C14—C13—C12 | 118.8 (2) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.3 | C14—C13—H12 | 120.6 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.7 (2) | C12—C13—H12 | 120.6 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C13—C14—C15 | 120.7 (2) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C13—C14—Cl | 119.54 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 122.6 (2) | C15—C14—Cl | 119.78 (18) |
| C4—C5—C10 | 118.7 (2) | C14—C15—C16 | 119.4 (2) |
| C6—C5—C10 | 118.7 (2) | C14—C15—H14 | 120.3 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 120.1 (2) | C16—C15—H14 | 120.3 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.0 | C15—C16—C11 | 122.0 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.0 | C15—C16—H15 | 119.0 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 121.9 (2) | C11—C16—H15 | 119.0 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.1 | N2—B—N1 | 115.57 (19) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.1 | N2—B—C11 | 122.17 (18) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 120.0 (2) | N1—B—C11 | 122.22 (19) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 120.0 | ||
| B—N2—C1—C2 | −179.4 (2) | C6—C5—C10—C1 | 178.8 (2) |
| B—N2—C1—C10 | 0.1 (3) | C2—C1—C10—C9 | 179.5 (2) |
| N2—C1—C2—C3 | −179.5 (2) | N2—C1—C10—C9 | −0.1 (3) |
| C10—C1—C2—C3 | 1.0 (3) | C2—C1—C10—C5 | −0.4 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.3 (4) | N2—C1—C10—C5 | −179.92 (19) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.1 (4) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | −0.9 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −179.1 (2) | B—C11—C12—C13 | 177.9 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C10 | −0.5 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.3 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 179.6 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 1.5 (4) |
| C10—C5—C6—C7 | 0.9 (3) | C12—C13—C14—Cl | −178.80 (19) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −0.2 (4) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −1.4 (4) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.4 (4) | Cl—C14—C15—C16 | 178.9 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9—N1 | −179.2 (2) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.2 (4) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.2 (3) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 0.9 (4) |
| B—N1—C9—C8 | 179.2 (2) | B—C11—C16—C15 | −177.8 (2) |
| B—N1—C9—C10 | −0.2 (3) | C1—N2—B—N1 | −0.2 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10—C5 | 0.5 (3) | C1—N2—B—C11 | 177.6 (2) |
| N1—C9—C10—C5 | 179.96 (18) | C9—N1—B—N2 | 0.2 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10—C1 | −179.3 (2) | C9—N1—B—C11 | −177.60 (19) |
| N1—C9—C10—C1 | 0.1 (3) | C12—C11—B—N2 | 178.0 (2) |
| C4—C5—C10—C9 | −179.77 (19) | C16—C11—B—N2 | −3.3 (3) |
| C6—C5—C10—C9 | −1.1 (3) | C12—C11—B—N1 | −4.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—C10—C1 | 0.1 (3) | C16—C11—B—N1 | 174.4 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2···Cli | 0.78 (2) | 2.93 (2) | 3.666 (2) | 158 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x−1, y+1/2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: OM2441).
References
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Kaupp, G., Naimi-Jamal, M. R. & Stepanenko, V. (2003). Chem. Eur. J. 9, 4156–4160. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Letsinger, R. L. & Hamilton, S. B. (1958). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80, 5412–5413.
- Oxford Diffraction (2008). CrysAlis CCD and CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Pailer, M. & Fenzl, W. (1961). Monatsh. Chem. 92, 1294–1299.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2003). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Slabber, C. A. (2011). MSc thesis, University of KwaZulu Natal, South Africa.
- Weber, L., Werner, V., Fox, M. A., Marder, R. T., Schwedler, S., Brockhinke, A., Stammler, H.-G. & Neumann, B. (2009). Dalton Trans. pp. 1339–1351. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811025487/om2441sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811025487/om2441Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811025487/om2441Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report