Abstract
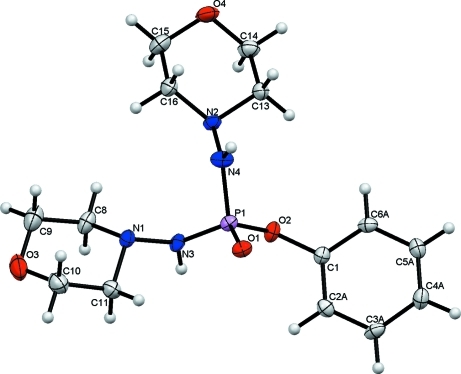
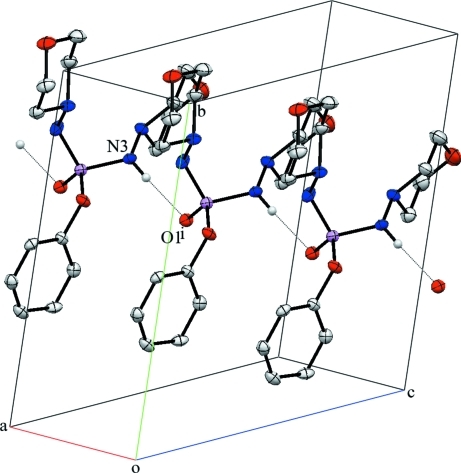
In the title compound, C14H23N4O4P, the P atom is in a distorted tetrahedral environment with bond angles in the range 96.87 (6)–119.86 (6)°. The two morpholinyl groups adopt a chair conformation. The phenyl ring is disordered over two sets of sites with equal occupancies [0.500 (2)]. In the crystal, adjacent molecules are linked via N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds into an extended chain running parallel to the a axis. Only one of the amidate N—H groups is involved in hydrogen bonding.
Related literature
For background to compounds having a P(=O)(O)(N)(N) skeleton, see: Sabbaghi et al. (2010 ▶). For bond lengths and angles in related structures, see: Ghadimi et al. (2009 ▶).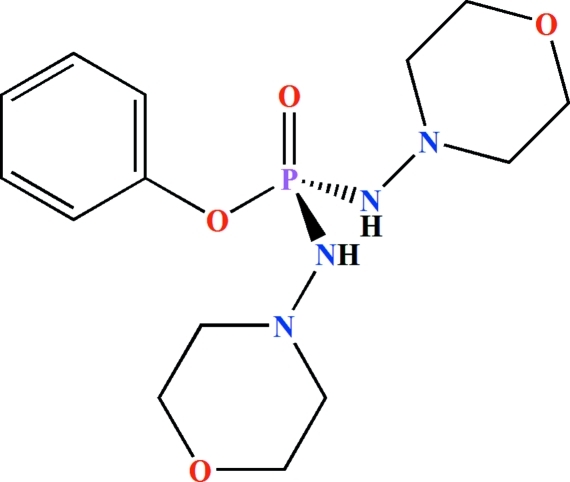
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H23N4O4P
M r = 342.33
Triclinic,
a = 4.7469 (2) Å
b = 12.3528 (5) Å
c = 14.2149 (5) Å
α = 90.542 (3)°
β = 98.389 (4)°
γ = 93.009 (4)°
V = 823.35 (6) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.19 mm−1
T = 120 K
0.20 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur S diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.877, T max = 1.000
10043 measured reflections
2888 independent reflections
2272 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.021
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.029
wR(F 2) = 0.070
S = 0.99
2888 reflections
262 parameters
162 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.32 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis CCD (Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶); data reduction: CrysAlis RED; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: enCIFer (Allen et al., 2004 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811029734/gk2392sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811029734/gk2392Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811029734/gk2392Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3—H3N⋯O1i | 0.823 (15) | 2.093 (16) | 2.8951 (16) | 164.9 (15) |
Symmetry code: (i) 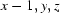 .
.
Acknowledgments
Support of this investigation by Ferdowsi University of Mashhad is gratefully acknowledged.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Structure determination of the title compound, P(O)[OC6H5][NHNC4H8O]2 (Fig. 1), was performed as a part of a project in our laboratory on the synthesis of compounds having a P(═O)(O)(N)(N) skeleton (Sabbaghi et al., 2010). Single crystals of title compound were obtained from a mixture of CH3OH/CH3CN (4:1 v/v) after slow evaporation at room temperature.
