Abstract
Otoliths are biocalcified bodies connected to the sensory system in the inner ears of fish. Their layered, biorhythm-following formation provides individual records of the age, the individual history and the natural environment of extinct and living fish species. Such data are critical for ecosystem and fisheries monitoring. They however often lack validation and the poor understanding of biomineralization mechanisms has led to striking examples of misinterpretations and subsequent erroneous conclusions in fish ecology and fisheries management. Here we develop and validate a numerical model of otolith biomineralization. Based on a general bioenergetic theory, it disentangles the complex interplay between metabolic and temperature effects on biomineralization. This model resolves controversial issues and explains poorly understood observations of otolith formation. It represents a unique simulation tool to improve otolith interpretation and applications, and, beyond, to address the effects of both climate change and ocean acidification on other biomineralizing organisms such as corals and bivalves.
Introduction
Otoliths, biomineralized aragonite bodies in the fish inner ear, have long been recognized as key biological archives. Many species deposit seasonally alternating opaque and translucent zones (Fig. 1) that provide proxies of age critical in fish population dynamics [1]. By providing dated morphological, structural and chemical signatures, otoliths are also keys for past and present environment reconstructions [2] and life trait characterization [3], [4], [5], [6]. Such data are critical for marine ecosystem and fisheries monitoring. Due to the poor understanding of biomineralization mechanisms, otolith proxies however often lack validation and are open to subjective interpretations [1], [7]. Inaccurate otolith-based age estimation of orange roughy off New Zealand [8] and walleye pollock in the Bering Sea [9] are among the most striking examples of misinterpretations that have contributed to the overexploitation of fish populations.
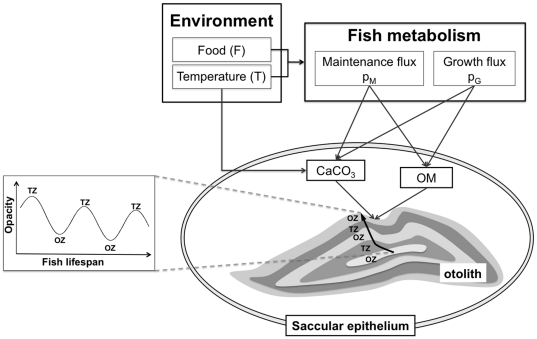
Figure 1. Model for otolith biomineralization.
Otolith formation corresponds to an accretion of successive layers of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) embedded in an organic matrix (OM) which precursors are synthesized by the saccular epithelium. At a yearly scale seasonal environmental and physiological variations induce opacity changes with an alternated deposition of translucent (TZ) and opaque (OZ) zones appearing respectively as dark and bright zones under reflected light. We here state the otolith as a metabolic product as defined by the Dynamic Energy Budget (DEB) theory for metabolic organization [18]; Otolith formation is driven by fish growth (pG) and maintenance (pM) metabolic fluxes which depend on the individual state and the temperature and feeding conditions the fish experiences. We also account for the temperature-dependent dynamics of CaCO3 precipitation [15].
Both metabolism and temperature are known to play key roles in otolith biomineralization [1], [10], [11]. As highlighted by meta-analyses [1], [12], disentangling these two factors is however challenging. In temperate waters, the formation of translucent zones is generally considered to occur during winter whereas opaque zones would be formed during rapid growth periods in spring and summer (Fig. 1). However, this statement is often not valid. Opposite patterns have been reported as well as additional non-periodical zones that may lead to erroneous age and growth estimations [13]. Neither experimental studies monitoring temperature and feeding conditions [10], [11] nor proposed otolith biomineralization models [14], [15], [16] have been able to explain the complex interplay between fish metabolism and temperature on otolith formation. In particular, consideration of mineral factors alone [15] has been challenged by recent characterizations of the role of organic compounds in otolith biomineralization [17].
