Abstract
In the title compound, C11H9NO2, the mean planes formed by the phenyl and acryl group are almost orthogonal to each other, with a dihedral angle of 88.61 (7)°. The carbonitrile side chain is almost linear, the C—C—N angle being 179.54 (16)°. In the crystal, molecules are linked by intermolecular O—H⋯O interactions into infinite chains running parallel to the b axis.
Related literature
For uses of acrylonitrile derivatives, see: Ohsumi et al. (1998 ▶). For related structures, see: Cobo et al. (2005 ▶); Nizam Mohideen et al. (2007 ▶).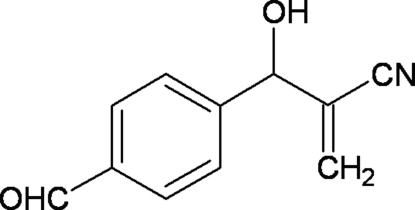
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H9NO2
M r = 187.19
Monoclinic,
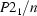
a = 7.6089 (5) Å
b = 6.0895 (3) Å
c = 20.5135 (14) Å
β = 93.615 (2)°
V = 948.59 (10) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.30 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
12108 measured reflections
2778 independent reflections
2109 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.025
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.045
wR(F 2) = 0.137
S = 1.04
2778 reflections
128 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681102976X/pv2428sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681102976X/pv2428Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681102976X/pv2428Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2⋯O1i | 0.82 | 1.99 | 2.8107 (15) | 175 |
Symmetry code: (i) 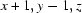 .
.
Acknowledgments
CMS and KS thank Dr Babu Varghese, SAIF, IIT, Chennai, India, for the X-ray intensity data collection and Dr V. Murugan, Head of the Department of Physics, for providing facilities in the department to carry out this work.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Acrylonitrile derivatives have been shown to possess antitubercular and antitumour activities (Ohsumi et al., 1998).
In the title compound (Fig. 1), the mean planes formed by the phenyl ring C2—C7 and acryl group (N1/C8—C11) are almost orthogonal to each other with a dihedral angle 88.61 (7)°. The bond length C9—C11 [1.4338 (18) Å] is significantly shorter than the expected value for a C—C single bond because of conjugation effects (Nizam Mohideen et al., 2007). The mean plane of C2—C1—O1 is slightly twisted out of the mean plane of phenyl ring C2—C7 with a dihedral angle 2.62 (9)°. The carbonitrile side chain (C9—C11—N1) is almost linear, with the angle around central carbon atom being 179.54 (16)°. The title compound exhibits structural similarities with closely related structures (Cobo et al.2005, Nizam Mohideen et al.2007).
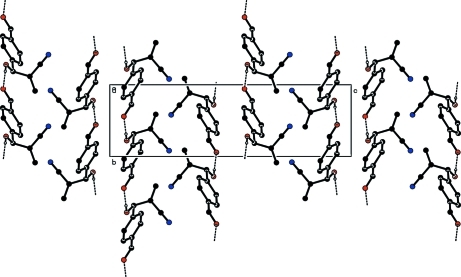
In the title compound, the crystal packing is stabilized by O2—H2···O1 intermolecular interactions which link the molecules into infinite chains running parallel to the b-axis (Tab. 1 & Fig. 2).
Experimental
To a reaction mixture of terephthalaldehyde (1 mmol) and acrylonitrile (2 mmol) was added a catalytic quantity of 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane (10–15 mol %). The reaction mixture was left standing at room temperature in a stoppered sample flask. The progress of the reaction was monitored by Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) over a period of several days. After 6 days the TLC revealed the presence of a product. The reaction mixture was dissolved in ethyl acetate and washed with aqueous HCl solution (0.25 M) and water followed by brine solution. The organic layer was separated and dried over sodium sulfate, filtering and evaporation of the organic solvent under reduced pressure. The product was seperated by flash column chromatography using hexane and ethyl acetate (4:1) as an eluent to give colorless solid. The product was dissolved in chloroform and heated for two minutes. The resulting solution was subjected to crystallization by slow evaporation of the solvent resulting in single crystals suitable for XRD studies.