The P═O (1.4705 (10) Å), P—O (1.5975 (10) Å) and P—N (1.6295 (13) Å & 1.6331 (13) Å) bond lengths and the C—O—P angle (122.17 (8)°) are standard for this category of compounds (Ghadimi et al., 2009). The P atom has a distorted tetrahedral configuration (Fig. 1), the bond angles at the P atom vary in the range from 96.87 (6)° [the angle O2—P1—N3] to 119.86 (6)° [the angle O1—P1—N3].
In the crystal, the molecules are hydrogen-bonded in a linear arrangement parallel to [100] through N3—H3N···O1i [symmetry code: (i) x - 1, y, z] hydrogen bond (Table 1, Fig. 2).
Experimental
To a solution of phenyldichlorophosphate (2.507 mmol) in chloroform (15 ml), a solution of aminomorpholine (10.028 mmol) in chloroform (30 ml) was added at 273 K. After 4 h of stirring, the solvent was evaporated in vacuum. The solid was washed with distilled water. Single crystals, suitable for crystallography, were obtained from a solution of the title compound in methanol and acetonitrile (4:1) after slow evaporation at room temperature. IR (KBr, cm-1): 3278, 3107, 2945, 2869, 2830, 1588, 1488, 1223, 1107, 926, 869, 759, 698.
Refinement
All carbon bound H atoms were placed at calculated positions and were refined as riding with their Uiso set to 1.2Ueq of the respective carrier atoms. Nitrogen bound H atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and refined isotropically. The disordered phenyl group was modeled over two sites using similarity restraints on anisotropic displacement parameters.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with ellipsoids shown at the 50% probability level. The disorder is not shown.
Fig. 2.
Partial packing view showing the formation of the chain through N—H···O hydrogen bond (shown as dotted lines). H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity. [Symmetry code: (i) x - 1, y, z]
Crystal data
| C14H23N4O4P | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 342.33 | F(000) = 364 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.381 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 4.7469 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 5042 reflections |
| b = 12.3528 (5) Å | θ = 3.3–27.2° |
| c = 14.2149 (5) Å | µ = 0.19 mm−1 |
| α = 90.542 (3)° | T = 120 K |
| β = 98.389 (4)° | Prism, colorless |
| γ = 93.009 (4)° | 0.20 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm |
| V = 823.35 (6) Å3 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur S diffractometer | 2888 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 2272 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.021 |
| Detector resolution: 8.4353 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 3.3° |
| ω scans | h = −5→5 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2009) | k = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.877, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −16→9 |
