Abstract
The title compound, C19H20O5, was synthesized by reaction of 4-methoxyacetophenone and 3,4,5-trimethoxy-benzaldehyde. The aromatic rings form a dihedral angle of 36.39 (7)°. Two intramolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds occur. The crystal packing features weak C—H⋯O interactions.
Related literature
For background to chalcones and the biological activity and derivatives, see: Dhar (1981 ▶); Dimmock et al. (1999 ▶). For their applications as organic non-linear optical materials, see: Sarojini et al. (2006 ▶) and for their choleretic and hepatoprotective activity, see: Ni et al. (2004 ▶). For the synthesis of chalcones, see: Patil et al. (2009 ▶). For the potential use of these compounds or chalcone-rich plant extracts as drugs or food preservatives, see: Di Carlo et al. (1999 ▶). For related structures, see: Sathiya Moorthi et al. (2005 ▶); Cai et al. (2011 ▶); Vijay Kumar et al. (2011 ▶); Bibila Mayaya Bisseyou et al. (2007 ▶). The title compound wss prepared by an aldol Claisen–Schmidt condensation reaction, see: Bandgar et al. (2009 ▶, 2010 ▶); Hathaway (1987 ▶).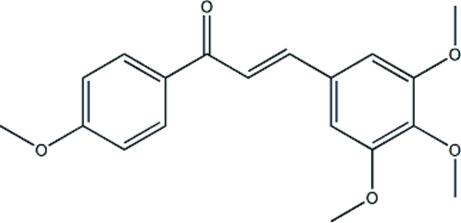
Experimental
Crystal data
C19H20O5
M r = 328.35
Monoclinic,

a = 7.5770 (1) Å
b = 16.2530 (3) Å
c = 14.0850 (3) Å
β = 107.528 (1)°
V = 1654.02 (5) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.10 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.2 × 0.1 × 0.1 mm
Data collection
Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer
27371 measured reflections
3733 independent reflections
2907 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.130
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.056
wR(F 2) = 0.174
S = 1.02
3733 reflections
222 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3
Data collection: COLLECT (Hooft, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); data reduction: DENZO (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶) and SCALEPACK; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811028984/zj2014sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811028984/zj2014Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811028984/zj2014Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C9—H9⋯O2 | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.415 (2) | 165 |
| C16—H16A⋯O2 | 0.96 | 2.55 | 3.484 (2) | 165 |
| C18—H18C⋯O1i | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.332 (2) | 142 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Brazilian Federal Agency CAPES.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Chalcones are a medicinally important class of compounds and are known for possessing various biological activities such as antibacterial, antiviral, anthelmintic, amoebicidal, antiulcer, insecticidal, antiprotozoal, anticancer, cytotoxic, immunosuppressive activities and other bioactivities (Dhar, 1981; Dimmock et al., 1999). Recently, some chalcones were approved for therapeutical use, such as methoxychalcone (E)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2,4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, marketed in France and Italy, with choleretic and hepatoprotective activities (Ni et al., 2004). Moreover, a literature survey showed dimethoxy and trimethoxychalcone derivatives as effective anti-inflammatory agents (Bandgar et al., 2010).
The (E)-3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one is a methoxychalcone which the structure shows two aromatic rings linked by prop-2-en-1-one group. The refined molecular structure is shown in Fig. 1. Due to p-π conjugation, the Csp2—O bonds [O2—C7 = 1.2249 (2) Å] are significantly shorter than the Csp3—O bonds [O1—C19 = 1.4240 (2) Å; O3—C18 = 1.415 (2) Å; O4—C17 = 1.413 (2) Å and O5—C16 = 1.4294 (2) Å]. The methoxy substituted groups around the benzene rings are almost planar and the dihedral angles C5—C6—C7—C8, C6—C7—C8—C9, C7—C8—C9—C10 and C8—C9—C10—C11 are -23.0 (2)°, 169.3 (2)°, 177.7 (2)° and -4.4 (2)°, respectively, indicating the molecule has a non-planar conformation.
The crystal structure is stabilized by C—H···O contacts (Table 1). There is intermolecular hydrogen bonding involving C9 acting as H-bond donor, via H9, to O2 in the adjacent molecules at -x+1, -y+1, -z resulting in a dimer.
