Abstract
In the title compound, C18H17N3O4, the amino group of the glycine methyl ester fragment is involved in an intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond. The phenyl and furyl rings form dihedral angles of 10.20 (4) and 54.56°, respectively, with the pyrazole ring. In the crystal, molecules related by translation along the b axis are linked into chains via weak intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For a related structure, see: Zhang et al. (2007 ▶). For details of the synthesis, see: Jensen (1959 ▶). For applications of pyrazolone derivatives in coordination chemistry, see: Casas et al. (2007 ▶). For the antibacterial activity of pyrazolone derivatives, see: Li et al. (2000 ▶); Zhang et al. (2008 ▶).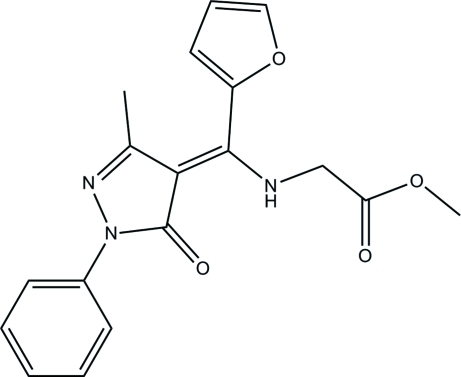
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H17N3O4
M r = 339.35
Triclinic,

a = 7.499 (4) Å
b = 9.503 (5) Å
c = 11.749 (6) Å
α = 96.712 (7)°
β = 91.654 (8)°
γ = 90.337 (7)°
V = 831.2 (7) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.10 mm−1
T = 295 K
0.48 × 0.14 × 0.08 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
6492 measured reflections
2915 independent reflections
1805 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.034
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.051
wR(F 2) = 0.150
S = 1.01
29015 reflections
232 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT-Plus (Bruker, 2005 ▶); data reduction: SAINT-Plus; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811026158/cv5123sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811026158/cv5123Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811026158/cv5123Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3—H3A⋯O1 | 0.97 (3) | 1.89 (3) | 2.704 (3) | 140 (2) |
| C14—H14⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.386 (4) | 164 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the study on structure–activity relationships of helicid analogues.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Pyrazolones constitute an important class of heterocycles due to their properties and applications (Casas et al., 2007). Schiff bases derived from 1-phenyl-3-methyl-4-(2-furoyl)-5-pyrazolone (PMFP) have found extensive application in coordination chemistry and due to their antibacterial activity (Zhang et al., 2007, 2008; Li et al., 2000). In order to expand this field, we present here the title compound (I).
In (I) (Fig. 1), the phenyl ring (C1-C6) is twisted at 10.20 (4)° from the mean plane of pyrazole ring. The pyrazole ring and the O1/C10/C9/C11/N3 mean form a dihedral angle of 5.62 (4)°. The bond length of C9—C11(1.390 (3) Å) between the usual C—C and C=C bonds indicates the delocalization of the electrons. Strong intramolecular hydrogen bond N3—H3A···O1(Table 1) is indicative of the enamine-keto form.
In the crystal structure, molecules related by translation along axis b are linked into chains via weak intermolecular C—H···O hydrogen bonds.
Experimental
PMFP was synthesized according to the method proposed by Jensen (1959). A mixture of a 10 ml PMFP (2 mmol, 0.5366 g) anhydrous ethanol solution, and 10 ml Glycine methyl ester hydrochloride anhydrous ethanol solution (2 mmol, 0.2511 g)solution was refluxed for ca.7 h, adding a few drops of glacial acetic acid as a catalyst. Then ethanol was removed by evaporation and the resulting black precipitate formed was filtered off, washed with cold anhydrous ethanol and dried in air. Black block single crystals suitable for analysis were obtained by slowly evaporation of a solution in anhydrous ethanol at room temperature for a few days.
