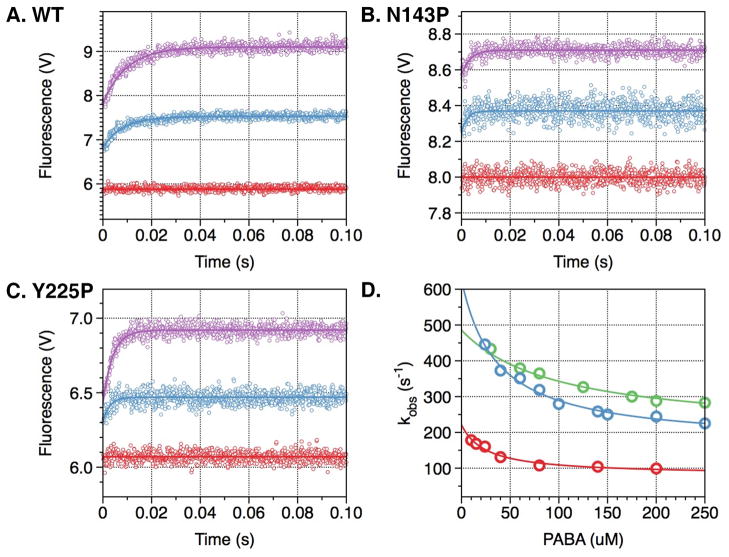
Figure 2. PABA binding to thrombin wild type and mutants N143P and Y225P.
Kinetic traces of PABA binding to thrombin wild type (A) and mutants N143P (B) and Y225P (C). In all cases, binding of PABA obeys a two-step mechanism, with a fast phase completed within the dead time (<0.5 ms) of the spectrometer, followed by a single-exponential slow phase. Traces were recorded in the presence of 40 μM (cyan) or 200 μM (purple) PABA. Controls with 200 μM PABA in buffer are shown in red. (D) The kobs for the slow phase decreases with increasing [PABA]. The values were obtained from analysis of the kinetic traces (A-C) and analyzed according to eq 3 in the text with best-fit parameter values reported in Table 2 for wild type (red), N143P (green) and Y225P (cyan). Experimental conditions are: 1 μM enzyme, 50 mM Tris, 0.1% PEG8000, pH 8.0, at 15 °C. The value of kobs features an inverse hyperbolic dependence on [PABA], thereby proving the existence of the E*-E equilibrium preceding PABA binding.