Experimental
The title compound, C19H20O5, has been prepared by the aldol Claisen-Schmidt condensation (Hathaway, 1987; Bandgar et al., 2009) by the reaction of a mixture of 4-methoxy-acetophenone (0,3 mg; 2 mmol) and 3,4,5-trimethoxy-benzaldehyde (0,39 mg; 2 mmol) and NaOH (50% p/v) at 257 K for 24 h. The light yellow solid (m.p. 404.25 - 405.65 K) thus obtained was filtered, washed with water and dried. Crystals of suitable quality for single crystal X-ray diffraction were grown in methanol.
Refinement
The space group P21/c was uniquely assigned from the systematic absences. All the H-atoms were placed in calculated positions and treated as riding atoms [Caro—H = 0.93 Å and Csp3—H = 0.96 Å), with a displacement parameter Uiso set equal to 1.2 times Ueq that of the parent atom, and Csp3 and aromatic H.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structre showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
The packing viewed along c axis with C—H···O interactions, indicating the dimer
Crystal data
| C19H20O5 | F(000) = 696 |
| Mr = 328.35 | Dx = 1.319 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.5770 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 14574 reflections |
| b = 16.2530 (3) Å | θ = 2.6–27.5° |
| c = 14.0850 (3) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| β = 107.528 (1)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 1654.02 (5) Å3 | Prism, pale yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.2 × 0.1 × 0.1 mm |
Data collection
| Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer | 2907 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.130 |
| Detector resolution: 9 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.8° |
| CCD scans | h = −9→8 |
| 27371 measured reflections | k = −20→21 |
| 3733 independent reflections | l = −18→17 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.056 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.174 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.115P)2 + 0.1311P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.02 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 3733 reflections | Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3 |
| 222 parameters | Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.085 (10) |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C6 | 0.28843 (19) | 0.01968 (8) | 0.72913 (10) | 0.0440 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.2444 (2) | 0.01579 (9) | 0.91868 (10) | 0.0478 (4) | |
| O5 | −0.33915 (16) | 0.26263 (7) | 0.32667 (8) | 0.0592 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.3073 (2) | 0.01831 (8) | 0.62695 (11) | 0.0465 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.21258 (17) | 0.01994 (7) | 1.00875 (8) | 0.0613 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.06505 (17) | 0.22341 (7) | 0.13696 (8) | 0.0594 (3) | |
| C13 | −0.1306 (2) | 0.24141 (9) | 0.23514 (10) | 0.0496 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.41266 (17) | −0.03016 (7) | 0.60508 (9) | 0.0623 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.0304 (2) | 0.20629 (8) | 0.22489 (9) | 0.0472 (3) | |
| C11 | −0.0614 (2) | 0.18197 (9) | 0.39957 (10) | 0.0478 (3) | |
| H11 | −0.0896 | 0.1757 | 0.459 | 0.057* | |
| C1 | 0.3390 (2) | −0.04924 (8) | 0.78977 (11) | 0.0475 (3) | |
| H1 | 0.3901 | −0.0943 | 0.7669 | 0.057* | |
| C9 | 0.21256 (19) | 0.09013 (9) | 0.46478 (10) | 0.0464 (3) | |
| H9 | 0.3105 | 0.0638 | 0.4504 | 0.056* | |
| C15 | 0.1421 (2) | 0.15689 (9) | 0.29994 (10) | 0.0471 (3) | |
| H15 | 0.2474 | 0.1324 | 0.2917 | 0.057* | |
| C10 | 0.09579 (19) | 0.14423 (8) | 0.38773 (9) | 0.0451 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.2205 (2) | 0.08797 (9) | 0.76692 (11) | 0.0501 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.1881 | 0.1351 | 0.728 | 0.06* | |
| O4 | −0.24822 (19) | 0.28028 (7) | 0.15454 (8) | 0.0700 (4) | |