Refinement
H atoms bonded to N3 was located in a difference map and isotropically refined. Other H atoms were placed in calculated positions [C—H 0.93-0.97 Å], and refined as riding, with Uiso(H)=1.2-1.5 Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) showing the atomic numbering and 30% probability displacement ellipsoids. Dotted line indicates hydrogen bond.
Crystal data
| C18H17N3O4 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 339.35 | F(000) = 356 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.356 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.499 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 1502 reflections |
| b = 9.503 (5) Å | θ = 2.9–22.6° |
| c = 11.749 (6) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| α = 96.712 (7)° | T = 295 K |
| β = 91.654 (8)° | Block, black |
| γ = 90.337 (7)° | 0.48 × 0.14 × 0.08 mm |
| V = 831.2 (7) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 1805 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.034 |
| graphite | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.6° |
| phi and ω scans | h = −8→8 |
| 6492 measured reflections | k = −11→11 |
| 2915 independent reflections | l = −13→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.051 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.150 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.01 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0826P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2915 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 232 parameters | Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.2043 (3) | 0.1986 (3) | 0.7105 (2) | 0.0509 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.1118 (4) | 0.1820 (3) | 0.6063 (3) | 0.0697 (8) | |
| H2 | 0.0454 | 0.1000 | 0.5838 | 0.084* | |
| C3 | 0.1192 (5) | 0.2881 (4) | 0.5362 (3) | 0.0888 (10) | |
| H3 | 0.0555 | 0.2778 | 0.4666 | 0.107* | |
| C4 | 0.2192 (5) | 0.4093 (4) | 0.5672 (3) | 0.0848 (10) | |
| H4 | 0.2235 | 0.4799 | 0.5188 | 0.102* | |
| C5 | 0.3120 (4) | 0.4247 (3) | 0.6696 (3) | 0.0725 (8) | |
| H5 | 0.3797 | 0.5064 | 0.6909 | 0.087* | |
| C6 | 0.3064 (4) | 0.3203 (3) | 0.7418 (2) | 0.0599 (7) | |
| H6 | 0.3707 | 0.3313 | 0.8112 | 0.072* | |
| C7 | 0.0294 (4) | −0.2611 (3) | 0.8061 (2) | 0.0648 (8) | |
| H7A | −0.0553 | −0.2639 | 0.7430 | 0.097* | |
| H7B | −0.0311 | −0.2784 | 0.8741 | 0.097* | |
| H7C | 0.1178 | −0.3325 | 0.7892 | 0.097* | |
| C8 | 0.1184 (3) | −0.1175 (2) | 0.8250 (2) | 0.0493 (6) | |
| C9 | 0.2063 (3) | −0.0467 (2) | 0.9256 (2) | 0.0446 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.2473 (3) | 0.0934 (2) | 0.8965 (2) | 0.0464 (6) | |
| C11 | 0.2438 (3) | −0.0855 (2) | 1.0341 (2) | 0.0461 (6) | |
| C12 | 0.2315 (3) | −0.2330 (2) | 1.0582 (2) | 0.0507 (6) | |
| C13 | 0.2946 (3) | −0.3534 (2) | 1.0035 (2) | 0.0605 (7) | |
| H13 | 0.3546 | −0.3628 | 0.9349 | 0.073* | |
| C14 | 0.2530 (4) | −0.4631 (3) | 1.0695 (3) | 0.0741 (9) | |
| H14 | 0.2804 | −0.5585 | 1.0534 | 0.089* | |
| C15 | 0.1673 (4) | −0.4029 (3) | 1.1587 (3) | 0.0827 (10) | |
| H15 | 0.1234 | −0.4516 | 1.2163 | 0.099* | |
| C16 | 0.6100 (4) | 0.1991 (3) | 1.4644 (3) | 0.0859 (10) | |
| H16A | 0.7236 | 0.2106 | 1.4309 | 0.129* | |
| H16B | 0.6277 | 0.1728 | 1.5403 | 0.129* | |
| H16C | 0.5461 | 0.2867 | 1.4681 | 0.129* | |
| C17 | 0.4484 (3) | 0.1167 (3) | 1.2930 (2) | 0.0533 (6) | |