| 10043 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.029 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.070 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 0.99 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0404P)2P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2888 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 262 parameters | Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3 |
| 162 restraints | Δρmin = −0.32 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| P1 | 0.34183 (7) | 0.63069 (3) | 0.29935 (3) | 0.01615 (12) | |
| O1 | 0.55619 (19) | 0.55524 (7) | 0.33888 (7) | 0.0196 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.11776 (19) | 0.58245 (7) | 0.21233 (7) | 0.0196 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.1822 (2) | 0.80213 (10) | 0.63761 (8) | 0.0382 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.3795 (2) | 1.01932 (8) | 0.11186 (8) | 0.0310 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.1088 (3) | 0.67116 (10) | 0.36409 (9) | 0.0180 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.1500 (3) | 0.48228 (11) | 0.16832 (11) | 0.0169 (3) | |
| C2A | 0.1144 (7) | 0.3882 (2) | 0.2144 (3) | 0.0201 (8) | 0.500 (2) |
| H2AA | 0.0754 | 0.3896 | 0.2781 | 0.024* | 0.500 (2) |
| C3A | 0.1348 (8) | 0.2902 (2) | 0.1688 (3) | 0.0228 (8) | 0.500 (2) |
| H3AA | 0.1112 | 0.2236 | 0.2004 | 0.027* | 0.500 (2) |
| C4A | 0.192 (5) | 0.2917 (13) | 0.0735 (11) | 0.0236 (19) | 0.500 (2) |
| H4AA | 0.2198 | 0.2253 | 0.0426 | 0.028* | 0.500 (2) |
| C5A | 0.2073 (6) | 0.3829 (2) | 0.0270 (2) | 0.0222 (8) | 0.500 (2) |
| H5AA | 0.2332 | 0.3813 | −0.0381 | 0.027* | 0.500 (2) |
| C6A | 0.1858 (6) | 0.4815 (2) | 0.0724 (2) | 0.0193 (8) | 0.500 (2) |
| H6AA | 0.1953 | 0.5475 | 0.0388 | 0.023* | 0.500 (2) |
| C2B | −0.0552 (7) | 0.4023 (2) | 0.1721 (2) | 0.0220 (8) | 0.500 (2) |
| H2BA | −0.2160 | 0.4145 | 0.2028 | 0.026* | 0.500 (2) |
| C3B | −0.0253 (8) | 0.3024 (3) | 0.1303 (3) | 0.0276 (9) | 0.500 (2) |
| H3BA | −0.1718 | 0.2470 | 0.1306 | 0.033* | 0.500 (2) |
| C4B | 0.203 (5) | 0.2816 (13) | 0.0897 (11) | 0.023 (2) | 0.500 (2) |
| H4BA | 0.2230 | 0.2116 | 0.0642 | 0.027* | 0.500 (2) |
| C5B | 0.4184 (6) | 0.3673 (2) | 0.0852 (2) | 0.0255 (9) | 0.500 (2) |
| H5BA | 0.5776 | 0.3553 | 0.0538 | 0.031* | 0.500 (2) |
| C6B | 0.3922 (6) | 0.4675 (2) | 0.1271 (2) | 0.0214 (8) | 0.500 (2) |
| H6BA | 0.5358 | 0.5241 | 0.1274 | 0.026* | 0.500 (2) |
| N1 | 0.2242 (2) | 0.72689 (9) | 0.45092 (9) | 0.0187 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.0377 (3) | 0.81391 (12) | 0.46689 (12) | 0.0274 (4) | |
| H8A | −0.1571 | 0.7832 | 0.4706 | 0.033* | |
| H8B | 0.0268 | 0.8651 | 0.4134 | 0.033* | |
| C9 | 0.1576 (4) | 0.87271 (13) | 0.55883 (13) | 0.0374 (5) | |
| H9A | 0.3480 | 0.9064 | 0.5530 | 0.045* | |
| H9B | 0.0319 | 0.9314 | 0.5703 | 0.045* | |
| C10 | 0.3616 (4) | 0.71670 (14) | 0.62119 (12) | 0.0330 (4) | |
| H10A | 0.3772 | 0.6673 | 0.6759 | 0.040* | |
| H10B | 0.5552 | 0.7478 | 0.6160 | 0.040* | |
| C11 | 0.2460 (3) | 0.65330 (12) | 0.53168 (11) | 0.0257 (4) | |
| H11A | 0.3746 | 0.5950 | 0.5217 | 0.031* | |
| H11B | 0.0557 | 0.6194 | 0.5373 | 0.031* | |