| C12 | −0.1763 (2) | 0.22889 (9) | 0.32326 (10) | 0.0475 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.2007 (2) | 0.08672 (9) | 0.86115 (11) | 0.0528 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.1583 | 0.1332 | 0.8861 | 0.063* | |
| C2 | 0.3152 (2) | −0.05237 (9) | 0.88338 (10) | 0.0502 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.3463 | −0.0996 | 0.9221 | 0.06* | |
| C8 | 0.1902 (2) | 0.07561 (9) | 0.55307 (10) | 0.0503 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.0955 | 0.103 | 0.5694 | 0.06* | |
| C17 | −0.2865 (3) | 0.36460 (11) | 0.16310 (12) | 0.0693 (5) | |
| H17A | −0.3621 | 0.3708 | 0.2064 | 0.104* | |
| H17B | −0.3508 | 0.3863 | 0.0985 | 0.104* | |
| H17C | −0.1724 | 0.394 | 0.1902 | 0.104* | |
| C16 | −0.3984 (2) | 0.24404 (11) | 0.41148 (12) | 0.0602 (4) | |
| H16A | −0.4186 | 0.1859 | 0.4141 | 0.09* | |
| H16B | −0.5116 | 0.2728 | 0.4064 | 0.09* | |
| H16C | −0.3049 | 0.261 | 0.4709 | 0.09* | |
| C18 | 0.2381 (3) | 0.19903 (12) | 0.12726 (13) | 0.0702 (5) | |
| H18A | 0.3358 | 0.22 | 0.1825 | 0.105* | |
| H18B | 0.2513 | 0.2205 | 0.0663 | 0.105* | |
| H18C | 0.2446 | 0.1401 | 0.1265 | 0.105* | |
| C19 | 0.2388 (3) | −0.05277 (12) | 1.06778 (12) | 0.0666 (5) | |
| H19A | 0.1621 | −0.096 | 1.0306 | 0.1* | |
| H19B | 0.2058 | −0.0421 | 1.1273 | 0.1* | |
| H19C | 0.3663 | −0.0692 | 1.0852 | 0.1* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C6 | 0.0425 (7) | 0.0436 (7) | 0.0430 (7) | −0.0002 (5) | 0.0086 (5) | 0.0042 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0491 (8) | 0.0517 (8) | 0.0401 (7) | −0.0033 (6) | 0.0098 (6) | 0.0043 (5) |
| O5 | 0.0536 (7) | 0.0738 (7) | 0.0466 (6) | 0.0147 (5) | 0.0095 (5) | 0.0039 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0463 (7) | 0.0433 (7) | 0.0502 (8) | 0.0004 (6) | 0.0150 (6) | 0.0046 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0772 (8) | 0.0628 (7) | 0.0459 (6) | 0.0058 (5) | 0.0215 (5) | 0.0096 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0722 (8) | 0.0672 (7) | 0.0393 (5) | 0.0078 (5) | 0.0175 (5) | 0.0058 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0562 (9) | 0.0490 (7) | 0.0348 (7) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0006 (6) | −0.0041 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0736 (8) | 0.0566 (6) | 0.0648 (7) | 0.0189 (5) | 0.0331 (6) | 0.0119 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0581 (8) | 0.0468 (7) | 0.0336 (6) | −0.0044 (6) | 0.0090 (6) | −0.0039 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0491 (8) | 0.0547 (8) | 0.0367 (6) | 0.0003 (6) | 0.0087 (5) | −0.0003 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0497 (8) | 0.0413 (7) | 0.0470 (7) | 0.0024 (6) | 0.0078 (6) | 0.0017 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0444 (7) | 0.0478 (7) | 0.0452 (7) | 0.0016 (5) | 0.0109 (6) | 0.0023 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0495 (7) | 0.0492 (7) | 0.0409 (7) | −0.0006 (6) | 0.0112 (6) | −0.0008 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0459 (7) | 0.0467 (7) | 0.0382 (6) | −0.0028 (6) | 0.0057 (5) | −0.0002 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0577 (8) | 0.0432 (7) | 0.0489 (7) | 0.0076 (6) | 0.0152 (6) | 0.0092 (6) |
| O4 | 0.0862 (9) | 0.0722 (8) | 0.0379 (6) | 0.0246 (6) | −0.0021 (5) | −0.0010 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0463 (8) | 0.0503 (8) | 0.0407 (7) | 0.0023 (6) | 0.0050 (6) | −0.0043 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0623 (9) | 0.0463 (7) | 0.0494 (8) | 0.0075 (6) | 0.0163 (7) | 0.0041 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0556 (8) | 0.0428 (7) | 0.0462 (7) | 0.0006 (6) | 0.0062 (6) | 0.0096 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0484 (8) | 0.0562 (8) | 0.0453 (7) | 0.0087 (6) | 0.0125 (6) | 0.0053 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0765 (11) | 0.0667 (10) | 0.0584 (9) | 0.0204 (9) | 0.0110 (8) | 0.0105 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0577 (9) | 0.0657 (10) | 0.0594 (9) | 0.0082 (7) | 0.0210 (8) | 0.0027 (7) |