| C18 | 0.3474 (3) | −0.0089 (2) | 1.2339 (2) | 0.0538 (7) | |
| H18A | 0.4205 | −0.0928 | 1.2334 | 0.065* | |
| H18B | 0.2405 | −0.0242 | 1.2756 | 0.065* | |
| H3A | 0.309 (3) | 0.107 (3) | 1.094 (2) | 0.065 (8)* | |
| N1 | 0.1955 (2) | 0.09022 (19) | 0.78289 (18) | 0.0501 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.1101 (3) | −0.0388 (2) | 0.74126 (18) | 0.0540 (6) | |
| N3 | 0.2991 (3) | 0.0135 (2) | 1.11800 (17) | 0.0498 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.3157 (2) | 0.19626 (16) | 0.95855 (14) | 0.0587 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.1511 (3) | −0.26029 (18) | 1.15579 (17) | 0.0717 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.4695 (3) | 0.22735 (19) | 1.25441 (17) | 0.0740 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.5077 (2) | 0.08888 (19) | 1.39454 (17) | 0.0684 (5) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0540 (14) | 0.0451 (14) | 0.0541 (16) | 0.0075 (11) | 0.0107 (12) | 0.0048 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0727 (18) | 0.0695 (19) | 0.067 (2) | −0.0029 (15) | −0.0007 (16) | 0.0103 (16) |
| C3 | 0.099 (2) | 0.098 (3) | 0.073 (2) | 0.001 (2) | −0.0079 (19) | 0.029 (2) |
| C4 | 0.103 (2) | 0.071 (2) | 0.086 (3) | 0.0040 (19) | 0.010 (2) | 0.0325 (19) |
| C5 | 0.090 (2) | 0.0497 (17) | 0.079 (2) | 0.0030 (15) | 0.0129 (18) | 0.0110 (15) |
| C6 | 0.0764 (18) | 0.0431 (15) | 0.0602 (17) | 0.0008 (13) | 0.0075 (14) | 0.0051 (13) |
| C7 | 0.0724 (17) | 0.0433 (15) | 0.0753 (19) | −0.0130 (13) | 0.0006 (15) | −0.0057 (13) |
| C8 | 0.0486 (14) | 0.0396 (13) | 0.0582 (16) | 0.0015 (11) | 0.0102 (12) | −0.0031 (13) |
| C9 | 0.0488 (13) | 0.0317 (12) | 0.0516 (15) | 0.0004 (10) | 0.0073 (11) | −0.0037 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0476 (13) | 0.0376 (13) | 0.0523 (16) | 0.0022 (10) | 0.0064 (11) | −0.0037 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0430 (13) | 0.0352 (13) | 0.0589 (16) | 0.0015 (10) | 0.0111 (11) | −0.0029 (12) |
| C12 | 0.0510 (14) | 0.0375 (13) | 0.0633 (16) | −0.0027 (11) | 0.0126 (12) | 0.0017 (11) |
| C13 | 0.0667 (16) | 0.0362 (14) | 0.0769 (18) | 0.0007 (12) | 0.0145 (14) | −0.0040 (13) |
| C14 | 0.080 (2) | 0.0348 (15) | 0.107 (2) | 0.0035 (13) | 0.0123 (18) | 0.0032 (15) |
| C15 | 0.107 (2) | 0.0366 (16) | 0.107 (3) | −0.0150 (15) | 0.020 (2) | 0.0167 (16) |
| C16 | 0.093 (2) | 0.090 (2) | 0.068 (2) | −0.0136 (19) | −0.0048 (17) | −0.0150 (18) |
| C17 | 0.0572 (15) | 0.0503 (16) | 0.0520 (17) | 0.0034 (12) | 0.0090 (13) | 0.0026 (13) |
| C18 | 0.0562 (15) | 0.0431 (14) | 0.0618 (18) | −0.0002 (11) | 0.0050 (13) | 0.0046 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0560 (12) | 0.0388 (11) | 0.0533 (13) | −0.0014 (9) | 0.0035 (10) | −0.0036 (10) |
| N2 | 0.0573 (13) | 0.0410 (12) | 0.0612 (14) | −0.0026 (9) | 0.0054 (10) | −0.0052 (11) |
| N3 | 0.0633 (13) | 0.0348 (11) | 0.0507 (13) | 0.0006 (9) | 0.0020 (10) | 0.0025 (10) |
| O1 | 0.0786 (12) | 0.0353 (9) | 0.0598 (11) | −0.0064 (8) | −0.0016 (9) | −0.0035 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0906 (13) | 0.0409 (10) | 0.0846 (14) | −0.0075 (9) | 0.0310 (11) | 0.0049 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0962 (14) | 0.0482 (12) | 0.0768 (14) | −0.0107 (10) | −0.0018 (11) | 0.0063 (10) |
