Abstract
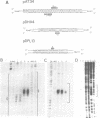
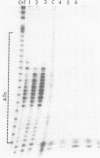
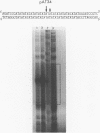
A 34 base pair tract of the simple repeating dinucleotide d(AT)n-d(AT)n cloned into a 2.4 kb polylinker plasmid vector undergoes a structural transition in response to negative superhelical coiling. The transition has been characterized by 2 dimensional gel electrophoresis, mapping of S1, P1 and T7 endonuclease 1 sensitive sites, and mapping of sites that are sensitive to modification by bromoacetaldehyde. After S1 nuclease treatment it is possible to trap supercoiled species that are nicked on one or both strands near the center of the palindrome. These data show that the alternate state adopted by the d(AT)n-dAT)n insert is a cruciform rather than a Z conformation. Unlike other B-cruciform transitions the transition in d(AT)n-d(AT)n has a low activation energy and the transition is facilitated by the presence of magnesium ions. Evidence from in-vivo topoisomer distributions is presented which shows that under conditions of blocked protein synthesis the d(AT)n-d(AT)n insert will spontaneously adopt the cruciform state in-vivo in E. coli.
Full text
PDF




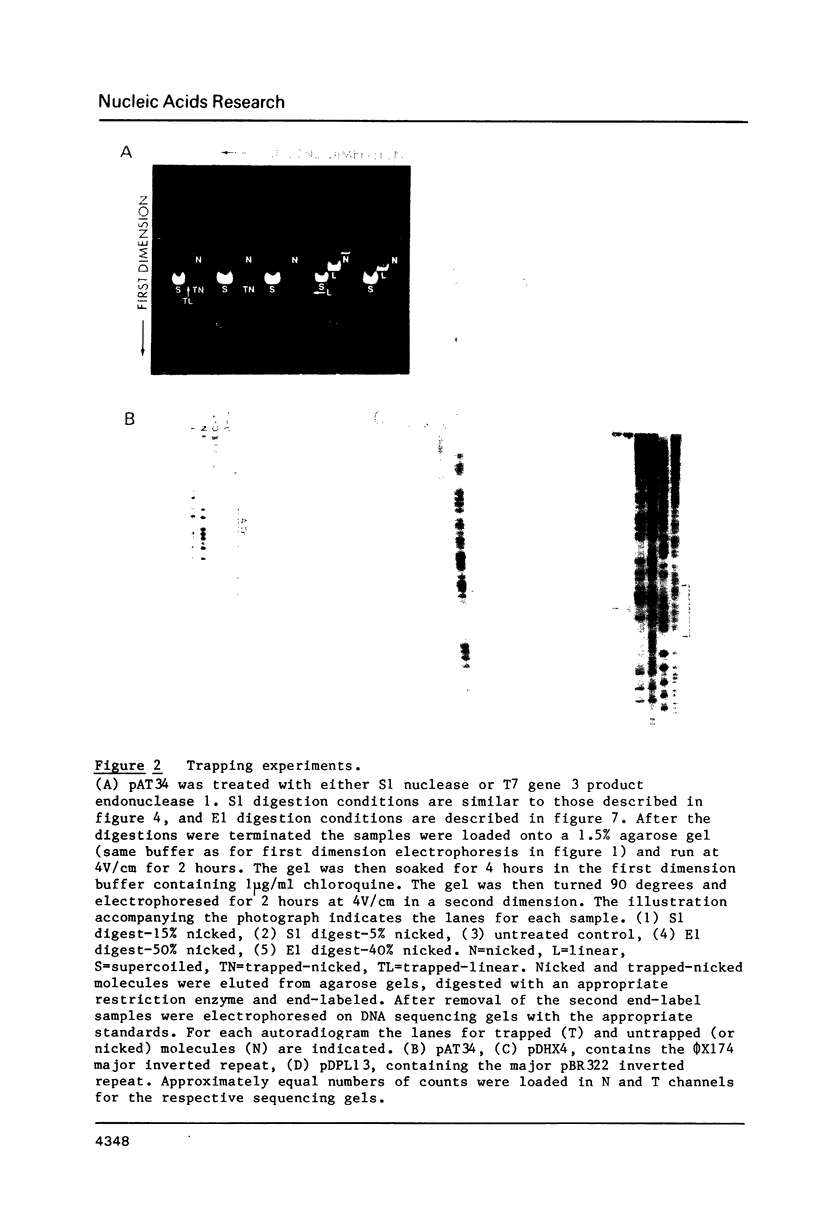

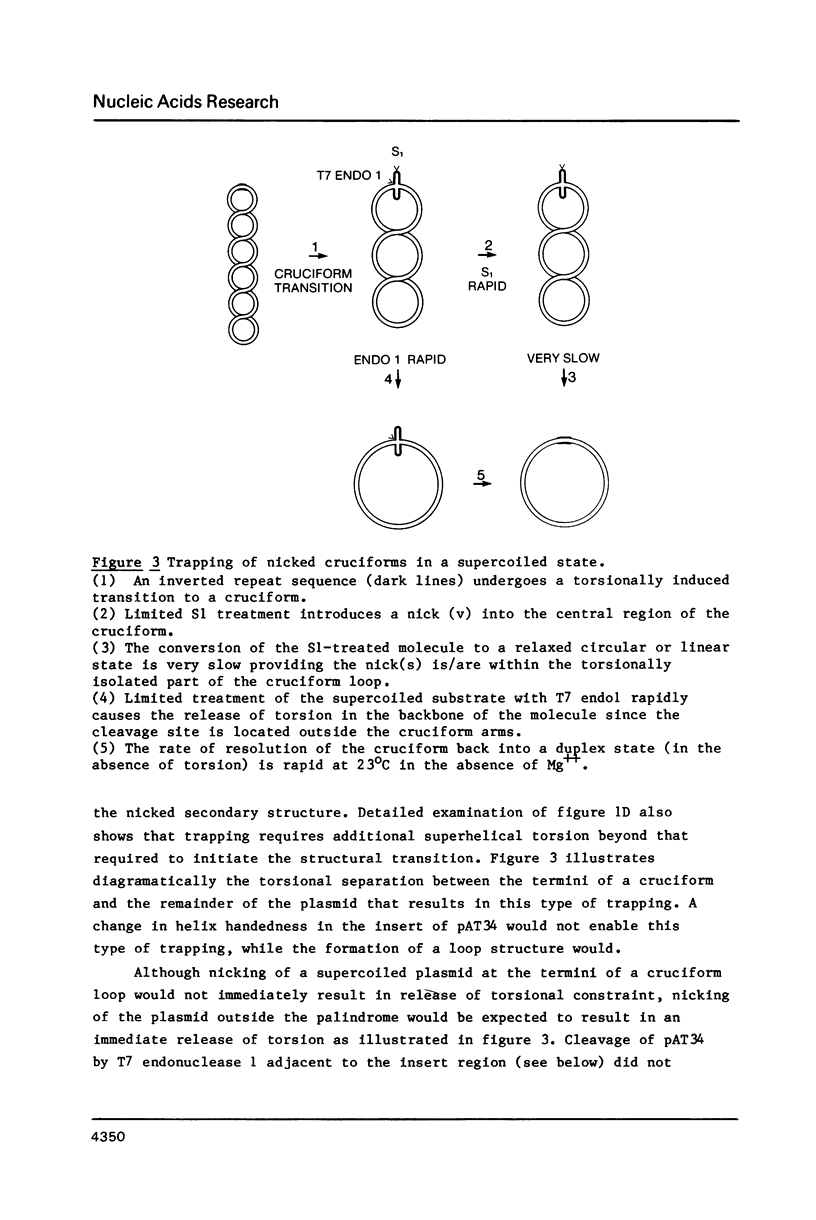












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J., Feldman J., Nasmyth K. A., Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Broach J. R., Hicks J. B. Sites required for position-effect regulation of mating-type information in yeast. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):989–998. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azorin F., Nordheim A., Rich A. Formation of Z-DNA in negatively supercoiled plasmids is sensitive to small changes in salt concentration within the physiological range. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):649–655. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01479.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Worcel A. Isolation, characterization, and structure of the folded interphase genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor C. R., Efstratiadis A. Possible structures of homopurine-homopyrimidine S1-hypersensitive sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8059–8072. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Wang J. C. Cruciform formation in a negatively supercoiled DNA may be kinetically forbidden under physiological conditions. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. R., BALDWIN R. L. X-ray studies on two synthetic DNA copolymers. J Mol Biol. 1963 Apr;6:251–255. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank-Kamenetskii M. D., Vologodskii A. V. Thermodynamics of the B-Z transition in superhelical DNA. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):481–482. doi: 10.1038/307481a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Nash H. A. DNA gyrase: an enzyme that introduces superhelical turns into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., O'Dea M. H., Mizuuchi K. Slow cruciform transitions in palindromic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5545–5549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E., Drlica K. Regulation of bacterial DNA supercoiling: plasmid linking numbers vary with growth temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4046–4050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. Facile transition of poly[d(TG) x d(CA)] into a left-handed helix in physiological conditions. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):632–634. doi: 10.1038/302632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. The in-vivo occurrence of Z DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Dec;1(3):593–609. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M., Weintraub H., McKnight S. L. Transcription of DNA injected into Xenopus oocytes is influenced by template topology. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):38–43. doi: 10.1038/302038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick M. W., Klysik J., Singleton C. K., Zarling D. A., Jovin T. M., Hanau L. H., Erlanger B. F., Wells R. D. Intervening sequences in human fetal globin genes adopt left-handed Z helices. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7268–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick M. W., Klysik J., Singleton C. K., Zarling D. A., Jovin T. M., Hanau L. H., Erlanger B. F., Wells R. D. Intervening sequences in human fetal globin genes adopt left-handed Z helices. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7268–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Jack A., Viswamitra M. A., Kennard O., Shakked Z., Steitz T. A. A hypothesis on a specific sequence-dependent conformation of DNA and its relation to the binding of the lac-repressor protein. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudritskaya Z. G., Danilov V. I. Quantum mechanical study of bases interactions in various associates in atomic dipole approximation. J Theor Biol. 1976 Jul 7;59(2):303–318. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(76)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie A. G., Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Ratliff R. L. Polymorphism of DNA double helices. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 15;143(1):49–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Hallam L. R. Thermodynamics of the ColE1 cruciform. Comparisons between probing and topological experiments using single topoisomers. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):179–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90436-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Kemper B. Cruciform-resolvase interactions in supercoiled DNA. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Markham A. F. Dynamics of cruciform extrusion in supercoiled DNA: use of a synthetic inverted repeat to study conformational populations. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):527–533. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luchnik A. N., Bakayev V. V., Glaser V. M. DNA supercoiling: changes during cellular differentiation and activation of chromatin transcription. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):793–801. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Panyutin I. G., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Evidence of cruciform structures in superhelical DNA provided by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 21;153(2):298–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80628-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel R., Gellert M. Regulation of the genes for E. coli DNA gyrase: homeostatic control of DNA supercoiling. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Kemper B., Hays J., Weisberg R. A. T4 endonuclease VII cleaves holliday structures. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. R., Lee J. S., Pulleyblank D. E., Murray N. L., Evans D. H. Review: ethidium fluorescence assays. Part 1. Physicochemical studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 10;7(3):547–569. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.3.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Lafer E. M., Peck L. J., Wang J. C., Stollar B. D., Rich A. Negatively supercoiled plasmids contain left-handed Z-DNA segments as detected by specific antibody binding. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Nordheim A., Rich A., Wang J. C. Flipping of cloned d(pCpG)n.d(pCpG)n DNA sequences from right- to left-handed helical structure by salt, Co(III), or negative supercoiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4560–4564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Energetics of B-to-Z transition in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Transcriptional block caused by a negative supercoiling induced structural change in an alternating CG sequence. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90316-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D., Michalak M., Daisley S. L., Glick R. A method for the purification of E. coli plasmid DNA by homogeneous lysis and polyethylene glycol precipitation. Mol Biol Rep. 1983 Aug;9(3):191–195. doi: 10.1007/BF00775367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson S. M., Higgins C. F., Lilley D. M. The genetic control of DNA supercoiling in Salmonella typhimurium. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1745–1752. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryoji M., Worcel A. Chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes: in vivo studies. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Pulleyblank D. E., Vinograd J. The problems of eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA packaging and in vivo conformation posed by superhelix density heterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1183–1205. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Carlson J. O., Pettijohn D. E. Torsional tension in the DNA double helix measured with trimethylpsoralen in living E. coli cells: analogous measurements in insect and human cells. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):773–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90440-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Klysik J., Wells R. D. Conformational flexibility of junctions between contiguous B- and Z-DNAs in supercoiled plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2447–2451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. DNA supercoiling: another level for regulating gene expression. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):599–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirdivant S. M., Kłysik J., Wells R. D. Energetic and structural inter-relationship between DNA supercoiling and the right- to left-handed Z helix transitions in recombinant plasmids. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10159–10165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockton J. F., Miller F. D., Jorgenson K. F., Zarling D. A., Morgan A. R., Rattner J. B., van de Sande J. H. Left-handed Z-DNA regions are present in negatively supercoiled bacteriophage PM2 DNA. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2123–2128. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01712.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Gaillard C., Prunell A. Helical periodicity of DNA, Poly(dA) . poly(dT) and poly(dA-dT). poly(dA-dT) in solution. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(2):215–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06389.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Higgins N. P., Brown P. O., Peebles C. L., Cozzarelli N. R. Energy coupling in DNA gyrase and the mechanism of action of novobiocin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4838–4842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeponteau B., Lundell M., Martinson H. Torsional stress promotes the DNAase I sensitivity of active genes. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):469–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90454-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Helical repeat of DNA in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):200–203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. A dominant role for DNA secondary structure in forming hypersensitive structures in chromatin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1191–1203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]