Abstract
Bacteriological investigations of seals of the German North and Baltic seas resulted in the isolation of bacteria of the genus Streptococcus belonging to Lancefield's serological groups C, F, and L. According to biochemical, serological, and 16S ribosomal DNA analysis, the group C and group F streptococci were identified as Streptococcus phocae. The group L streptococci could be classified as Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. dysgalactiae.
The harbor seal (Phoca vitulina) is the most common representative of the pinnipeds in the Wadden Sea of the German North Sea (8, 12). The grey seal (Halichoerus grypus) is also resident in the Wadden Sea, but in much lower numbers than the harbor seal. Both mammals are present in the Wadden Sea for the whole year (14). Harbor and grey seals are occasionally found on the German coast of the Baltic Sea. During the seal epidemic caused by phocine distemper virus in the North and Baltic seas in 1988 and 1989, 60% of the harbor seal population died. Only a few grey seals were affected in this period. Until 2001, the number of harbor seals increased again to approximately 20,000 individuals in the Wadden Sea. Grey seals could be found in numbers from 50 to 100 in the same area (3). Between May 2002 and February 2003, a new epidemic occurred in the North and Baltic seas, again associated with the occurrence of phocine distemper virus (11). A total of about 22,500 harbor seals and 824 grey seals died during this new epidemic (www.waddensea-secretariat.org).
However, during all these periods, beta-hemolytic streptococci were isolated from seal carcasses (4, 5, 6). The present study was performed to identify and further characterize these beta-hemolytic streptococci.
A total of 72 beta-hemolytic streptococci isolated from 57 organs of 39 harbor seals and 9 organs of 4 grey seals were investigated in this study. The beta-hemolytic streptococci were isolated from approximately 30% of 226 seal organs investigated between 1995 and 2000. Other bacteria isolated from these organs were Escherichia coli (48%), Pseudomonas spp. (17%), Neisseria spp. (13%), Staphylococcus epidermidis (13%), and alpha-hemolytic (1%) and gamma-hemolytic (46%) streptococci. Of the 72 beta-hemolytic streptococci, 61 were isolated from 39 harbor seals of the German North Sea, 2 were from two grey seals of the North Sea, and 9 were from two grey seals from the Baltic Sea. The animal designations, the places of discovery of the seals, and the tissues from which the beta-hemolytic streptococci were isolated are shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1.
Origins of 72 beta-hemolytic streptococci isolated from 39 harbor seals and 4 grey seals of the North and Baltic seas
| Animal designationa | Locationb | Status of animal when foundc | Tissue(s) of origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | Amrum | K | Lung |
| P2 | Dagebüll | K | Spleen |
| P3 | Nordstrand | K | Liver, spleen |
| P4 | St. Peter-Ording | S | Liver, lung, kidney, spleen |
| P5 | Kampen on Sylt | S | Liver |
| P6 | — | S | Intestine |
| P7 | Pellworm | — | Lung |
| P8 | St. Peter-Ording | K | Lung |
| P9 | St. Peter-Ording | N | Lung |
| P10 | Ulvesbüll | K | Lung |
| P11 | Rantum on Sylt | K | Articulation; lung |
| P12 | Friedrichskoog | K | Lung |
| P13 | Hörnum on Sylt | K | Extremity |
| P14 | Amrum | S | Articulation |
| P15 | Amrum | S | Articulation |
| P16 | Wenningstedt on Sylt | K | Articulation, liver, lung |
| P17 | Amrum | K | Lung |
| P18 | Lorenzenplate | A | Anus |
| P19 | Hörnum on Sylt | K | Lung |
| P20 | — | S | Liver |
| P21 | List on Sylt | K | Lung (2) |
| P22 | Hörnum on Sylt | K | Liver, lung, spleen |
| P23 | Hörnum on Sylt | S | Skin |
| P24 | Sealstation Helgoland | D | Eye |
| P25 | Pellworm | S | Tongue |
| P26 | Amrum | S | Lung |
| P27 | Helgoland | K | Blubber, eye, lung, spleen |
| P28 | Pellworm | K | Eye |
| P29 | Friedrichskoog | K | Eye |
| P30 | Helgoland | K | Tongue |
| P31 | Oland | K | Eye |
| P32 | St. Peter-Ording | K | Liver |
| P33 | Hörnum on Sylt | S | Lung (2) |
| P34 | Rantum on Sylt | K | Liver, lung, kidney |
| P35 | List on Sylt | K | Liver, lung (2), skin |
| P36 | Hörnum on Sylt | S | Intestine |
| P37 | Helgoland | S | Lung |
| P38 | List on Sylt | K | Eye, liver, lung (2) |
| P39 | Sealstation Friedrichskoog | A | Eye |
| H1 | St. Peter-Ording | K | Lung |
| H2 | Kleiner Haft | N | Intestine, liver (2), lung (2), kidney, spleen, tongue |
| H3 | Vitt on Rügen | S | Lung |
| H4 | Sealstation Friedrichskoog | A | Mouth |
P, P. vitulina; H, H. grypus.