| O4 | 0.0828 (13) | 0.0657 (13) | 0.0548 (12) | −0.0119 (10) | −0.0029 (10) | 0.0016 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.382 (4) | C11—N3 | 1.335 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.390 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.464 (3) |
| C1—N1 | 1.412 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.341 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.377 (4) | C12—O2 | 1.361 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C13—C14 | 1.408 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.377 (5) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C14—C15 | 1.320 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.365 (4) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C15—O2 | 1.366 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.380 (4) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C16—O4 | 1.453 (3) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.505 (3) | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9600 | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C7—H7B | 0.9600 | C17—O3 | 1.204 (3) |
| C7—H7C | 0.9600 | C17—O4 | 1.317 (3) |
| C8—N2 | 1.303 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.498 (4) |
| C8—C9 | 1.431 (3) | C18—N3 | 1.440 (3) |
| C9—C11 | 1.390 (3) | C18—H18A | 0.9700 |
| C9—C10 | 1.446 (3) | C18—H18B | 0.9700 |
| C10—O1 | 1.247 (3) | N1—N2 | 1.409 (3) |
| C10—N1 | 1.377 (3) | N3—H3A | 0.97 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.7 (2) | C13—C12—O2 | 109.9 (2) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 119.3 (2) | C13—C12—C11 | 131.8 (2) |
| C6—C1—N1 | 121.1 (2) | O2—C12—C11 | 118.2 (2) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.3 (3) | C12—C13—C14 | 107.2 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.4 | C12—C13—H13 | 126.4 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.4 | C14—C13—H13 | 126.4 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.2 (3) | C15—C14—C13 | 106.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.4 | C15—C14—H14 | 127.0 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.4 | C13—C14—H14 | 127.0 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.4 (3) | C14—C15—O2 | 111.5 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.3 | C14—C15—H15 | 124.2 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.3 | O2—C15—H15 | 124.2 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.6 (3) | O4—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.7 | O4—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.7 | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.8 (3) | O4—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.1 | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.1 | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7A | 109.5 | O3—C17—O4 | 125.1 (3) |
| C8—C7—H7B | 109.5 | O3—C17—C18 | 125.1 (3) |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 | O4—C17—C18 | 109.8 (2) |
| C8—C7—H7C | 109.5 | N3—C18—C17 | 110.5 (2) |
| H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 | N3—C18—H18A | 109.6 |
| H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 | C17—C18—H18A | 109.6 |
| N2—C8—C9 | 112.3 (2) | N3—C18—H18B | 109.6 |
| N2—C8—C7 | 117.8 (2) | C17—C18—H18B | 109.6 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 129.8 (2) | H18A—C18—H18B | 108.1 |
| C11—C9—C8 | 133.2 (2) | C10—N1—N2 | 111.56 (19) |
| C11—C9—C10 | 121.9 (2) | C10—N1—C1 | 129.3 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10 | 104.8 (2) | N2—N1—C1 | 118.9 (2) |