| C18 | 0.0911 (13) | 0.0769 (11) | 0.0506 (9) | 0.0143 (9) | 0.0333 (9) | 0.0034 (7) |
| C19 | 0.0736 (11) | 0.0730 (11) | 0.0529 (9) | 0.0016 (8) | 0.0188 (8) | 0.0205 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C6—C1 | 1.3906 (19) | C9—C10 | 1.4682 (19) |
| C6—C5 | 1.395 (2) | C9—H9 | 0.93 |
| C6—C7 | 1.4889 (19) | C15—C10 | 1.3986 (19) |
| C3—O1 | 1.3626 (17) | C15—H15 | 0.93 |
| C3—C2 | 1.387 (2) | C5—C4 | 1.380 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.3906 (19) | C5—H5 | 0.93 |
| O5—C12 | 1.3645 (18) | O4—C17 | 1.413 (2) |
| O5—C16 | 1.4294 (19) | C4—H4 | 0.93 |
| C7—O2 | 1.2249 (18) | C2—H2 | 0.93 |
| C7—C8 | 1.4771 (19) | C8—H8 | 0.93 |
| O1—C19 | 1.4240 (19) | C17—H17A | 0.96 |
| O3—C14 | 1.3699 (16) | C17—H17B | 0.96 |
| O3—C18 | 1.415 (2) | C17—H17C | 0.96 |
| C13—O4 | 1.3685 (17) | C16—H16A | 0.96 |
| C13—C14 | 1.393 (2) | C16—H16B | 0.96 |
| C13—C12 | 1.400 (2) | C16—H16C | 0.96 |
| C14—C15 | 1.393 (2) | C18—H18A | 0.96 |
| C11—C12 | 1.390 (2) | C18—H18B | 0.96 |
| C11—C10 | 1.394 (2) | C18—H18C | 0.96 |
| C11—H11 | 0.93 | C19—H19A | 0.96 |
| C1—C2 | 1.384 (2) | C19—H19B | 0.96 |
| C1—H1 | 0.93 | C19—H19C | 0.96 |
| C9—C8 | 1.326 (2) | ||
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.15 (13) | O5—C12—C11 | 123.77 (13) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 119.52 (12) | O5—C12—C13 | 116.13 (12) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 122.33 (12) | C11—C12—C13 | 120.06 (13) |
| O1—C3—C2 | 124.72 (12) | C5—C4—C3 | 119.79 (13) |
| O1—C3—C4 | 115.06 (13) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.22 (13) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 |
| C12—O5—C16 | 117.36 (12) | C1—C2—C3 | 119.18 (12) |
| O2—C7—C8 | 121.82 (14) | C1—C2—H2 | 120.4 |
| O2—C7—C6 | 120.82 (12) | C3—C2—H2 | 120.4 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 117.33 (12) | C9—C8—C7 | 123.60 (13) |
| C3—O1—C19 | 118.02 (13) | C9—C8—H8 | 118.2 |
| C14—O3—C18 | 117.77 (12) | C7—C8—H8 | 118.2 |
| O4—C13—C14 | 118.37 (13) | O4—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| O4—C13—C12 | 121.95 (14) | O4—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C14—C13—C12 | 119.36 (12) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O3—C14—C15 | 124.40 (13) | O4—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O3—C14—C13 | 115.01 (12) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C15—C14—C13 | 120.59 (13) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 120.51 (12) | O5—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 119.7 | O5—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—H11 | 119.7 | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.57 (13) | O5—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 119.2 | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—H1 | 119.2 | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 125.52 (13) | O3—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 117.2 | O3—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 117.2 | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C14—C15—C10 | 119.90 (13) | O3—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C14—C15—H15 | 120 | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C10—C15—H15 | 120 | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—C15 | 119.49 (12) | O1—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 121.44 (12) | O1—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C15—C10—C9 | 119.06 (13) | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.99 (12) | O1—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.5 | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C13—O4—C17 | 118.42 (12) | ||