Amrum, Dagebüll, Friedrichskoog, Lorenzenplate, Helgoland, Hörnum, Kampen, List, Nordstrand, Oland, Pellworm, Rantum, St. Peter-Ording, Ulvesbüll, and Wenningstedt are all in the North Sea. Kleiner Haft and Vitt are in the Baltic Sea. —, no information available.
A, alive; D, died in a seal station; N, caught in fishing nets; K, killed because of poor condition; S, stranded; —, no information available.
The beta-hemolytic streptococci were cultivated under microaerobic conditions in a candle jar. For comparative purposes, Streptococcus phocae reference strains 8399 H1 (NCTC 12719) and 8190 R2, kindly provided by I. Skaar (Central Veterinary Laboratory, State Veterinary Laboratories of Norway, Oslo, Norway), were used.
The bacteria were investigated for serological properties by using autoclaved extracts (13) and group-specific antisera by agar gel diffusion and with a commercial grouping kit (Streptokokken-Identifizierungstest; Oxoid, Wesel, Germany) and for biochemical properties by using a commercial identification system (API 50 CH; bioMerieux, Laupheim, Germany).
The 16S rRNA gene of S. phocae 8399 H1 was amplified by use of the oligonucleotide primers described by Hutson et al. (10). The DNA preparation was performed as described previously (1, 2). The amplicon of the 16S rRNA gene of S. phocae 8399 H1 was sequenced using the facilities of the university (Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie, Justus-Liebig-Universität Gießen, Giessen, Germany).
A restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the 16S rRNA gene of the cultures was subsequently performed using the 16S ribosomal-DNA-specific oligonucleotide primer described by Bentley and Leigh (7) with the sequence 5′-GAG AGT TTG ATC TGG CTC AGC A-3′ as primer 1 and the oligonucleotide primer with the sequence 5′-CGG GTG TTA CAA ACT CTC GTG GT-3′ described previously (1, 2) as primer 2. The restriction enzymes EarI and HincII (BioLabs, Schwalbach, Germany) were selected with the computer program clone manager (version 4.1; Scientific and Educational Software) and used for restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. For this, 30 μl (EarI) and 14 μl (HincII) of the amplicons were incubated with 4 μl (EarI) and 3 μl (HincII) of the enzymes, respectively, for 2.5 h at 37°C. Before selecting the restriction enzymes the V2 region of the 16S rRNA gene of S. phocae 8399 H1 was comparatively investigated with 16S ribosomal DNA V2 regions of various streptococcal species. The latter were obtained from Bentley and Leigh (7) and Abdulmawjood and Lämmler (2).
Antibiotic susceptibilities were determined according to the recommendations of the Bundesinstitut für Gesundheitlichen Verbraucherschutz und Veterinärmedizin, Berlin, Germany.
Genomic DNA was prepared and digested with the restriction enzyme ApaI for macrorestriction analysis of the cultures as described previously (16, 17). The restriction patterns were analyzed according to the recommendations of Tenover et al. (18).