| O1—C10—N1 | 126.3 (2) | C8—N2—N1 | 106.2 (2) |
| O1—C10—C9 | 128.8 (2) | C11—N3—C18 | 126.3 (2) |
| N1—C10—C9 | 104.9 (2) | C11—N3—H3A | 113.8 (15) |
| N3—C11—C9 | 119.2 (2) | C18—N3—H3A | 119.8 (15) |
| N3—C11—C12 | 118.9 (2) | C12—O2—C15 | 105.4 (2) |
| C9—C11—C12 | 121.9 (2) | C17—O4—C16 | 117.5 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.5 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 176.1 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 179.4 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.4 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.1 (5) | C13—C14—C15—O2 | −0.4 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.4 (5) | O3—C17—C18—N3 | 7.8 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.0 (5) | O4—C17—C18—N3 | −173.49 (19) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.5 (4) | O1—C10—N1—N2 | −175.3 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.2 (4) | C9—C10—N1—N2 | 5.2 (2) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | −179.7 (2) | O1—C10—N1—C1 | −0.7 (4) |
| N2—C8—C9—C11 | 178.9 (2) | C9—C10—N1—C1 | 179.8 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9—C11 | 2.6 (4) | C2—C1—N1—C10 | −166.8 (2) |
| N2—C8—C9—C10 | 2.5 (3) | C6—C1—N1—C10 | 14.1 (4) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −173.8 (2) | C2—C1—N1—N2 | 7.4 (3) |
| C11—C9—C10—O1 | −0.9 (4) | C6—C1—N1—N2 | −171.6 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—O1 | 175.9 (2) | C9—C8—N2—N1 | 0.6 (2) |
| C11—C9—C10—N1 | 178.59 (19) | C7—C8—N2—N1 | 177.36 (19) |
| C8—C9—C10—N1 | −4.5 (2) | C10—N1—N2—C8 | −3.7 (2) |
| C8—C9—C11—N3 | −167.5 (2) | C1—N1—N2—C8 | −178.93 (18) |
| C10—C9—C11—N3 | 8.3 (3) | C9—C11—N3—C18 | −178.5 (2) |
| C8—C9—C11—C12 | 15.0 (4) | C12—C11—N3—C18 | −0.9 (3) |
| C10—C9—C11—C12 | −169.2 (2) | C17—C18—N3—C11 | 164.5 (2) |
| N3—C11—C12—C13 | −129.3 (3) | C13—C12—O2—C15 | −0.1 (3) |
| C9—C11—C12—C13 | 48.2 (4) | C11—C12—O2—C15 | −176.9 (2) |
| N3—C11—C12—O2 | 46.7 (3) | C14—C15—O2—C12 | 0.3 (3) |
| C9—C11—C12—O2 | −135.8 (2) | O3—C17—O4—C16 | −1.5 (4) |
| O2—C12—C13—C14 | −0.2 (3) | C18—C17—O4—C16 | 179.8 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H3A···O1 | 0.97 (3) | 1.89 (3) | 2.704 (3) | 140 (2) |
| C14—H14···O1i | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.386 (4) | 164 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y−1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CV5123).
References
- Bruker (2005). APEX2 and SAINT-Plus Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Casas, J. S., García-Tasende, M. S., Sanchez, A., Sordo, J. & Touceda, Á. (2007). Coord. Chem. Rev. 251, 1561–1589.
- Jensen, B. S. (1959). Acta Chem Scand 13, 1668–1670.
- Li, J.-Z., Li, G. & Yu, W.-J. (2000). J. Rare Earth, 18, 233–236.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-Q., Li, J.-Z., Zhang, Y. & Zhang, D. (2008). Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 24, 990–993.
- Zhang, H.-Q., Li, J.-Z., Zhang, Y., Zhang, D. & Su, Z.-H. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3536.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811026158/cv5123sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811026158/cv5123Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811026158/cv5123Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



