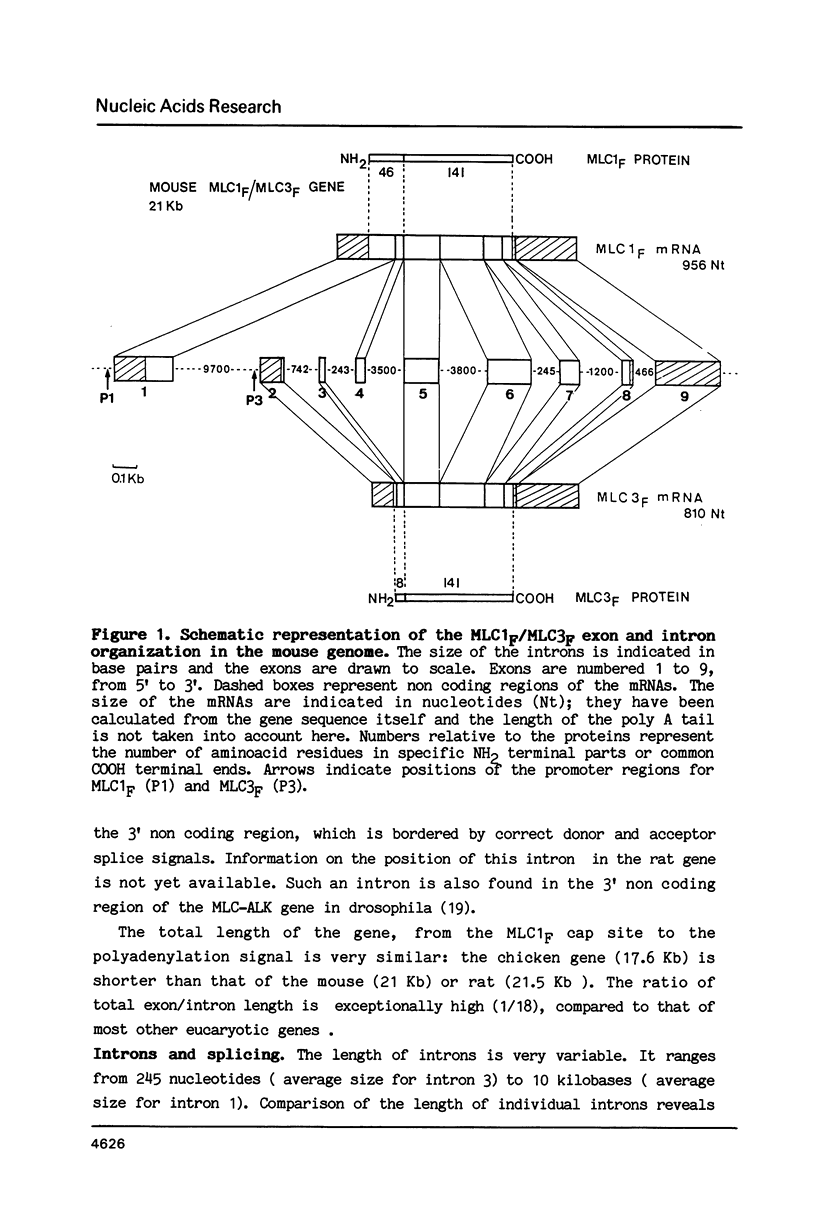
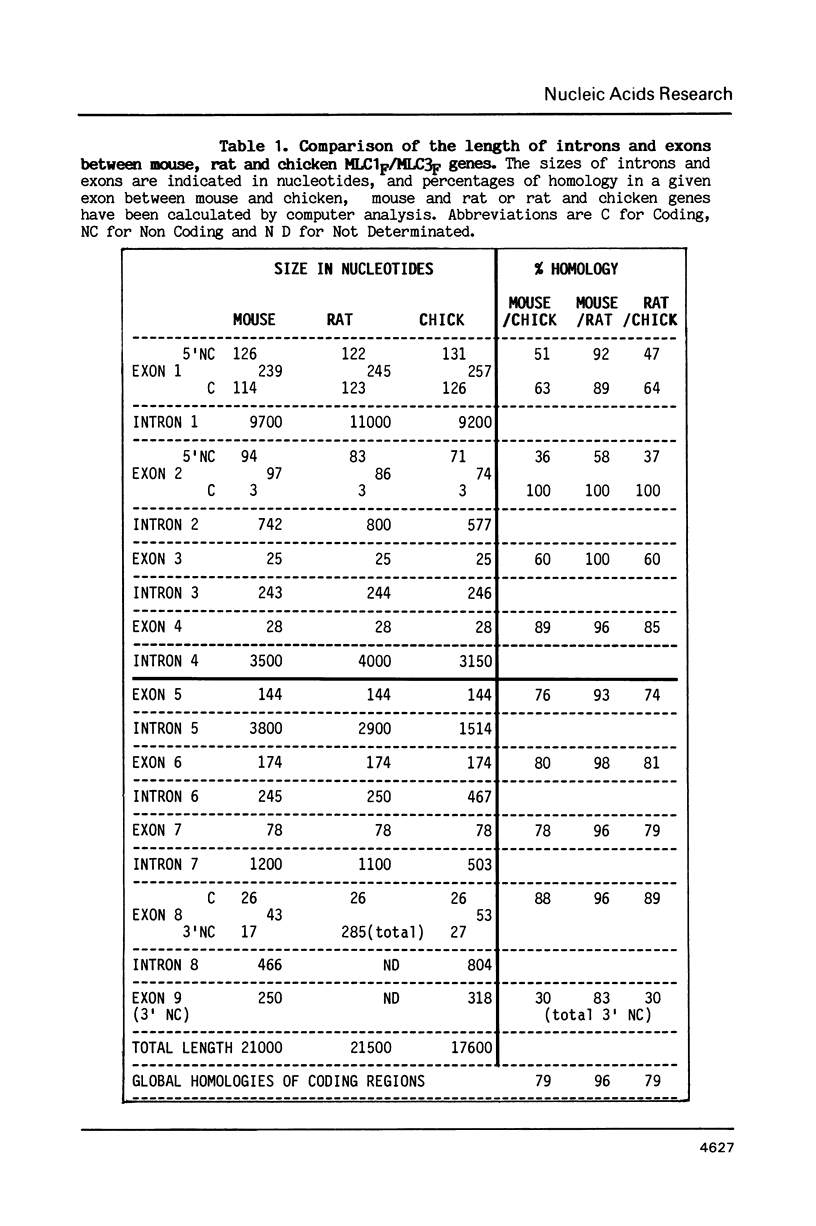
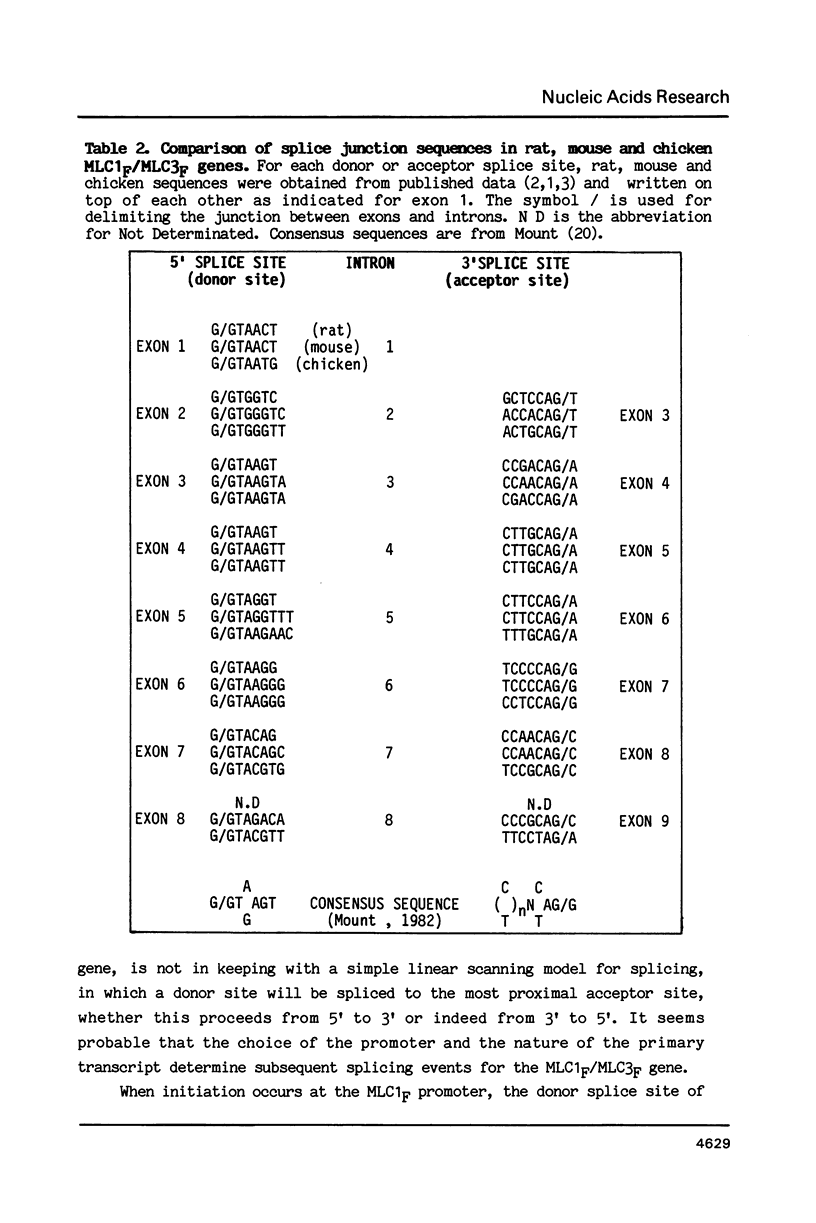
Abstract
A single locus in the mouse, rat and chicken encodes both alkali myosin light chains, MLC1F and MLC3F. This gene has two distinct promoters and gives rise to two different primary transcripts, which are processed by alternative and different modes of splicing to form MLC1F and MLC3F mRNAs. The MLC1F/MLC3F gene is very similar between mouse, rat and chicken, in terms of its overall structure, the length and location of the introns, and the splice site consensus sequences. Nucleotide sequences of coding regions are very conserved but 3' and 5' non coding regions of the mRNAs have diverged. In the MLC1F promoter regions, several blocks of nucleotides are highly conserved (more than 70% homology), especially a sequence of about 70 nucleotides, located between positions -80 and -150 relative to the Cap site. Conserved blocks of homology are also found in the MLC3F promoter regions, although the common sequences are shorter. The presence of such highly conserved nucleotide sequences in the 5' flanking regions suggests that these sequences are functionally important in initiation of transcription and regulation of expression of this complex gene. Primer extension experiments indicate multiple cap sites for MLC3F mRNA.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E., Diggelmann H. Glucocorticoid regulation of mouse mammary tumor virus: identification of a short essential DNA region. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1423–1429. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnay P., Treisman R., Mellon P., Chao M., Axel R., Maniatis T. Differences in human alpha- and beta-globin gene expression in mouse erythroleukemia cells: the role of intragenic sequences. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):251–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90547-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couble P., Chevillard M., Moine A., Ravel-Chapuis P., Prudhomme J. C. Structural organization of the P25 gene of Bombyx mori and comparative analysis of its 5' flanking DNA with that of the fibroin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1801–1814. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czosnek H., Nudel U., Mayer Y., Barker P. E., Pravtcheva D. D., Ruddle F. H., Yaffe D. The genes coding for the cardiac muscle actin, the skeletal muscle actin and the cytoplasmic beta-actin are located on three different mouse chromosomes. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1977–1979. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01687.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Jacobs H. T., Britten R. J. Very short repeats and coordinate induction of genes. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):468–470. doi: 10.1038/301468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. C., Knoll B. J., Riser M. E., O'Malley B. W. A 5'-flanking sequence essential for progesterone regulation of an ovalbumin fusion gene. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):551–554. doi: 10.1038/305551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. The structures of cytochrome c and the rates of molecular evolution. J Mol Evol. 1971;1(1):26–45. doi: 10.1007/BF01659392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkenthal S., Parker V. P., Davidson N. Developmental variations in the splicing pattern of transcripts from the Drosophila gene encoding myosin alkali light chain result in different carboxyl-terminal amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):449–453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornwald J. A., Kuncio G., Peng I., Ordahl C. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of the chick a-actin gene and its evolutionary relationship to the actin gene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):3861–3876. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.3861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes D. M., Mullis N. T., Comeau C. M., Crabtree G. R. Potential basis for regulation of the coordinately expressed fibrinogen genes: homology in the 5' flanking regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2313–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G., Weeds A. G. The amino-acid sequence of the alkali light chains of rabbit skeletal-muscle myosin. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 15;44(2):317–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F., Lowey S., Benfield P. A., Hobbs A. W. Distribution and properties of myosin isozymes in developing avian and mammalian skeletal muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):471–484. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grez M., Land H., Giesecke K., Schütz G., Jung A., Sippel A. E. Multiple mRNAs are generated from the chicken lysozyme gene. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. The adenovirus type 5 E1A transcriptional control region contains a duplicated enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry G. D., Dalgarno D. C., Marcus G., Scott M., Levine B. A., Trayer I. P. The occurrence of alpha-N-trimethylalanine as the N-terminal amino acid of some myosin light chains. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jul 19;144(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80558-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N., van Ooyen A. J., Kennedy N., Herrlich P., Ponta H., Groner B. Subfragments of the large terminal repeat cause glucocorticoid-responsive expression of mouse mammary tumor virus and of an adjacent gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3637–3641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühne T., Wieringa B., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Evidence against a scanning model of RNA splicing. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):727–733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01492.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Risby D. Light chains from fast and slow muscle myosins. Nature. 1971 Nov 12;234(5324):81–85. doi: 10.1038/234081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi V., Chambers A. P., Nadal-Ginard B. Cardiac alpha- and beta-myosin heavy chain genes are organized in tandem. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J., Varmus H. E. A small region of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat confers glucocorticoid hormone regulation on a linked heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5866–5870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Analysis of the expression of genes encoding animal mRNA by in vitro techniques. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;30:195–244. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60687-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda G., Maita T., Umegane T. The primary structure of L-1 light chain of chicken fast skeletal muscle myosin and its genetic implication. FEBS Lett. 1981 Apr 6;126(1):111–113. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer Y., Czosnek H., Zeelon P. E., Yaffe D., Nudel U. Expression of the genes coding for the skeletal muscle and cardiac actions in the heart. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1087–1100. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melloul D., Aloni B., Calvo J., Yaffe D., Nudel U. Developmentally regulated expression of chimeric genes containing muscle actin DNA sequences in transfected myogenic cells. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):983–990. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata T., Yasunaga T., Nishida T. Nucleotide sequence divergence and functional constraint in mRNA evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7328–7332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Muramatsu M., Ogata K. Alternative transcription and two modes of splicing results in two myosin light chains from one gene. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):333–338. doi: 10.1038/308333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Calvo J. M., Shani M., Levy Z. The nucleotide sequence of a rat myosin light chain 2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7175–7186. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordahl C. P., Cooper T. A. Strong homology in promoter and 3'-untranslated regions of chick and rat alpha-actin genes. Nature. 1983 May 26;303(5915):348–349. doi: 10.1038/303348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panthier J. J., Dreyfus M., Roux T. L., Rougeon F. Mouse kidney and submaxillary gland renin genes differ in their 5' putative regulatory sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5489–5493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., DeFranco D., Firestone G. L., Edgar B., Wrange O., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Sequence-specific binding of glucocorticoid receptor to MTV DNA at sites within and upstream of the transcribed region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periasamy M., Strehler E. E., Garfinkel L. I., Gubits R. M., Ruiz-Opazo N., Nadal-Ginard B. Fast skeletal muscle myosin light chains 1 and 3 are produced from a single gene by a combined process of differential RNA transcription and splicing. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13595–13604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole S. J., Firtel R. A. Conserved structural features are found upstream from the three co-ordinately regulated discoidin I genes of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 15;172(2):203–220. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert B., Barton P., Minty A., Daubas P., Weydert A., Bonhomme F., Catalan J., Chazottes D., Guénet J. L., Buckingham M. Investigation of genetic linkage between myosin and actin genes using an interspecific mouse back-cross. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):181–183. doi: 10.1038/314181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert B., Daubas P., Akimenko M. A., Cohen A., Garner I., Guenet J. L., Buckingham M. A single locus in the mouse encodes both myosin light chains 1 and 3, a second locus corresponds to a related pseudogene. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy R. K., Sreter F. A., Sarkar S. Changes in tropomyosin subunits and myosin light chains during development of chicken and rabbit striated muscles. Dev Biol. 1979 Mar;69(1):15–30. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90271-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Geisse S., Westphal H. M., Beato M. The glucocorticoid receptor binds to defined nucleotide sequences near the promoter of mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):749–752. doi: 10.1038/304749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Yamada Y., de Crombrugghe B. DNA sequence comparison of the regulatory signals at the 5' end of the mouse and chick alpha 2 type I collagen genes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7411–7415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvanayagam C. S., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., Selvanayagam P., Saunders G. F. Multiple origins of transcription for the human placental lactogen genes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14642–14646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sréter F. A., Bálint M., Gergely J. Structural and functional changes of myosin during development: comparison with adult fast, slow and cardiac myosin. Dev Biol. 1975 Oct;46(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R., McLachlan A. D. Codon preference and its use in identifying protein coding regions in long DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):141–156. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Tonomura Y. Developmental changes in the structure and kinetic properties of myosin adenosinetriphosphatase of rabbit skeletal fast muscle. J Biochem. 1975 Dec;78(6):1123–1133. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Activating protein factor binds in vitro to upstream control sequences in heat shock gene chromatin. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):81–84. doi: 10.1038/311081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Two protein-binding sites in chromatin implicated in the activation of heat-shock genes. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):229–234. doi: 10.1038/309229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakut R., Shani M., Givol D., Neuman S., Yaffe D., Nudel U. Nucleotide sequence of the rat skeletal muscle actin gene. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):857–859. doi: 10.1038/298857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]