Abstract
The title compound, C15H16BrNO, obtained from a two-step reaction, was prepared for use in transition metal chemistry as a phenolic ligand with bulky substituents. Intermolecular N—H⋯O and O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds are present in the crystal structure.
Related literature
For chirality induction in metal complexes, see: Fan et al. (2010 ▶); Amendola et al. (2010 ▶). For imine reduction, see: Menta & Prabhakar (1995 ▶).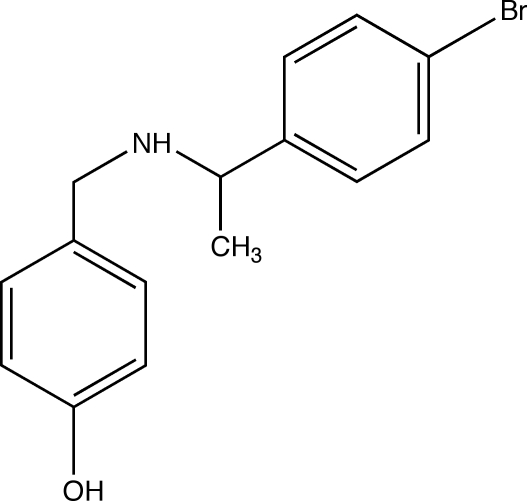
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H16BrNO
M r = 306.20
Monoclinic,
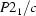
a = 12.1753 (10) Å
b = 8.1939 (7) Å
c = 14.0326 (11) Å
β = 93.333 (1)°
V = 1397.6 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.93 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.20 × 0.16 × 0.14 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2008a ▶) T min = 0.592, T max = 0.685
14961 measured reflections
3094 independent reflections
2119 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.031
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.031
wR(F 2) = 0.077
S = 1.00
3094 reflections
168 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.25 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1999 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008b ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008b ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811028339/fy2015sup1.cif
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811028339/fy2015Isup2.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811028339/fy2015Isup3.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1A⋯N1i | 0.82 | 2.05 | 2.794 (2) | 150 |
| N1—H1⋯O1ii | 0.75 (2) | 2.40 (2) | 3.144 (3) | 168 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 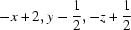 ; (ii)
; (ii) 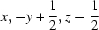 .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the NASA Space Grant (grant No. nnx10am80h). The author thanks Professor R. G. Raptis for providing access to the X-ray diffractometer and also thanks Dr Indranil Chakraborty for his help with the structure refinement.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
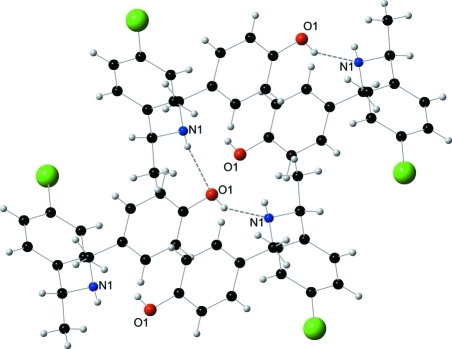
The title compound was prepared to be used as a ligand in order to induce chirality in transition metal complexes in combination with other bridging ligands. Here, we report the crystal structure of racemic 4-((1-(4-bromophenyl)ethylamino)methyl)phenol. In the crystal structure (Fig. 4), intermolecular hydrogen bonding was observed between N1—H1···O1 and O1—H1A···N1 (Table 1).
Experimental
An excess of racemic 4-bromo-α-methylbenzylamine (0.069 g, 0.45 mmol) was added to a solution of 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde (0.036 g, 0.29 mmol) in ethyl acetate. The solution was stirred overnight at room temperature. The solvent was removed under vacuum to obtain 4-((1-(4-bromophenyl)ethylimino)methyl)phenol as a white solid. The Schiff base was dissolved in anhydrous MeOH and an excess of NaBH4 was added in several portions to the reaction mixture. After 24 h, water was added to the solution, and stirring was continued for two more hours. Methanol was removed under vacuum and the remaining aqueous phase was extracted three times with ethyl acetate. The combinated organic extracts were dried with magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was removed under vacuum to obtain a white solid. The product was dissolved in acetone and crystals were obtained by vapor diffusion of pentane.
Refinement
All non-H atoms were refined anisotropically. H atoms were positioned geometrically (except the H on the N), with C—H = 0.96 (CH3), 0.97 (CH2), 0.98 (CH) and 0.93 (aromatic CH) Å, O—H = 0.82 Å and constrained with Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq(parent) for methyl H and O—H and Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(parent) for all other H atoms. The H on the N atom was generated with N—H = 0.87 Å, Uiso(H) = 0.033.