We here propose a bioenergetic model of otolith biomineralization in the framework of the Dynamic Energy Budget (DEB) theory [18] (Fig. 1). This general theory for metabolic organization describes how an organism assimilates and utilizes energy throughout its life cycle. The key feature here is the application of the concept of metabolic product, as defined by DEB theory [18]. The mineral and organic fractions of the otolith are regarded as individual metabolic products involving contributions from somatic growth (pG) and maintenance (pM) DEB energy fluxes (Fig. 1), and otolith opacity variations result from variations in the ratio between these two fractions [19]. Given that in vitro aragonite precipitation is temperature-dependent [15], temperature variations also directly act on the dynamics of the mineral fraction (Fig. 1). Mathematically, given the parameterization of metabolic fluxes pG and pM defined by DEB theory [18], otolith growth (Eq. 1) and opacity (Eq. 3) can be regarded as functions of the state of the individual (reserves and length) and of its environment (temperature and food density). The 1D simulation of otolith formation may be transformed into a 2D transverse section image of a growing otolith using calibrated shape deformation algorithms for otolith images [20].
Results and Discussion
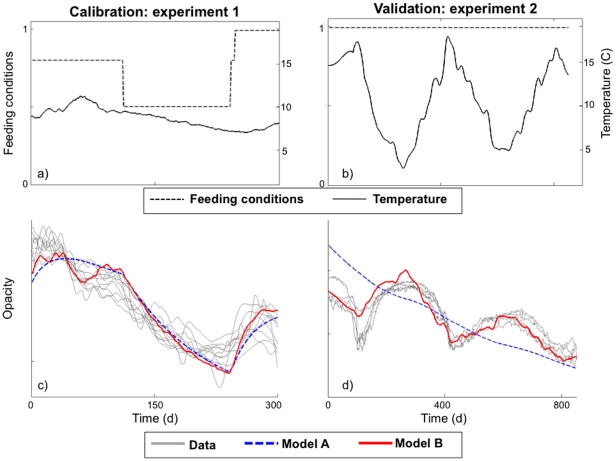
Model calibration and validation were carried out from two experimental cod otolith datasets. The calibration relied on a 300-day experiment on juvenile cod which experienced a shift to lower feeding conditions and varying temperatures (Fig. 2a; Fig. S1 & S2 and Table S1 & S2). The validation involved a 800-day experiment on juvenile cod which experienced seasonal temperature variations and constant feeding (Fig. 2b; Fig. S3 & S4). Metabolic effects alone induced most of the opacity variations in the first experiment but could not explain seasonal opacity signals in the second experiment (Fig. 2; Fig. S2 & S4). Temperature factor cC(T) was negatively correlated to opacity in the first experiment (Fig. 2, left column) and could not account for the overall decreasing opacity trend in the second experiment (Fig. S4). Only the interplay between the metabolic and temperature factors led to a reliable prediction (R2>0.9, p<0.001 in both cases). These results also outlined the different dynamics of feeding and temperature effects. Whereas temperature acted immediately through the regulation factor cC(T), food-induced effects were typically smoothed out, the reserves of the individual acting as a buffer.
Figure 2. Model calibration and validation on cod otoliths using two experimental datasets: 1) reduced feeding conditions (day 110 to day 220) with seasonal temperature variations (left column), and 2) constant feeding with seasonal temperature cycles over a two-and-a-half-year period (right column).
We report temperature and feeding conditions (a, b) and the comparison between model simulations and opacity data (c, d). We display opacity data (Data, gray) and model simulations without the temperature effect on calcium carbonate precipitation (Model A, blue) and with this temperature effect (Model B, red).