All 72 bacteria appeared to be gram-positive, catalase-negative cocci and were surrounded by a wide zone of complete β hemolysis.
According to the serogrouping results the 72 beta-hemolytic streptococci could be classified as serogroup C (n = 8), F (n = 61), and L (n = 3).
Biochemical properties of the bacteria were determined with the commercial test system API 50 CH. The 8 group C and the 61 group F streptococci displayed almost identical biochemical properties. The group C and group F streptococci were generally positive in fructose, glucose, maltose, mannose, N-acetylglucosamine, and ribose reactions and mostly negative for all the other substrates investigated. The three group L streptococcal isolates were uniformly positive in fructose, galactose, glucose, glycogen, maltose, mannose, N-acetyl-glucosamine, ribose, starch, sucrose, and trehalose reactions. According to cultural, serological, and biochemical properties, the 69 streptococci of serogroup C and F were classified as Streptococcus phocae and the three group L streptococci were classified as Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. dysgalactiae serovar L. The biochemical and serological properties of both species corresponded to the findings given by Skaar et al. (15) and Lämmler and Hahn (13), respectively.
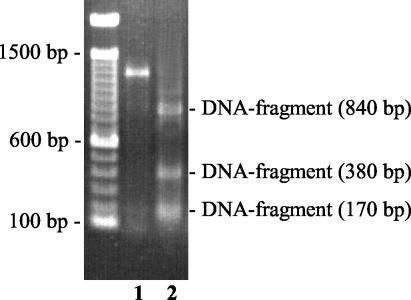
For molecular identification the 16S rRNA gene of the S. phocae reference strain 8399 H1, also including the V2 region, was sequenced (Fig. 1) and compared with 33 V2 region sequences of different streptococcal species and subspecies. The V2 region of S. phocae 8399 H1 appeared to be unique, showing differences of 4 to 16 nucleotides from the V2 region sequences of the other streptococcal species and subspecies investigated (data not shown). The subsequently selected restriction enzyme EarI specifically digested the 16S rRNA gene of all 69 S. phocae isolates, yielding three characteristic DNA fragments with sizes of 170, 380, and 840 bp (Fig. 2). HincII revealed two characteristic fragments for all 69 S. phocae with sizes of 180 and 1,230 bp (data not shown).
FIG. 1.
Sequence of the 16S rRNA gene of the S. phocae reference strain 8399 H1; the V2 region (26 nucleotides) of the 16S rRNA gene is marked separately (accession number AF235052).
FIG. 2.
Amplicon of the 16S rRNA gene of S. phocae 8399 H1 before (1,390 bp) (lane 1) and after (lane 2) digestion with EarI.
The species S. phocae was first mentioned by Skaar et al. (15). These authors isolated S. phocae from different organs of harbor seals. In addition, this species was detected in infections of fur seals (9). The appearance of group C- and group F-specific group antigen among S. phocae isolates has been described as a common property of this species (15).
Determination of antibiotic resistances revealed that all S. phocae and all S. dysgalactiae subsp. dysgalactiae serovar L isolates were uniformly sensitive to amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, bacitracin (0.04 IU), bacitracin (10 IU), cephacetrile, cefotaxime, cefoxitin, clindamycin, erythromycin, minocycline, ofloxacin, oxacillin, piperacillin, penicillin G, sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim, and tetracycline. Most of the S. phocae strains showed an intermediate reaction to gentamicin, and two of the S. dysgalactiae subsp. dysgalactiae serovar L strains were resistant and one strain was sensitive to gentamicin. Nearly all S. phocae and all S. dysgalactiae subsp. dysgalactiae serovar L isolates were resistant to kanamycin, nalidixic acid, and streptomycin. Only one S. phocae culture showed an intermediate reaction to streptomycin. The uniform sensitivity of the strains to almost all of the antibiotics tested could possibly be explained by a lack of contact of these animals and bacteria with the various antibiotics.