Figures
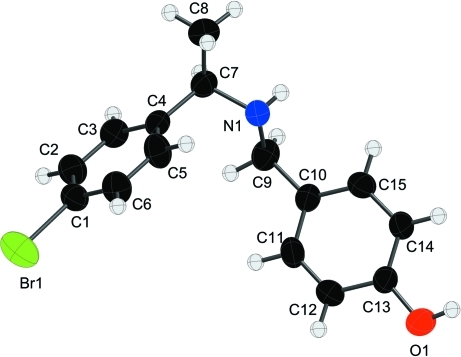
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of compound (I) with 50% probability displacement ellipsoid for non hydrogen atoms.
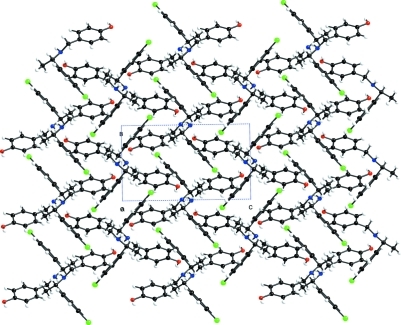
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of compound (I).
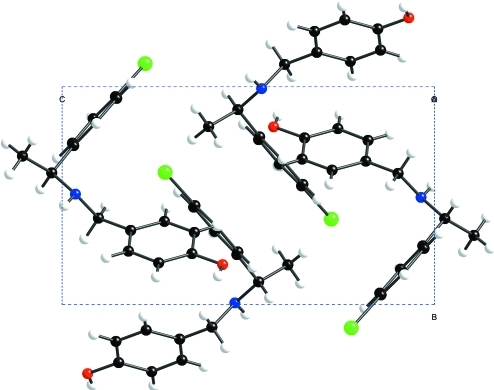
Fig. 3.
Molecular view along a axis.
Fig. 4.
Molecular structure of compound (I) with hydrogen bonding.
Crystal data
| C15H16BrNO | F(000) = 624 |
| Mr = 306.20 | Dx = 1.455 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 5896 reflections |
| a = 12.1753 (10) Å | θ = 2.3–26.2° |
| b = 8.1939 (7) Å | µ = 2.93 mm−1 |
| c = 14.0326 (11) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 93.333 (1)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1397.6 (2) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.16 × 0.14 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3094 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2119 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.031 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 27.2°, θmin = 2.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2008a) | h = −15→15 |
| Tmin = 0.592, Tmax = 0.685 | k = −10→10 |
| 14961 measured reflections | l = −17→18 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.031 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.077 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.00 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.031P)2 + 0.5405P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3094 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 168 parameters | Δρmax = 0.25 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. IR (KBr cm-1): 3448 (m), 3280 (m), 2970 (m), 2824 (m), 1613 (m, C=C), 1592 (m), 1516 (s), 1469 (m), 1373 (m), 1251 (s), 1174 (m), 1009 (s), 862 (w), 829 (s), 635 (w), 501 (w). 1H-NMR (500 MHz, d6-acetone) p.p.m.: 1.28–1.30 (d, 3H, CH3), 3.44–3.52 (dd, 2H, –CH2NH), 3.77–3.81 (m, 1H, CHCH3), 6.75–6.77 (d, 2H, aromatic protons in the phenyl ring), 7.10–7.11 (d, 2H, aromatic protons in bromophenyl ring), 7.35–7.37 (d, 2H, aromatic protons in bromophenyl ring), 7.48–7.50 (d, 2H, aromatic protons in the phenyl ring). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, d6-acetone) p.p.m.: 24.7 (CH3CH–), 51.5 (–CH2NH), 57.5 (–CHCH3), 115.8 and 132.1 (aromatic carbons in the phenyl ring), 132.1 (quaternary carbon), 120.6 (quaternary carbon, Br), 129.7 and 130.1 (aromatic carbons in the bromophenyl ring), 157.1 (quaternary carbon, OH). |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.50613 (2) | 1.10683 (4) | 0.22306 (2) | 0.07679 (13) | |
| C1 | 0.57389 (19) | 0.9552 (3) | 0.14304 (16) | 0.0493 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.51175 (19) | 0.8545 (3) | 0.08329 (17) | 0.0548 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.4354 | 0.8616 | 0.0801 | 0.066* | |
| C3 | 0.56405 (18) | 0.7419 (3) | 0.02779 (16) | 0.0491 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.5220 | 0.6728 | −0.0123 | 0.059* | |
| C4 | 0.67743 (17) | 0.7301 (3) | 0.03077 (15) | 0.0433 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.73784 (19) | 0.8363 (3) | 0.09060 (18) | 0.0585 (6) | |
| H5 | 0.8143 | 0.8322 | 0.0927 | 0.070* | |
| C6 | 0.6869 (2) | 0.9475 (3) | 0.14675 (18) | 0.0574 (6) | |
| H6 | 0.7285 | 1.0170 | 0.1869 | 0.069* | |
| C7 | 0.73506 (19) | 0.6046 (3) | −0.02810 (15) | 0.0477 (5) | |
| H7 | 0.6796 | 0.5310 | −0.0577 | 0.057* | |
| C8 | 0.7982 (2) | 0.6822 (3) | −0.10623 (18) | 0.0675 (7) | |
| H8A | 0.8519 | 0.7565 | −0.0783 | 0.101* | |
| H8B | 0.7481 | 0.7406 | −0.1492 | 0.101* | |
| H8C | 0.8346 | 0.5988 | −0.1406 | 0.101* | |
| C9 | 0.75156 (18) | 0.3972 (3) | 0.09742 (17) | 0.0533 (6) | |
| H9A | 0.7273 | 0.3024 | 0.0606 | 0.064* | |
| H9B | 0.6866 | 0.4527 | 0.1178 | 0.064* | |
| C10 | 0.81988 (17) | 0.3415 (3) | 0.18429 (15) | 0.0433 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.78927 (19) | 0.3829 (3) | 0.27448 (17) | 0.0533 (6) | |
| H11 | 0.7270 | 0.4470 | 0.2805 | 0.064* | |
| C12 | 0.8484 (2) | 0.3320 (3) | 0.35547 (17) | 0.0567 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.8266 | 0.3631 | 0.4152 | 0.068* | |