Refinement
The hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions with C—H = 0.93 to 0.98 Å and O—H = 0.82 Å and refined in the riding model with isotropic displacement parameters: Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) or 1.5Ueq(O).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
A view of the unit cell of the title compound viewed down a-axis; O—H···O intermolecular interactions are indicated by dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C11H9NO2 | F(000) = 392 |
| Mr = 187.19 | Dx = 1.311 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 2778 reflections |
| a = 7.6089 (5) Å | θ = 2.0–30.1° |
| b = 6.0895 (3) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 20.5135 (14) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 93.615 (2)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 948.59 (10) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2109 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.025 |
| graphite | θmax = 30.1°, θmin = 2.0° |
| ω scans | h = −10→10 |
| 12108 measured reflections | k = −8→5 |
| 2778 independent reflections | l = −28→28 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.045 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.137 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.068P)2 + 0.1498P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2778 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 128 parameters | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.29788 (17) | 1.2762 (2) | 0.08969 (7) | 0.0530 (3) | |
| H1 | 0.2060 | 1.2372 | 0.1152 | 0.064* | |
| C2 | 0.45120 (15) | 1.1299 (2) | 0.09117 (6) | 0.0402 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.59636 (15) | 1.17738 (19) | 0.05636 (6) | 0.0403 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.5982 | 1.3042 | 0.0312 | 0.048* | |
| C4 | 0.73929 (15) | 1.03554 (19) | 0.05910 (6) | 0.0377 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.8374 | 1.0683 | 0.0361 | 0.045* | |
| C5 | 0.73630 (14) | 0.84482 (18) | 0.09612 (5) | 0.0341 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.58917 (16) | 0.7961 (2) | 0.12973 (6) | 0.0440 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.5855 | 0.6670 | 0.1538 | 0.053* | |
| C7 | 0.44760 (16) | 0.9386 (2) | 0.12758 (6) | 0.0473 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.3496 | 0.9059 | 0.1507 | 0.057* | |
| C8 | 0.88910 (15) | 0.68441 (19) | 0.09921 (6) | 0.0386 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.8530 | 0.5530 | 0.0742 | 0.046* | |
| C9 | 0.94025 (16) | 0.6160 (2) | 0.16879 (6) | 0.0416 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.9246 (2) | 0.4136 (2) | 0.19036 (8) | 0.0658 (4) | |
| H10A | 0.9592 | 0.3799 | 0.2335 | 0.079* | |
| H10B | 0.8788 | 0.3045 | 0.1625 | 0.079* | |
| C11 | 1.01071 (18) | 0.7847 (2) | 0.21163 (7) | 0.0499 (3) | |
| N1 | 1.0657 (2) | 0.9196 (3) | 0.24571 (8) | 0.0783 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.28115 (14) | 1.44271 (18) | 0.05813 (6) | 0.0647 (3) | |
| O2 | 1.03273 (12) | 0.77961 (17) | 0.07008 (5) | 0.0550 (3) | |
| H2 | 1.1103 | 0.6874 | 0.0670 | 0.083* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0386 (6) | 0.0578 (8) | 0.0626 (8) | 0.0154 (6) | 0.0044 (6) | −0.0036 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0328 (5) | 0.0454 (6) | 0.0420 (6) | 0.0090 (4) | −0.0012 (4) | −0.0055 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0394 (6) | 0.0378 (6) | 0.0434 (6) | 0.0073 (4) | −0.0005 (5) | 0.0030 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0336 (5) | 0.0409 (6) | 0.0390 (6) | 0.0055 (4) | 0.0047 (4) | 0.0040 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0326 (5) | 0.0371 (5) | 0.0326 (5) | 0.0067 (4) | 0.0007 (4) | −0.0005 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0402 (6) | 0.0457 (6) | 0.0466 (7) | 0.0051 (5) | 0.0073 (5) | 0.0104 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0337 (6) | 0.0579 (7) | 0.0512 (7) | 0.0058 (5) | 0.0099 (5) | 0.0057 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0390 (6) | 0.0381 (5) | 0.0389 (6) | 0.0101 (4) | 0.0055 (4) | 0.0029 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0417 (6) | 0.0405 (6) | 0.0426 (6) | 0.0102 (5) | 0.0018 (5) | 0.0033 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0954 (12) | 