To analyze possibly existing epidemiological relations, the isolates were subjected to macrorestriction analysis of their chromosomal DNA by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) using the rare-cutting enzyme ApaI. PFGE analysis of 66 S. phocae cultures revealed 29 different DNA patterns. There were identical as well as nonidentical DNA fragment patterns for isolates from one animal and from different animals (Table 2). However, most of the DNA fingerprints were not identical, indicating that multiple bacterial clones were distributed among the harbor seal and grey seal population of the North and Baltic seas and that cross infections between animals seem to be rare. This is in contrast to previously investigated S. dysgalactiae subsp. dysgalactiae serovar L isolates from harbor porpoises of the North and Baltic seas. In that study, single S. dysgalactiae subsp. dysgalactiae serovar L clones or at least closely related clones could be found in the various specimens (17).
TABLE 2.
ApaI restriction patterns of 69 S. phocae isolates from 39 harbor seals and 4 grey seals from the North and Baltic seas
| Animal | Tissue of origin | Restriction patterna |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | Lung | I |
| P2 | Spleen | II |
| P3 | Liver | III |
| Spleen | III | |
| P4 | Liver | III |
| Lung | III | |
| Kidney | III | |
| Spleen | III | |
| P5 | Liver | IV |
| P6 | Intestine | III |
| P7 | Lung | V |
| P8 | Lung | — |
| P9 | Lung | VI |
| P10 | Lung | VII |
| P11 | Articulation | VII |
| Lung | VIII | |
| P12 | Lung | — |
| P13 | Extremity | I |
| P14 | Articulation | IX |
| P15 | Articulation | X |
| P16 | Articulation | II |
| Liver | XI | |
| Lung | II | |
| P17 | Lung | XII |
| P18 | Anus | X |
| P19 | Lung | XIII |
| P20 | Liver | XIV |
| P21 | Lung (isolate 1) | IV |
| Lung (isolate 2) | IV | |
| P22 | Liver | XIII |
| Lung | XIII | |
| Spleen | XV | |
| P23 | Skin | XI |
| P24 | Eye | VI |
| P25 | Tongue | I |
| P26 | Lung | XVI |
| P27 | Blubber | XVII |
| Eye | XVIII | |
| Lung | XVII | |
| Spleen | XVII | |
| P28 | Eye | XIX |
| P29 | Eye | VIII |
| P30 | Tongue | XX |
| P31 | Eye | XXI |
| P32 | Liver | X |
| P33 | Lung (isolate 1) | VII |
| Lung (isolate 2) | XXII | |
| P34 | Liver | XXIII |
| Lung | VII | |
| Kidney | VII | |
| P35 | Lung (isolate 1) | II |
| Lung (isolate 2) | XXIV | |
| Skin | XXV | |
| P36 | Intestine | XVI |
| P37 | Lung | X |
| P38 | Eye | XVII |
| Liver | XVII | |
| Lung (isolate 1) | XVII | |
| Lung (isolate 2) | XX | |
| P39 | Eye | — |
| H1 | Lung | XXVI |
| H2 | Intestine | XXVII |
| Liver (isolate 1) | XXVII | |
| Lung (isolate 1) | XXVII | |
| Lung (isolate 2) | XXVII | |
| Kidney | XXVIII | |
| Tongue | XXVIII | |
| H3 | Lung | XXVII |
| H4 | Mouth | XXIX |
—, the DNA of the cultures could not be digested by ApaI and separated by PFGE.
Because of the occurrence of multiple S. phocae clones obtained from seal organs and the isolation of the S. phocae together with other bacterial species, the importance of this bacterial species for various health conditions remains unclear.
(Parts of these results were presented at the 14th Annual Conference of the European Cetacean Society in Cork, Ireland, 2 to 5 April 2000.)