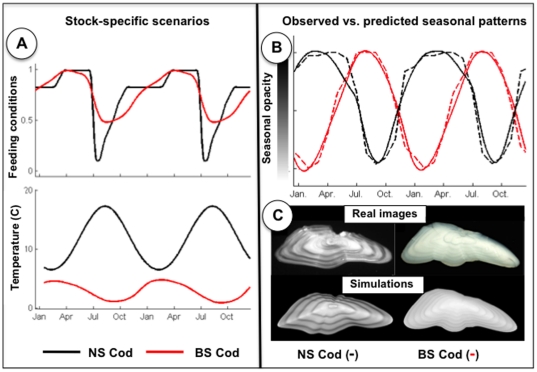
The proposed model opens up new prospects for the understanding of differences in otolith patterns of a given species within different ecosystems (Fig. 3). As an illustration, we considered two cod populations respectively in the Barents Sea (BS) and in the southern North Sea (NS) (Fig. 3). Their otoliths depict antiphasic seasonal opacity patterns (Fig. 3B). BS cod follows the general pattern with a winter translucent zone and an summer opaque zone, while NS cod forms an opaque zone in spring and a translucent one in late summer [21]. In addition, NS cod otolith images are much more contrasted than BS cod ones (Fig. 3C). By forcing the calibrated model with population-specific feeding and temperature scenarios stated from data available in the literature (Fig. S5, and Video S1), we explained these two population-specific characteristics. The smaller variations in both feeding and temperature conditions experienced by the BS cod result in otolith images with a lower contrast well redrawn by the model (Fig. 3C). Observed seasonal patterns (dashed lines, Fig. 3B), given as the relative proportions of opaque edges in monthly sampled otolith sets [21], were compared to normalized versions of the simulated opacity patterns (solid lines, Fig. 3B; Fig. S6). The model convincingly reproduced the seasonal patterns (R2>0.96 p<0.001). Neither of the two populations conforms to the generally assumed interpretation, i.e. slow-growth winter translucent zones and fast-growth summer opaque ones [1]. BS cod forms a late winter translucent zone which is induced by migration to warmer waters rather than slow-growth conditions (Fig. S8). The opposite pattern of the NS cod results from the late summer formation of a translucent zone due to low feeding activity with simultaneous high temperatures (Fig. S7). Besides, we showed that similar seasonal opacity patterns for different populations, here Barents sea cod and Norwegian coast cod populations, might not necessarily refer to similar feeding and temperature conditions but might also be observed with different population-specific scenarios (Fig. S9). These results highlight the complex interplay between temperature and feeding conditions each of which may individually have a positive or a negative effect on otolith growth and opacity. These interactions as well as the above-mentioned differences in their relative response dynamics explain why empirical studies have reached contradictory conclusions on the regulation of the formation of otolith structures among species and stocks [12].
Figure 3. Resolving the non-synchronous seasonality of opacity patterns of Barents Sea (BS) and southern North Sea (NS) cod otoliths: Feeding and temperature conditions (panel A) that explain otolith opacity patterns observed for southern North Sea (NS, black) and Barents Sea (BS, red) cod (panels B and C).
Observed seasonal patterns (dashed lines), given as the relative proportions of opaque edges in the monthly sampled otolith sets [21], are compared to normalized simulated opacity patterns (solid lines). Model simulations reproduce both the opposite seasonal opacity patterns (panel B) and the remarkable differences in the contrast of the otolith images of the two populations (panel C). The Supp. Mat. details the stock-specific scenarios (Text S1 & Fig. S5) and animated model simulations are provide as an electronic appendix (Video S1).
Improving the reliability of otolith-based individual and population data is critical to population dynamics and ecology. In this respect, our model provides a conceptual basis to interpret well-known but poorly understood otolith characteristics:
The coupling between otolith growth and fish somatic growth during high feeding periods [10], [22] results from the large contribution of the somatic growth flux (αCpG>>βCpG, Eq. 1). In contrast, low feeding periods [10], [22] lead to a decoupling due to the weaker but significant contribution of the maintenance flux in otolith growth (αCpG∼0 and βCpG>0, Eq. 1);
The correlation between otolith growth and fish respiration [23] follows naturally as CO2 production is also modelled as a weighted sum of metabolic processes in a DEB context [18];
The differences in the relative contributions from the somatic and maintenance fluxes (Eq. 3) result in metabolism-induced opacity changes; improved feeding conditions lead to a more opaque accretion [21]. They also explain the lifespan decrease of opacity as the growth flux decreases as the individual gets closer to its asymptotic size [19];
The greater otolith accretion at higher temperatures [11], [24] is a direct outcome of the temperature-dependent dynamics of the precipitation of aragonite (Eq. 1). This mechanism also accounts for the formation of a more opaque otolith zone when the fish experiences colder temperatures [11], [24].
Beyond these new mechanistic interpretations, scenario-based model simulations are of primary interest to interpret and predict otolith characteristics in response to environmental changes (e.g. climate). For instance, they provide new means for the discrimination of seasonal vs. non-seasonal otolith structures, a crucial issue for the improvement of the accuracy of individual age data [1]. Direct model inversion also presents a great potential for the reconstruction of individual life traits from otolith patterns. For instance, given temperature records obtained from data storage tags or estimated from the oxygen isotopic ratios of the otolith, modeled otolith accretion and opacity may be fitted to the recorded macrostructures of real otoliths by tuning individual feeding dynamics and growth. To our knowledge, the acquisition of feeding dynamics at the individual scale remains a challenge in non-monitored environments, but it is particularly important for the understanding and prediction of food web dynamics. The analysis of otolith chemical composition could also benefit from the proposed framework. Both element and isotopic signatures provide invaluable information on fish migration and population connectivity [4], [6]. However, they often depict complex interactions between endogenous and environmental factors [7] that may be deciphered by extensions of our approach.