| C13 | 0.94031 (17) | 0.2344 (3) | 0.34832 (16) | 0.0464 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.97270 (17) | 0.1923 (3) | 0.25915 (16) | 0.0511 (6) | |
| H14 | 1.0348 | 0.1279 | 0.2533 | 0.061* | |
| C15 | 0.91298 (18) | 0.2458 (3) | 0.17840 (16) | 0.0518 (6) | |
| H15 | 0.9359 | 0.2168 | 0.1186 | 0.062* | |
| N1 | 0.81141 (15) | 0.5077 (2) | 0.03586 (14) | 0.0449 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.99339 (13) | 0.1835 (2) | 0.43153 (11) | 0.0617 (4) | |
| H1A | 1.0488 | 0.1325 | 0.4195 | 0.093* | |
| H1 | 0.8475 (17) | 0.456 (3) | 0.0064 (14) | 0.033 (6)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.0736 (2) | 0.0705 (2) | 0.0891 (2) | 0.00063 (14) | 0.02858 (15) | −0.02241 (16) |
| C1 | 0.0551 (13) | 0.0417 (12) | 0.0522 (13) | 0.0010 (10) | 0.0123 (11) | 0.0010 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0435 (12) | 0.0577 (15) | 0.0637 (15) | −0.0006 (11) | 0.0079 (11) | −0.0007 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0467 (12) | 0.0487 (13) | 0.0512 (13) | −0.0049 (10) | −0.0029 (10) | −0.0018 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0472 (12) | 0.0412 (11) | 0.0411 (12) | 0.0027 (10) | −0.0006 (9) | 0.0042 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0421 (12) | 0.0566 (14) | 0.0763 (17) | 0.0020 (11) | −0.0012 (12) | −0.0133 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0556 (14) | 0.0496 (13) | 0.0665 (16) | −0.0027 (11) | −0.0014 (12) | −0.0107 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0506 (12) | 0.0489 (12) | 0.0427 (12) | 0.0025 (10) | −0.0040 (10) | 0.0009 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0771 (18) | 0.0749 (18) | 0.0510 (14) | 0.0131 (15) | 0.0094 (13) | 0.0074 (13) |
| C9 | 0.0430 (12) | 0.0539 (13) | 0.0626 (15) | −0.0028 (11) | −0.0008 (11) | 0.0085 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0399 (11) | 0.0394 (11) | 0.0506 (13) | −0.0017 (9) | 0.0035 (10) | 0.0084 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0475 (13) | 0.0493 (13) | 0.0641 (15) | 0.0123 (10) | 0.0108 (11) | 0.0055 (12) |
| C12 | 0.0605 (15) | 0.0623 (15) | 0.0489 (14) | 0.0114 (12) | 0.0153 (12) | 0.0037 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0433 (11) | 0.0479 (12) | 0.0483 (13) | 0.0001 (10) | 0.0070 (10) | 0.0112 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0435 (12) | 0.0584 (14) | 0.0524 (14) | 0.0099 (10) | 0.0107 (11) | 0.0078 (11) |
| C15 | 0.0477 (13) | 0.0623 (15) | 0.0462 (13) | 0.0050 (11) | 0.0091 (10) | 0.0009 (11) |
| N1 | 0.0432 (10) | 0.0470 (11) | 0.0448 (11) | 0.0061 (9) | 0.0044 (9) | 0.0020 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0559 (10) | 0.0796 (12) | 0.0501 (9) | 0.0145 (9) | 0.0084 (8) | 0.0167 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Br1—C1 | 1.895 (2) | C9—N1 | 1.473 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.375 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.506 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.372 (3) | C9—H9A | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.386 (3) | C9—H9B | 0.9700 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C10—C11 | 1.382 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.382 (3) | C10—C15 | 1.384 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C11—C12 | 1.375 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.390 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C7 | 1.516 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.384 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.376 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C13—O1 | 1.366 (3) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C13—C14 | 1.377 (3) |
| C7—N1 | 1.484 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.382 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.515 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9800 | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C8—H8A | 0.9600 | N1—H1 | 0.75 (2) |
| C8—H8B | 0.9600 | O1—H1A | 0.8200 |
| C8—H8C | 0.9600 | ||
| C6—C1—C2 | 120.7 (2) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—Br1 | 118.46 (18) | N1—C9—C10 | 113.10 (18) |