| N4 | 0.5044 (3) | 0.73922 (10) | 0.26441 (10) | 0.0217 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.3561 (2) | 0.82518 (9) | 0.21815 (9) | 0.0182 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.3853 (3) | 0.82364 (12) | 0.11680 (11) | 0.0219 (4) | |
| H13A | 0.2914 | 0.7562 | 0.0862 | 0.026* | |
| H13B | 0.5898 | 0.8251 | 0.1096 | 0.026* | |
| C14 | 0.2503 (3) | 0.92070 (12) | 0.06897 (12) | 0.0280 (4) | |
| H14A | 0.2714 | 0.9192 | 0.0007 | 0.034* | |
| H14B | 0.0440 | 0.9171 | 0.0737 | 0.034* | |
| C15 | 0.3467 (4) | 1.02243 (12) | 0.20977 (13) | 0.0334 (4) | |
| H15A | 0.1412 | 1.0206 | 0.2156 | 0.040* | |
| H15B | 0.4364 | 1.0911 | 0.2393 | 0.040* | |
| C16 | 0.4816 (3) | 0.92776 (12) | 0.26208 (12) | 0.0267 (4) | |
| H16A | 0.6896 | 0.9322 | 0.2603 | 0.032* | |
| H16B | 0.4514 | 0.9308 | 0.3295 | 0.032* | |
| H3N | −0.035 (3) | 0.6311 (12) | 0.3652 (11) | 0.024 (4)* | |
| H4N | 0.674 (4) | 0.7378 (13) | 0.2627 (12) | 0.032 (5)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| P1 | 0.01465 (19) | 0.01504 (19) | 0.0181 (3) | 0.00138 (14) | −0.00015 (16) | 0.00092 (16) |
| O1 | 0.0163 (5) | 0.0179 (5) | 0.0238 (7) | 0.0023 (4) | −0.0004 (4) | 0.0032 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0187 (5) | 0.0187 (5) | 0.0201 (7) | 0.0048 (4) | −0.0027 (5) | −0.0049 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0424 (7) | 0.0456 (7) | 0.0272 (8) | −0.0048 (6) | 0.0110 (6) | −0.0135 (6) |
| O4 | 0.0410 (7) | 0.0185 (6) | 0.0328 (8) | −0.0035 (5) | 0.0047 (6) | 0.0074 (5) |
| N3 | 0.0157 (6) | 0.0174 (6) | 0.0196 (8) | −0.0032 (5) | −0.0004 (6) | −0.0047 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0163 (7) | 0.0169 (7) | 0.0168 (9) | 0.0032 (6) | −0.0004 (6) | −0.0007 (7) |
| C2A | 0.0189 (16) | 0.0240 (16) | 0.0173 (19) | 0.0026 (13) | 0.0012 (15) | 0.0018 (14) |
| C3A | 0.0257 (18) | 0.0142 (15) | 0.026 (2) | −0.0001 (14) | −0.0026 (18) | 0.0050 (15) |
| C4A | 0.028 (3) | 0.023 (4) | 0.020 (4) | 0.006 (3) | 0.000 (4) | −0.005 (3) |
| C5A | 0.0229 (17) | 0.0264 (17) | 0.0173 (19) | 0.0017 (13) | 0.0037 (15) | −0.0025 (14) |
| C6A | 0.0189 (16) | 0.0177 (14) | 0.0203 (19) | −0.0018 (12) | 0.0000 (15) | 0.0051 (13) |
| C2B | 0.0207 (17) | 0.0256 (16) | 0.020 (2) | 0.0007 (13) | 0.0047 (16) | 0.0038 (14) |
| C3B | 0.0274 (19) | 0.0203 (16) | 0.033 (2) | −0.0035 (15) | 0.0000 (18) | 0.0058 (16) |
| C4B | 0.033 (3) | 0.012 (2) | 0.022 (5) | 0.009 (2) | −0.003 (4) | 0.005 (3) |
| C5B | 0.0223 (16) | 0.0326 (17) | 0.022 (2) | 0.0087 (13) | 0.0020 (15) | −0.0064 (15) |
| C6B | 0.0180 (16) | 0.0232 (15) | 0.022 (2) | 0.0006 (12) | 0.0003 (14) | 0.0008 (14) |
| N1 | 0.0203 (6) | 0.0183 (6) | 0.0169 (8) | 0.0005 (5) | 0.0007 (6) | −0.0030 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0283 (8) | 0.0213 (8) | 0.0322 (11) | 0.0036 (7) | 0.0028 (8) | −0.0077 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0410 (10) | 0.0298 (9) | 0.0412 (13) | 0.0025 (8) | 0.0063 (9) | −0.0134 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0393 (10) | 0.0366 (10) | 0.0228 (11) | −0.0037 (8) | 0.0059 (8) | −0.0001 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0318 (9) | 0.0248 (8) | 0.0207 (10) | −0.0010 (7) | 0.0052 (8) | 0.0026 (8) |