The biomineralization of other structures such as coral skeletons and bivalve shells also lacks a comprehensive understanding. The proposed framework provides a generic basis for modeling their formation. The biomineralization mechanisms we considered, a metabolism-driven control parameterized by somatic growth (assumption A1) and maintenance energy fluxes and a temperature-specific effect on precipitation dynamics and (assumption A2) are generic and their implementation exploits a theory for metabolic organization already applied to fish, bivalves and corals [25], [26]. DEB-based biomineralization models could then provide simulation tools to addres the effects of climate change on a large variety of calcifying organisms [27]. Furthermore, by providing a framework where pH conditions could impact i) metabolic processes and ii) CaCO3 precipitation directly and indirectly via their impact on metabolic processes, we strongly believe that these models represent a promising starting point to investigate the consequences of ocean acidification on biocalcifying organisms [28].
Methods
A generic model of otolith formation
The biomineralization of otoliths is primarily controlled by organic compounds in the endolymph [17]. These organic compounds being synthesized by specialized cells of the saccular epithelium, we here relate otolith formation to fish bioenergetics in the framework of the DEB theory [18]. Our model relies on two basic assumptions:
A1-Both the aragonite fraction and the organic matrix of an otolith are metabolic products. In DEB theory, such compounds are formed during metabolic processes but do not require maintenance and are not used to fuel other metabolic processes [18]. This applies to fish otoliths as they are inert biomineralized structures whose formation is primarily controlled by physiological factors [17];
A2-The precipitation of the mineral fraction of the otolith is temperature-dependent. This assumption is supported by in-vitro analysis of aragonite precipitation [15].
From (A1), the dynamics of the volumes of the mineral and organic fractions of the otolith, respectively VC (µm3) and VP (µm3), are derived as functions of the somatic growth flux (pG, J.d−1) and the maintenance flux (pM, J.d−1) of an individual fish:
| (1) |
| (2) |
where αC, βC, αP, βP (µm3.J−1) are model parameters. The regulation factor cC(T), stated as an Arrhenius law (Text S1, Section 1), accounts for the temperature effect on mineral precipitation dynamics (A2). As defined by DEB theory [18], the growth and maintenance fluxes (pG and pM) are functions of the state of the individual (reserves and length) and of its environment (temperature and food density) (Text S1, Section 1). Given that the organic fraction accounts for less than 5% of the otolith volume [17], we neglect its contribution and the otolith volume is predicted by the volume of the mineral fraction.
Otolith opacity O relates to variations in the ratio between the volumes ΔVP and ΔVC of the organic and mineral fractions of the newly precipitated material [19]:
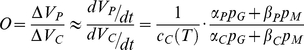 |
(3) |
The temporal simulation of otolith formation is transformed into a 2D transverse section image of an otolith using calibrated shape deformation algorithms [20]. This allows comparing simulated otolith images to real ones. We let the reader refer to the Supp. Mat. for further details on the modeling assumptions (Text S1, Section 1) and model parameters (Table S1 & S2).
Model validation and calibration
We used otolith data from two different cod rearing experiments for model calibration and validation. In Experiment 1, one-year-old fish ranging from 30 to 35 cm were reared under seasonal temperature variations in high feeding conditions for 100 days, lower feeding conditions for the subsequent 120 days and ad libitum conditions for the last 80 days [10]. In Experiment 2, fish were 7 months old at the start of the experiment. They were fed ad libitum for 22 months and experienced seasonal temperature conditions [29]. In both cases, calibrated otolith data (i.e., time-referenced otolith growth and opacity data) were available along with the fish growth data.
The otolith data from Experiment 1 along with published data [30] were used to calibrate the DEB otolith model and the dataset from Experiment 2 was used as a validation dataset. The Supp. Mat. (Text S1, Table S1 & S2) further details model calibration and validation and reports calibrated model parameters.