0.0465 (8) | 0.0535 (8) | 0.0048 (8) | −0.0100 (8) | 0.0109 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0546 (7) | 0.0469 (7) | 0.0476 (7) | 0.0105 (6) | −0.0009 (6) | 0.0022 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0984 (12) | 0.0638 (8) | 0.0706 (9) | 0.0003 (8) | −0.0120 (8) | −0.0121 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0556 (6) | 0.0605 (6) | 0.0781 (7) | 0.0279 (5) | 0.0057 (5) | 0.0043 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0419 (5) | 0.0599 (6) | 0.0653 (6) | 0.0204 (4) | 0.0195 (4) | 0.0194 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—O1 | 1.2055 (18) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.4664 (16) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C8—O2 | 1.4036 (15) |
| C2—C3 | 1.3829 (17) | C8—C9 | 1.5139 (16) |
| C2—C7 | 1.3853 (18) | C8—H8 | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.3871 (15) | C9—C10 | 1.3173 (18) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C9—C11 | 1.4338 (18) |
| C4—C5 | 1.3887 (15) | C10—H10A | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C10—H10B | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3835 (16) | C11—N1 | 1.1410 (19) |
| C5—C8 | 1.5168 (14) | O2—H2 | 0.8200 |
| C6—C7 | 1.3818 (17) | ||
| O1—C1—C2 | 125.37 (14) | C6—C7—C2 | 120.24 (11) |
| O1—C1—H1 | 117.3 | C6—C7—H7 | 119.9 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 117.3 | C2—C7—H7 | 119.9 |
| C3—C2—C7 | 119.84 (10) | O2—C8—C9 | 110.75 (10) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.51 (12) | O2—C8—C5 | 109.36 (9) |
| C7—C2—C1 | 118.64 (12) | C9—C8—C5 | 111.56 (9) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.92 (11) | O2—C8—H8 | 108.4 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C9—C8—H8 | 108.4 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C5—C8—H8 | 108.4 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.20 (11) | C10—C9—C11 | 120.17 (13) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.9 | C10—C9—C8 | 123.43 (12) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.9 | C11—C9—C8 | 116.39 (11) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.58 (10) | C9—C10—H10A | 120.0 |
| C6—C5—C8 | 118.90 (10) | C9—C10—H10B | 120.0 |
| C4—C5—C8 | 121.50 (10) | H10A—C10—H10B | 120.0 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 120.20 (11) | N1—C11—C9 | 179.54 (16) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.9 | C8—O2—H2 | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.9 | ||
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | 1.9 (2) | C3—C2—C7—C6 | 0.60 (19) |
| O1—C1—C2—C7 | −177.02 (14) | C1—C2—C7—C6 | 179.52 (12) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | −1.32 (18) | C6—C5—C8—O2 | −171.48 (11) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 179.80 (11) | C4—C5—C8—O2 | 10.23 (15) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.69 (18) | C6—C5—C8—C9 | −48.61 (15) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.66 (17) | C4—C5—C8—C9 | 133.09 (11) |
| C3—C4—C5—C8 | 178.94 (10) | O2—C8—C9—C10 | −122.89 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −1.38 (19) | C5—C8—C9—C10 | 115.05 (15) |
| C8—C5—C6—C7 | −179.71 (11) | O2—C8—C9—C11 | 56.40 (14) |
| C5—C6—C7—C2 | 0.8 (2) | C5—C8—C9—C11 | −65.67 (14) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2···O1i | 0.82 | 1.99 | 2.8107 (15) | 175 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y−1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: PV2428).
References
- Bruker (2004). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cobo, D., Quiroga, J., Cobo, J., Low, J. N. & Glidewell, C. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o3639–o3641.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Nizam Mohideen, M., Kannan, P. S., Subbiah Pandi, A., Ramesh, E. & Raghunathan, R. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o4756.
- Ohsumi, K., Nakagawa, R., Fukuda, Y., Hatanaka, T., Morinaga, Y., Nihei, Y., Ohishi, K., Suga, Y., Akiyama, Y. & Tsuji, T. (1998). J. Med. Chem. 41, 3022–3032. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681102976X/pv2428sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681102976X/pv2428Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681102976X/pv2428Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report