| N4 | 0.0140 (6) | 0.0227 (7) | 0.0279 (9) | 0.0020 (5) | 0.0007 (6) | 0.0088 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0222 (6) | 0.0142 (6) | 0.0172 (8) | 0.0013 (5) | −0.0011 (6) | 0.0035 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0272 (8) | 0.0201 (8) | 0.0177 (10) | −0.0015 (6) | 0.0022 (7) | −0.0006 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0341 (9) | 0.0240 (8) | 0.0241 (11) | −0.0027 (7) | −0.0006 (8) | 0.0055 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0449 (10) | 0.0179 (8) | 0.0381 (12) | −0.0018 (7) | 0.0097 (9) | −0.0020 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0345 (9) | 0.0223 (8) | 0.0224 (10) | −0.0063 (7) | 0.0040 (8) | −0.0034 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| P1—O1 | 1.4705 (10) | C5B—C6B | 1.387 (4) |
| P1—O2 | 1.5975 (10) | C5B—H5BA | 0.9500 |
| P1—N4 | 1.6295 (13) | C6B—H6BA | 0.9500 |
| P1—N3 | 1.6331 (13) | N1—C8 | 1.4645 (17) |
| O2—C1 | 1.4068 (16) | N1—C11 | 1.4663 (19) |
| O3—C9 | 1.421 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.510 (2) |
| O3—C10 | 1.4286 (19) | C8—H8A | 0.9900 |
| O4—C15 | 1.4233 (19) | C8—H8B | 0.9900 |
| O4—C14 | 1.4249 (17) | C9—H9A | 0.9900 |
| N3—N1 | 1.4297 (17) | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| N3—H3N | 0.823 (15) | C10—C11 | 1.505 (2) |
| C1—C2A | 1.354 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9900 |
| C1—C2B | 1.358 (3) | C10—H10B | 0.9900 |
| C1—C6B | 1.384 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| C1—C6A | 1.399 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C2A—C3A | 1.382 (4) | N4—N2 | 1.4186 (16) |
| C2A—H2AA | 0.9500 | N4—H4N | 0.811 (16) |
| C3A—C4A | 1.421 (17) | N2—C16 | 1.4656 (18) |
| C3A—H3AA | 0.9500 | N2—C13 | 1.4674 (18) |
| C4A—C5A | 1.316 (15) | C13—C14 | 1.510 (2) |
| C4A—H4AA | 0.9500 | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| C5A—C6A | 1.389 (4) | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| C5A—H5AA | 0.9500 | C14—H14A | 0.9900 |
| C6A—H6AA | 0.9500 | C14—H14B | 0.9900 |
| C2B—C3B | 1.388 (4) | C15—C16 | 1.512 (2) |
| C2B—H2BA | 0.9500 | C15—H15A | 0.9900 |
| C3B—C4B | 1.33 (2) | C15—H15B | 0.9900 |
| C3B—H3BA | 0.9500 | C16—H16A | 0.9900 |
| C4B—C5B | 1.44 (2) | C16—H16B | 0.9900 |
| C4B—H4BA | 0.9500 | ||
| O1—P1—O2 | 114.63 (5) | N1—C8—H8A | 109.9 |
| O1—P1—N4 | 108.95 (6) | C9—C8—H8A | 109.9 |
| O2—P1—N4 | 108.62 (6) | N1—C8—H8B | 109.9 |
| O1—P1—N3 | 119.86 (6) | C9—C8—H8B | 109.9 |
| O2—P1—N3 | 96.87 (6) | H8A—C8—H8B | 108.3 |
| N4—P1—N3 | 106.95 (7) | O3—C9—C8 | 112.07 (14) |
| C1—O2—P1 | 122.17 (8) | O3—C9—H9A | 109.2 |
| C9—O3—C10 | 109.51 (13) | C8—C9—H9A | 109.2 |
| C15—O4—C14 | 109.64 (12) | O3—C9—H9B | 109.2 |
| N1—N3—P1 | 115.73 (9) | C8—C9—H9B | 109.2 |
| N1—N3—H3N | 116.7 (11) | H9A—C9—H9B | 107.9 |