Analysis of seasonal otolith patterns
We applied the calibrated cod otolith model to the analysis of the opposite seasonal opacity patterns of two cod populations, namely Barents Sea cod and Southern North Sea cod [21]. The definition of two population-specific feeding and temperature scenarios relied on data available in the literature (Fig. S5):
For the NS cod population, the yearly temperature conditions are given by the dynamics of surface temperatures in the southern North Sea [21]. Following [31], mid-level and high-level feeding conditions were respectively assumed from December to February and between March and July while a low feeding behaviour corresponding to temperature highs was considered from August to October;
For the BS cod population, the considered temperature conditions were issued from records of data storage tags [32] showing a long southward migration to warmer temperatures in winter. In accordance with this seasonal migration, we assumed that feeding conditions improved in the winter and spring with a peak in feeding conditions, corresponding to the seasonal feeding on capelin in March–April [33], followed by lower feeding conditions form August to November prior to the start of the southward migration in December.
For the two populations, we compared simulated otolith images to real ones as well as the observed and predicted seasonal opacity patterns. These observed seasonal opacity patterns from [21] were given as the percentage of opaque otolith edges for monthly sampled cod otolith sets. The seasonal patterns of the model simulations were issued as detrended and normalized version of the predicted opacitie series.
Supporting Information
Model simulations for a shift in feeding conditions (Exp. 1): first row, feeding conditions, temperature conditions (a–b); second row somatic and otolith distal radius (c–d). Model simulations (red) are compared to otolith data (gray) for the known feeding and temperature conditions. The model parameters are given in Tables S1 and S2.
(TIF)
Model simulations for a shift in feeding conditions (Exp. 1): otolith data (gray, thin solid lines) for the known feeding and temperature conditions are compared to the model simulations for two parameter settings: a model with no temperature-specific effect (i.e., parameter TAC set to 0) (R2 = 0.93, p<0.001, blue dashed line) and the calibrated otolith model (Table S1 & S2) (R2 = 0.96, p<0.001, red, solid line).
(TIF)
Model simulation for constant feeding conditions and seasonal temperature cycles (Exp. 2): first row (from left to right), feeding and temperature conditions (a–b); second row, somatic growth and otolith distal radius (c–d). The simulation of the calibrated model (red) is compared to individual data (gray).
(TIF)
Simulation of opacity patterns for constant feeding conditions and seasonal temperature cycles (Exp. 2). Real opacity data (gray, thin solid lines) are compared to three different simulations: a simulation of the calibrated model (Table S1 & S2) (red, solid line), a simulation with no temperature regulation (blue, dashed line) and a simulation where otolith opacity depends only on temperature (magenta, dashed-dotted line). The correlation coefficients with the real data were R2 = 0.90, R2 = 0.66 and R2 = 0.43, respectively (p<0.001 in all cases).
(TIF)
Model simulations for Southern North Sea cod (NS, black) and Barents Sea cod (BS, red): food density series (a), temperature series (b), somatic growth patterns (c), and otolith opacity patterns (d). The somatic growth data (panel c, dashed lines) were obtained from Bolle et al. (Jørgensen 1992) for the both populations.
(TIF)
Seasonality of the timing of otolith zone formation for the simulated and real data for NS and BS cod: feeding conditions (a), temperature conditions (b), and seasonal opacity patterns (c). BS cod are represented by red and NS cod by black. We compared the average proportions of translucent otolith edges for real otoliths taken from Høie et al. (Høie, Millner et al. 2009) (dashed lines) to identify simulated seasonal opacity patterns (solid lines).
(TIF)
Seasonal otolith opacity patterns for NS cod with constant and non-constant feeding conditions: feeding conditions (a), temperature conditions (b), and seasonal opacity patterns (c). We display two simulations: the one reported in Fig. S6 (solid lines, R2 = 0.96, p>0.001) and a scenario assuming a constant feeding with the temperature conditions used in Fig. S6 (dotted lines, R2 = 0.64, p>0.001). Simulated opacity patterns are compared to the otolith data (dashed, see Fig. S5).
(TIF)
Seasonal otolith opacity patterns for BS cod with constant and non-constant feeding conditions: feeding conditions (a), temperature conditions (b), and seasonal opacity patterns (c). We display two simulations: the one reported in Fig. S6 (solid lines, R2 = 0.96, p>0.001) and a scenario assuming a constant feeding with the temperature conditions used in Fig. S6 (dotted lines, R2 = 0.54, p>0.001). The simulated opacity patterns are compared to the real otolith data (dashed line, see Fig. S5).