| C1—C6—C7—O2 | −21.4 (2) | C1—C6—C5—C4 | −1.2 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—O2 | 158.90 (15) | C7—C6—C5—C4 | 178.5 (2) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | 156.7 (2) | C14—C13—O4—C17 | −120.1 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −23.0 (2) | C12—C13—O4—C17 | 66.4 (2) |
| C2—C3—O1—C19 | −5.5 (2) | C16—O5—C12—C11 | −3.9 (2) |
| C4—C3—O1—C19 | 174.5 (2) | C16—O5—C12—C13 | 173.9 (2) |
| C18—O3—C14—C15 | −9.2 (2) | C10—C11—C12—O5 | 175.0 (2) |
| C18—O3—C14—C13 | 171.6 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −2.6 (2) |
| O4—C13—C14—O3 | 7.7 (2) | O4—C13—C12—O5 | −4.4 (2) |
| C12—C13—C14—O3 | −178.7 (2) | C14—C13—C12—O5 | −177.7 (2) |
| O4—C13—C14—C15 | −171.4 (2) | O4—C13—C12—C11 | 173.5 (2) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | 2.1 (2) | C14—C13—C12—C11 | 0.1 (2) |
| C5—C6—C1—C2 | 3.0 (2) | C6—C5—C4—C3 | −1.7 (2) |
| C7—C6—C1—C2 | −176.6 (2) | O1—C3—C4—C5 | −177.3 (2) |
| O3—C14—C15—C10 | 179.0 (2) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 2.8 (2) |
| C13—C14—C15—C10 | −1.9 (2) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | −2.0 (2) |
| C12—C11—C10—C15 | 2.9 (2) | O1—C3—C2—C1 | 179.1 (2) |
| C12—C11—C10—C9 | −176.0 (2) | C4—C3—C2—C1 | −1.0 (2) |
| C14—C15—C10—C11 | −0.6 (2) | C10—C9—C8—C7 | 177.7 (2) |
| C14—C15—C10—C9 | 178.3 (2) | O2—C7—C8—C9 | −12.8 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −4.4 (2) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 169.1 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—C15 | 176.7 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C9—H9···O2i | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.415 (2) | 165 |
| C16—H16A···O2ii | 0.96 | 2.55 | 3.484 (2) | 165 |
| C18—H18C···O1iii | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.332 (2) | 142 |
Symmetry codes: (i) ; (ii) ; (iii) x, y, z−1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: ZJ2014).
References
- Bandgar, B. P., Gawande, S. S., Bodade, R. G., Gawande, N. M. & Khobragade, C. N. (2009). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17, 8168–8173. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bandgar, B. P., Gawande, S. S., Bodade, R. G., Totre, J. V. & Khobragade, C. N. (2010). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18, 1364–1370. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bibila Mayaya Bisseyou, Y., Soro, A. P., Sissouma, D., Giorgi, M. & Ebby, N. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o4758–o4759.
- Cai, Y., Wang, Z., Li, Z., Zhang, M. & Wu, J. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Dhar, D. N. (1981). The Chemistry of Chalcones and Related Compounds, p. 213. New York: Wiley-Interscience.
- Di Carlo, G., Mascolo, N., Izzo, A. A. & Capasso, F. (1999). Life Sci. 65, 337–353. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dimmock, J. R., Raghavan, S. K., Logan, B. M. & Bigam, G. E. (1999). Curr. Med. Chem. 6, 1125–1149.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Hathaway, B. A. (1987). J. Chem. Educ. 64, 367–368.
- Hooft, R. W. W. (1998). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Ni, L., Meng, Q. M. & Siroski, J. (2004). Exp. Opin. 14, 1669–1691.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Patil, C. B., Mahajan, S. K. & katti, S. A. (2009). J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 3, 11–22.
- Sarojini, B. K., Narayana, B., Ashalatha, B. V., Indira, J. & Lobo, K. G. (2006). J. Cryst. Growth, 295, 54–59.
- Sathiya Moorthi, S., Chinnakali, K., Nanjundan, S., Selvam, P., Fun, H.-K. & Yu, X.-L. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o743–o745.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Vijay Kumar, D., Thippeswamy, G. B., Jayashree, B. S. & Sridhar, M. A. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o1492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811028984/zj2014sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811028984/zj2014Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811028984/zj2014Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