| P1—N3—H3N | 116.9 (11) | O3—C10—C11 | 111.43 (13) |
| C2A—C1—C6B | 103.2 (2) | O3—C10—H10A | 109.3 |
| C2B—C1—C6B | 122.9 (2) | C11—C10—H10A | 109.3 |
| C2A—C1—C6A | 120.6 (2) | O3—C10—H10B | 109.3 |
| C2B—C1—C6A | 103.1 (2) | C11—C10—H10B | 109.3 |
| C2A—C1—O2 | 120.66 (18) | H10A—C10—H10B | 108.0 |
| C2B—C1—O2 | 117.71 (18) | N1—C11—C10 | 109.01 (13) |
| C6B—C1—O2 | 119.37 (17) | N1—C11—H11A | 109.9 |
| C6A—C1—O2 | 118.26 (16) | C10—C11—H11A | 109.9 |
| C1—C2A—C3A | 120.0 (3) | N1—C11—H11B | 109.9 |
| C1—C2A—H2AA | 120.0 | C10—C11—H11B | 109.9 |
| C3A—C2A—H2AA | 120.0 | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.3 |
| C2A—C3A—C4A | 118.2 (7) | N2—N4—P1 | 122.73 (9) |
| C2A—C3A—H3AA | 120.9 | N2—N4—H4N | 118.0 (12) |
| C4A—C3A—H3AA | 120.9 | P1—N4—H4N | 117.8 (12) |
| C5A—C4A—C3A | 121.4 (13) | N4—N2—C16 | 108.27 (11) |
| C5A—C4A—H4AA | 119.3 | N4—N2—C13 | 109.67 (11) |
| C3A—C4A—H4AA | 119.3 | C16—N2—C13 | 109.55 (11) |
| C4A—C5A—C6A | 120.4 (8) | N2—C13—C14 | 109.89 (12) |
| C4A—C5A—H5AA | 119.8 | N2—C13—H13A | 109.7 |
| C6A—C5A—H5AA | 119.8 | C14—C13—H13A | 109.7 |
| C5A—C6A—C1 | 119.0 (3) | N2—C13—H13B | 109.7 |
| C5A—C6A—H6AA | 120.5 | C14—C13—H13B | 109.7 |
| C1—C6A—H6AA | 120.5 | H13A—C13—H13B | 108.2 |
| C1—C2B—C3B | 118.6 (3) | O4—C14—C13 | 111.09 (12) |
| C1—C2B—H2BA | 120.7 | O4—C14—H14A | 109.4 |
| C3B—C2B—H2BA | 120.7 | C13—C14—H14A | 109.4 |
| C4B—C3B—C2B | 122.1 (8) | O4—C14—H14B | 109.4 |
| C4B—C3B—H3BA | 119.0 | C13—C14—H14B | 109.4 |
| C2B—C3B—H3BA | 119.0 | H14A—C14—H14B | 108.0 |
| C3B—C4B—C5B | 118.9 (13) | O4—C15—C16 | 111.29 (13) |
| C3B—C4B—H4BA | 120.6 | O4—C15—H15A | 109.4 |
| C5B—C4B—H4BA | 120.6 | C16—C15—H15A | 109.4 |
| C6B—C5B—C4B | 119.7 (9) | O4—C15—H15B | 109.4 |
| C6B—C5B—H5BA | 120.2 | C16—C15—H15B | 109.4 |
| C4B—C5B—H5BA | 120.2 | H15A—C15—H15B | 108.0 |
| C1—C6B—C5B | 117.8 (3) | N2—C16—C15 | 110.24 (13) |
| C1—C6B—H6BA | 121.1 | N2—C16—H16A | 109.6 |
| C5B—C6B—H6BA | 121.1 | C15—C16—H16A | 109.6 |
| N3—N1—C8 | 108.48 (11) | N2—C16—H16B | 109.6 |
| N3—N1—C11 | 111.34 (11) | C15—C16—H16B | 109.6 |
| C8—N1—C11 | 109.63 (13) | H16A—C16—H16B | 108.1 |
| N1—C8—C9 | 108.73 (13) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H3N···O1i | 0.823 (15) | 2.093 (16) | 2.8951 (16) | 164.9 (15) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: GK2392).
References
- Allen, F. H., Johnson, O., Shields, G. P., Smith, B. R. & Towler, M. (2004). J. Appl. Cryst. 37, 335–338.
- Ghadimi, S., Pourayoubi, M. & Ebrahimi Valmoozi, A. A. (2009). Z. Naturforsch. Teil B, 64, 565–569.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Oxford Diffraction (2009). CrysAlis CCD and CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Sabbaghi, F., Mancilla Percino, T., Pourayoubi, M. & Leyva, M. A. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811029734/gk2392sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811029734/gk2392Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811029734/gk2392Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report