(TIF)
Seasonality of the timing of otolith zone formation for BS and Norwegian coastal (NC) cod: feeding conditions (a), temperature conditions (b) and seasonal opacity patterns (c). BS cod are shown in red and NC cod in magenta. Both populations are known to display the same seasonal otolith opacity pattern. We compared the average proportions of translucent otolith edges for real otoliths taken from Høie et al. (Høie, Millner et al. 2009) (dashed lines) with simulated seasonal opacity patterns (solid lines).
(TIF)
- 1. A generic bioenergetic model of otolith biomineralization. This section further details model assumptions and equations.
- 2. Model calibration and validation. This section details calibration and validation dataset and results, and report calibrated model parameters.
- 3. Resolving the seasonal timing of the formation of opaque and translucent zones in fish otoliths of different cod populations. This section details the analysis, from model simulations, of the non-synchronous and synchronous seasonal opacity otolith patterns of several cod populations, namely Barrents Sea, Southern North Sea and Norwegian coast cod populations.
(DOC)
Variables, parameter values and equations for individual growth and somatic maintenance in a standard DEB model.
(TIFF)
Variables, parameter values and equations for otolith biomineralization.
(TIFF)
Acknowledgments
We thank P. Klein, R.M. Nisbet for comments on the manuscript.
Footnotes
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Funding: This study was partially funded by National Science Foundation (NSF) grants EF-0742521 and DEB-0717259 to L.P. and ANR grant OTOCAL to R.F. No additional external funding was received for this study. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Campana SE. Accuracy, precision and quality control in age determination, including a review of the use and abuse of age validation methods. J Fish Biol. 2001;59:197–242. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ivany LC, Patterson WP, Lohmann KC. Cooler winters as a possible cause of mass extinctions at the eocene/oligocene boundary. Nature. 2000;407:887–890. doi: 10.1038/35038044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Carpenter SJ, Erickson JM, Holland FD. Migration of a Late Cretaceous fish. Nature. 2003;423:70–74. doi: 10.1038/nature01575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rooker JR, Secor DH, De Metrio G, Schloesser R, Block BA, et al. Natal Homing and Connectivity in Atlantic Bluefin Tuna Populations. Science. 2008;322:742–744. doi: 10.1126/science.1161473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Thorrold SR, Latkoczy C, Swart PK, Jones CM. Natal homing in a marine fish metapopulation. Science. 2001;291:297–299. doi: 10.1126/science.291.5502.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tsukamoto K, Nakai I, Tesch WV. Do all freshwater eels migrate? Nature. 1998;396:635–636. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Elsdon TS, Wells BK, Campana SE, Gillanders BM, Jones CM, et al. Otolith chemistry to describe movements and life-history measurements of fishes: hypotheses, assumptions, limitations, and inferences using five methods. Oceanography and Marine Biology: an Annual Review. 2008;46:297–330. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Andrews AH, Tracey DM, Dunn MR. Lead–radium dating of orange roughy (Hoplostethus atlanticus): validation of a centenarian life span. Can J Fish Aq Sc. 2009;66:1130–1140. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Beamish RJ, McFarlane GA. A discussion of the importance of aging errors, and an application to walleye pollock: the world's largest fishery. In: Secor DH, et al., editors. Recent Developments in Fish Otolith Research. University of South Carolina Press; 1996. pp. 545–565. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Høie H, Folkvord A, Mosegaard H, Li L, Clausen LAW, et al. Restricted fish feeding reduces cod otolith opacity. J App Ichthyol. 2008;24:138–143. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Neat FC, Wright P, Fryer RJ. Temperature effects on otolith pattern formation in Atlantic cod Gadus morhua. J Fish Biol. 2008;73:2527–2541. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Beckman DW, Wilson AW. Seasonal timing of opaque zone formation in fish otoliths. In: Secor DH, et al., editors. Recent developments in fish otolith research. Univ. of South Carolina Press; 1996. pp. 27–43. [Google Scholar]