| C2—C1—Br1 | 120.85 (18) | N1—C9—H9A | 109.0 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.3 (2) | C10—C9—H9A | 109.0 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.4 | N1—C9—H9B | 109.0 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.4 | C10—C9—H9B | 109.0 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.3 (2) | H9A—C9—H9B | 107.8 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.3 | C11—C10—C15 | 117.3 (2) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.3 | C11—C10—C9 | 120.04 (19) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 117.8 (2) | C15—C10—C9 | 122.6 (2) |
| C3—C4—C7 | 121.6 (2) | C12—C11—C10 | 121.7 (2) |
| C5—C4—C7 | 120.55 (19) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.1 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.3 (2) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.1 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.3 | C11—C12—C13 | 120.2 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.3 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 119.5 (2) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.3 | O1—C13—C14 | 123.6 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.3 | O1—C13—C12 | 117.3 (2) |
| N1—C7—C4 | 109.06 (17) | C14—C13—C12 | 119.1 (2) |
| N1—C7—C8 | 109.62 (19) | C13—C14—C15 | 120.1 (2) |
| C4—C7—C8 | 112.33 (19) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.0 |
| N1—C7—H7 | 108.6 | C15—C14—H14 | 120.0 |
| C4—C7—H7 | 108.6 | C10—C15—C14 | 121.6 (2) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 108.6 | C10—C15—H15 | 119.2 |
| C7—C8—H8A | 109.5 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.2 |
| C7—C8—H8B | 109.5 | C9—N1—C7 | 111.68 (17) |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 | C9—N1—H1 | 107.4 (16) |
| C7—C8—H8C | 109.5 | C7—N1—H1 | 109.6 (16) |
| H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 | C13—O1—H1A | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.3 (4) | N1—C9—C10—C15 | −64.5 (3) |
| Br1—C1—C2—C3 | −178.17 (17) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | 0.1 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.6 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 178.9 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.7 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −1.0 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C7 | 178.6 (2) | C11—C12—C13—O1 | −177.9 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.4 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 1.4 (4) |
| C7—C4—C5—C6 | −178.0 (2) | O1—C13—C14—C15 | 178.5 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.7 (4) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.8 (4) |
| Br1—C1—C6—C5 | 178.81 (19) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | 0.5 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.7 (4) | C9—C10—C15—C14 | −178.2 (2) |
| C3—C4—C7—N1 | −126.1 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | −0.2 (4) |
| C5—C4—C7—N1 | 53.2 (3) | C10—C9—N1—C7 | −160.10 (19) |
| C3—C4—C7—C8 | 112.2 (2) | C4—C7—N1—C9 | 71.1 (2) |
| C5—C4—C7—C8 | −68.5 (3) | C8—C7—N1—C9 | −165.5 (2) |
| N1—C9—C10—C11 | 116.7 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1A···N1i | 0.82 | 2.05 | 2.794 (2) | 150. |
| N1—H1···O1ii | 0.75 (2) | 2.40 (2) | 3.144 (3) | 168 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FY2015).
References
- Amendola, V., Boiocchi, M., Brega, V., Fabbrizzi, L. & Mosca, L. (2010). Inorg. Chem. 49, 997–1007. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (1999). SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2005). APEX2 Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Fan, L. L., Guo, F. S., Yun, L., Lin, Z. J., Herchel, R. & Leng, J. D. (2010). Dalton Trans 39, 1771–1780. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Menta, G. & Prabhakar, C. (1995). J. Org. Chem 60, 4638–4640.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008a). SADABS. University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008b). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811028339/fy2015sup1.cif
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811028339/fy2015Isup2.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811028339/fy2015Isup3.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report