REFERENCES
- 1.Abdulmawjood, A., and C. Lämmler. 1999. Amplification of 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences for the identification of streptococci of Lancefield group B. Res. Vet. Sci. 67:159-162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Abdulmawjood, A., and C. Lämmler. 2000. Determination of intraspecies variations of the V2 region of the 16S rRNA gene of Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus. Res. Vet. Sci. 68:33-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Abt, K. F., N. Hoyer, L. Koch, and D. Adelung. 2002. The dynamics of grey seals (Halichoerus grypus) of Amrum in south eastern North Sea—evidence of an open population. J. Sea Res. 47:55-67. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bandomir, B., S. Marxen, J. Taylor, U. Siebert, and D. Adelung. 1999. Totfundmonitoring von Robben in Schleswig-Holstein 1998. Bericht an das Ministerium für Umwelt, Natur und Forsten des Landes Schleswig-Holstein, Forschungs- und Technologiezentrum Westküste. Universität Kiel, Büsum, Germany.
- 5.Bandomir, B., U. Siebert, and D. Adelung. 2000. Untersuchungen zum Gesundheitszustand von Robben in Schleswig-Holstein 1999. Bericht an das Ministerium für Umwelt, Natur und Forsten des Landes Schleswig-Holstein, Forschungs- und Technologiezentrum Westküste. Universität Kiel, Büsum, Germany.
- 6.Bandomir, B., U. Siebert, und D. Adelung. 2000. Untersuchungen zum Gesundheitszustand von Robben in Schleswig-Holstein 2000. Bericht an das Ministerium für Umwelt, Natur und Forsten des Landes Schleswig-Holstein, Forschungs- und Technologiezentrum Westküste. Universität Kiel, Büsum, Germany.
- 7.Bentley, R. W., and J. A. Leigh. 1995. Development of PCR-based hybridization protocol for identification of streptococcal species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 33:1296-1302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bonner, W. N. 1989. The natural history of seals. Christopher Helm, London, Great Britain.
- 9.Henton, M. M., O. Zapke, and P. A. Basson. 1999. Streptococcus phocae infections associated with starvation in cape fur seals. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 70:98-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hutson, R. A., D. E. Thompson, and M. D. Collins. 1993. Genetic interrelationships of saccharolytic Clostridium botulinum types B, E and F and related clostridia as revealed by small-subunit rRNA gene sequences. Microbiol. Lett. 108:103-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jensen, T., M. van de Bildt, H. H. Dietz, T. H. Andersen, A. S. Hammer, T. Kuiken, and A. Osterhaus. 2002. Another phocine distemper outbreak in Europe. Science 297:209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.King, J. E. (ed.). 1983. Seals of the world. Cornell University Press, New York, N.Y.
- 13.Lämmler, C., and G. Hahn. 1994. Streptokokken. In H. Blobel and T. Schließer (ed.), Handbuch der bakteriellen Infektionen bei Tieren, vol. 2. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena, Germany.
- 14.Schwarz, J., and G. Heidemann. 1994. Zum Status der Bestände der Seehund- und Kegelrobbenpopulation im Wattenmeer, p. 296-303. In J. L. Lozán, E. Rachor, K. Reise, H. Westernhagen, and W. Lenz (ed.), Warnsignale aus dem Wattenmeer. Blackwell Wissenschafts-Verlag, Berlin, Germany.
- 15.Skaar, I., P. Gaustad, T. Tønjum, B. Holm, and H. Stenwig. 1994. Streptococcus phocae sp. nov., a new species isolated from clinical specimens from seals. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 44:646-650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Soedermanto, I., F. H. Pasaribu, I. W. T. Wibawan, and C. Lämmler. 1996. Identification and molecular characterization of serological group C streptococci isolated from diseased pigs and monkeys in Indonesia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 34:2201-2204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Swenshon, M., C. Lämmler, and U. Siebert. 1998. Identification and molecular characterization of beta-hemolytic streptococci isolated from harbor porpoises (Phocoena phocoena) of the North and Baltic seas. J. Clin. Microbiol. 36:1902-1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tenover, F. C., R. D. Arbeit, R. V. Goering, P. A. Mickelsen, B. E. Murray, D. H. Persing, and B. Swaminathan. 1995. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 33:2233-2239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]