- 13.de Pontual H, Groison AL, Piñeiro C, Bertignac M. Evidence of underestimation of European hake growth in the Bay of Biscay, and its relationship with bias in the agreed method of age estimation. ICES J Mar Sci. 2006;63:1674–1681. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hussy K, Mosegaard H. Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) growth and otolith accretion characteristics modelled in a bioenergetics context. Can J Fish Aquat Sci. 2004;61:1021–1031. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Romanek CS, Gauldie RW. A predictive model of otolith growth in fish based on the chemistry of the endolymph. Comp Biochem Phys A, Physiology. 1996;114:71–79. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Schirripa MJ, Goodyear CP. Simulation of alternative assumptions of fish otolith-somatic growth with a bioenergetics model. Ecol Mod. 1997;102:209–223. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Allemand D, Mayer-Gostan N, de Pontual H, Boeuf G, Payan P. Fish Otolith Calcification in Relation to Endolymph Chemistry. In: al. Be, editor. Handbook of biomineralization. Wiley; 2007. pp. 291–308. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kooijman SALM. Dynamic Energy Budget theory for Metabolic Organisation. Cambridge University Press; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hussy K, Mosegaard H, Jessen F. Effect of age and temperature on amino acid composition and the content of different protein types of juvenile Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) otoliths. Can J Fish Aquat Sci. 2004;61:1012–1020. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fablet R, Pujolle S, Chessel A, Benzinou A, Cao F. 2D Image-based reconstruction of shape deformation of biological structures using a level-set representation. Comp Vis Im Und. 2008;111:295–306. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Høie H, Millner R, McCUllyc S, Nedreassb KH, Pilling GM, et al. Latitudinal differences in the timing of otolith growth: A comparison between the Barents Sea and southern North Sea. Fish Res. 2009;96:319–322. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Campana SE. How Reliable are Growth Back-Calculations Based on Otoliths? Can J Fish Aquat Sci. 1990;47:2219–2227. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wright PJ, Fallon-Cousins P, Armstrong JD. The relationship between otolith accretion and resting metabolic rate in juvenile Atlantic salmon during a change in temperature. J Fish Biol. 2001;59:657–666. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mosegaard H, Titus R. al. Ke, editor. Daily growth rates of otoliths in yolk sac fry of two salmonids at five different temperatures. 1987. pp. 221–227.
- 25.Cardoso J, van der Veer HW, Kooijman SALM. Body-size scaling relationships in bivalve species: A comparison of field data with predictions by the Dynamic Energy Budget (DEB) theory. J Sea Res. 2006;56:125–139. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Muller E, Kooijman SALM, Edmunds PJ, Doyle FJ, Nisbet RM. Dynamic Energy Budgets in syntrophic symbiotic relationships between heterotrophic hosts and photoautotrophic symbionts. J Theor Biol. 2009;259:44–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2009.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Millner RS, Pilling GM, McCully S, Høie H. Changes in the timing of otolith zone formation in North Sea cod from otolith records: an early indicator of climate-induced temperature stress? Marine Biology 2010 [Google Scholar]
- 28.Checkley DM, Dickson AG, Takahashi M, Radich JA, Eisenkolb N, et al. Elevated CO2 Enhances Otolith Growth in Young Fish. Science. 2009;324:1683–1683. doi: 10.1126/science.1169806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.IBACS. WP6 report: Long time rearing for monitoring of near natural conditions. 2006. IBACS project (Integrated Approach to the Biological Basis of Age Estimation in Commercially Important Fish Species, QQLRT-2001-01610)
- 30.van der Veer H, Freitas V, Cardosa J, Lika K, Campos J, et al. Temperature tolerance and energetics, a Dynamic Energy Budget-based comparison of North Atlantic marine species. 2010. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences Special issue “Developments in Dynamic Energy Budget theory and its applications”. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 31.Pilling GM, Millner RS, Easey MW, Maxwell DL, Tidd AN. Phenology and North Sea cod Gadus morhua L.: has climate change affected otolith annulus formation and growth? J Fish Biol. 2007;70:584–599. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Godø OR, Michalsen K. Migratory behaviour of north-east Arctic cod, studied by use of data storage tags. Fish Res. 2000;48:127–140. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yaragina NA, Marshall CT. Trophic influences on interannual and seasonal variation in the liver condition index of Northeast Arctic cod (Gadus morhua). ICES J Mar Sci. 2000;57:42–55. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Model simulations for a shift in feeding conditions (Exp. 1): first row, feeding conditions, temperature conditions (a–b); second row somatic and otolith distal radius (c–d). Model simulations (red) are compared to otolith data (gray) for the known feeding and temperature conditions. The model parameters are given in Tables S1 and S2.
(TIF)
Model simulations for a shift in feeding conditions (Exp. 1): otolith data (gray, thin solid lines) for the known feeding and temperature conditions are compared to the model simulations for two parameter settings: a model with no temperature-specific effect (i.e., parameter TAC set to 0) (R2 = 0.93, p<0.001, blue dashed line) and the calibrated otolith model (Table S1 & S2) (R2 = 0.96, p<0.001, red, solid line).
(TIF)
Model simulation for constant feeding conditions and seasonal temperature cycles (Exp. 2): first row (from left to right), feeding and temperature conditions (a–b); second row, somatic growth and otolith distal radius (c–d). The simulation of the calibrated model (red) is compared to individual data (gray).
(TIF)
Simulation of opacity patterns for constant feeding conditions and seasonal temperature cycles (Exp. 2). Real opacity data (gray, thin solid lines) are compared to three different simulations: a simulation of the calibrated model (Table S1 & S2) (red, solid line), a simulation with no temperature regulation (blue, dashed line) and a simulation where otolith opacity depends only on temperature (magenta, dashed-dotted line). The correlation coefficients with the real data were R2 = 0.90, R2 = 0.66 and R2 = 0.43, respectively (p<0.001 in all cases).
(TIF)
Model simulations for Southern North Sea cod (NS, black) and Barents Sea cod (BS, red): food density series (a), temperature series (b), somatic growth patterns (c), and otolith opacity patterns (d). The somatic growth data (panel c, dashed lines) were obtained from Bolle et al. (Jørgensen 1992) for the both populations.
(TIF)
Seasonality of the timing of otolith zone formation for the simulated and real data for NS and BS cod: feeding conditions (a), temperature conditions (b), and seasonal opacity patterns (c). BS cod are represented by red and NS cod by black. We compared the average proportions of translucent otolith edges for real otoliths taken from Høie et al. (Høie, Millner et al. 2009) (dashed lines) to identify simulated seasonal opacity patterns (solid lines).
(TIF)
Seasonal otolith opacity patterns for NS cod with constant and non-constant feeding conditions: feeding conditions (a), temperature conditions (b), and seasonal opacity patterns (c). We display two simulations: the one reported in Fig. S6 (solid lines, R2 = 0.96, p>0.001) and a scenario assuming a constant feeding with the temperature conditions used in Fig. S6 (dotted lines, R2 = 0.64, p>0.001). Simulated opacity patterns are compared to the otolith data (dashed, see Fig. S5).
(TIF)
Seasonal otolith opacity patterns for BS cod with constant and non-constant feeding conditions: feeding conditions (a), temperature conditions (b), and seasonal opacity patterns (c). We display two simulations: the one reported in Fig. S6 (solid lines, R2 = 0.96, p>0.001) and a scenario assuming a constant feeding with the temperature conditions used in Fig. S6 (dotted lines, R2 = 0.54, p>0.001). The simulated opacity patterns are compared to the real otolith data (dashed line, see Fig. S5).
(TIF)
Seasonality of the timing of otolith zone formation for BS and Norwegian coastal (NC) cod: feeding conditions (a), temperature conditions (b) and seasonal opacity patterns (c). BS cod are shown in red and NC cod in magenta. Both populations are known to display the same seasonal otolith opacity pattern. We compared the average proportions of translucent otolith edges for real otoliths taken from Høie et al. (Høie, Millner et al. 2009) (dashed lines) with simulated seasonal opacity patterns (solid lines).
(TIF)
- 1. A generic bioenergetic model of otolith biomineralization. This section further details model assumptions and equations.
- 2. Model calibration and validation. This section details calibration and validation dataset and results, and report calibrated model parameters.
- 3. Resolving the seasonal timing of the formation of opaque and translucent zones in fish otoliths of different cod populations. This section details the analysis, from model simulations, of the non-synchronous and synchronous seasonal opacity otolith patterns of several cod populations, namely Barrents Sea, Southern North Sea and Norwegian coast cod populations.
(DOC)
Variables, parameter values and equations for individual growth and somatic maintenance in a standard DEB model.
(TIFF)
Variables, parameter values and equations for otolith biomineralization.
(TIFF)