Abstract
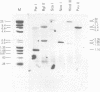
The rabbit genome encodes an opal suppressor tRNA gene. The coding region is strictly conserved between the rabbit gene and the corresponding gene in the human genome. The rabbit opal suppressor gene contains the consensus sequence in the 3' internal control region but like the human and chicken genes, the rabbit 5' internal control region contains two additional nucleotides. The 5' flanking sequences of the rabbit and the human opal suppressor genes contain extensive regions of homology. A subset of these homologies is also present 5' to the chicken opal suppressor gene. Both the rabbit and the human genomes also encode a pseudogene. That of the rabbit lacks the 3' half of the coding region. Neither pseudogene has homologous regions to the 5' flanking regions of the genes. The presence of 5' homologies flanking only the transcribed genes and not the pseudogenes suggests that these regions may be regulatory control elements specifically involved in the expression of the eukaryotic opal suppressor gene. Moreover the strict conservation of coding sequences indicates functional importance for the opal suppressor tRNA genes.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bienz M., Kubli E., Kohli J., de Henau S., Grosjean H. Nonsense suppression in eukaryotes: the use of the Xenopus oocyte as an in vivo assay system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5169–5178. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Kubli E., Kohli J., deHenau S., Huez G., Marbaix G., Grosjean H. Usage of the three termination codons in a single eukaryotic cell, the Xenopus laevis oocyte. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3835–3850. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R., Haar R. A., Capecchi N. E., Sveda M. M. The isolation of a suppressible nonsense mutant in mammalian cells. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):371–381. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Castagnoli L., Cortese R. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1983;18:59–88. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60579-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. G., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. DNA sequence preference of the progesterone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooley L., Schaack J., Burke D. J., Thomas B., Söll D. Transcription factor binding is limited by the 5'-flanking regions of a Drosophila tRNAHis gene and a tRNAHis pseudogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2714–2722. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco D., Schmidt O., Söll D. Two control regions for eukaryotic tRNA gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3365–3368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco D., Sharp S., Söll D. Identification of regulatory sequences contained in the 5'-flanking region of Drosophila lysine tRNA2 genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12424–12429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond A., Dudock B., Hatfield D. Structure and properties of a bovine liver UGA suppressor serine tRNA with a tryptophan anticodon. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):497–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Burke D. J., Sharp S., Schaack J., Söll D. The 5- flanking sequences of Drosophila tRNAArg genes control their in vitro transcription in a Drosophila cell extract. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14738–14744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier A., Guérin M. A., Corlet J., Clarkson S. G. Structure and in vitro transcription of a glycine tRNA gene from Bombyx mori. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1547–1552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamulin V., Mao J., Appel B., Sumner-Smith M., Yamao F., Söll D. Six Schizosaccharomyces pombe tRNA genes including a gene for a tRNALys with an intervening sequence which cannot base-pair with the anticodon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8537–8546. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. D., Clarkson S. G., Tocchini-Valentini G. Transcription initiation of eucaryotic transfer RNA genes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J. H., Rooney R. J., Harding J. D. Structure and evolution of mammalian tRNA genes: sequence of a mouse tRNAiMet gene, the 5'-flanking region of which is homologous to a human gene. Gene. 1984 May;28(2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield D. L., Dudock B. S., Eden F. C. Characterization and nucleotide sequence of a chicken gene encoding an opal suppressor tRNA and its flanking DNA segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4940–4944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield D., Diamond A., Dudock B. Opal suppressor serine tRNAs from bovine liver form phosphoseryl-tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6215–6219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipskind R. A., Clarkson S. G. 5'-flanking sequences that inhibit in vitro transcription of a xenopus laevis tRNA gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90545-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovemann B., Sharp S., Yamada H., Söll D. Analysis of a drosophila tRNA gene cluster. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):889–895. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudziak R. M., Laski F. A., RajBhandary U. L., Sharp P. A., Capecchi M. R. Establishment of mammalian cell lines containing multiple nonsense mutations and functional suppressor tRNA genes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90413-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Raymond G. J. Three regions of a yeast tRNALeu3 gene promote RNA polymerase III transcription. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5990–5994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Abelson J. The yeast tRNATyr gene intron is essential for correct modification of its tRNA product. Nature. 1983 Apr 21;302(5910):681–687. doi: 10.1038/302681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp G., Beckmann J. S., Johnson P. F., Fuhrman S. A., Abelson J. Transcription and processing of intervening sequences in yeast tRNA genes. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):221–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D., Bradford-Wilcox J., Young L. S., Sprague K. U. A short 5' flanking region containing conserved sequences is required for silkworm alanine tRNA gene activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3416–3420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laski F. A., Belagaje R., RajBhandary U. L., Sharp P. A. An amber suppressor tRNA gene derived by site-specific mutagenesis: cloning and function in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5813–5817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney J. E., Harding J. D. Structure and evolution of a mouse tRNA gene cluster encoding tRNAAsp, tRNAGly and tRNAGlu and an unlinked, solitary gene encoding tRNAAsp. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8761–8775. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma D. P., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E., Roe B. A. Nucleotide sequences of two regions of the human genome containing tRNAAsn genes. Gene. 1984 May;28(2):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90264-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani T., Hashimoto A. Purification and properties of suppressor seryl-tRNA: ATP phosphotransferase from bovine liver. FEBS Lett. 1984 Apr 24;169(2):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80342-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvihill E. R., LePennec J. P., Chambon P. Chicken oviduct progesterone receptor: location of specific regions of high-affinity binding in cloned DNA fragments of hormone-responsive genes. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):621–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Cordell B., Valenzuela P., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Structure and processing of yeast precursor tRNAs containing intervening sequences. Nature. 1978 Aug 3;274(5670):438–445. doi: 10.1038/274438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill V. A., Eden F. C., Pratt K., Hatfield D. L. A human opal suppressor tRNA gene and pseudogene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2501–2508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden R. C., Beckman J. S., Abelson J., Kang H. S., Söll D., Schmidt O. In vitro transcription and processing of a yeast tRNA gene containing an intervening sequence. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajput B., Duncan L., DeMille D., Miller R. C., Jr, Spiegelman G. B. Transcription of cloned transfer RNA genes from Drosophila melanogaster in a homologous cell-free extract. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6541–6550. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R., Schütz G., von der Ahe D., Beato M. Sequences in the promoter region of the chicken lysozyme gene required for steroid regulation and receptor binding. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):503–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos T., Zasloff M. Comparative analysis of human chromosomal segments bearing nonallelic dispersed tRNAimet genes. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):699–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90433-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaack J., Sharp S., Dingermann T., Burke D. J., Cooley L., Söll D. The extent of a eukaryotic tRNA gene. 5'- and 3'-flanking sequence dependence for transcription and stable complex formation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1461–1467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague K. U., Larson D., Morton D. 5' flanking sequence signals are required for activity of silkworm alanine tRNA genes in homologous in vitro transcription systems. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. P., Summers W. C., Laski F. A., RajBhandary U. L., Sharp P. A. Functional suppression in mammalian cells of nonsense mutations in the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene by suppressor tRNA genes. J Virol. 1983 Aug;47(2):376–379. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.2.376-379.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Venegas A., Weinberg F., Bishop R., Rutter W. J. Structure of yeast phenylalanine-tRNA genes: an intervening DNA segment within the region coding for the tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Germond J. E., Brown-Luedi M., Givel F., Wahli W. Sequence homologies in the region preceding the transcription initiation site of the liver estrogen-responsive vitellogenin and apo-VLDLII genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8611–8626. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. F., Capecchi M., Laski F. A., RajBhandary U. L., Sharp P. A., Palese P. Measurement of suppressor transfer RNA activity. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):873–875. doi: 10.1126/science.6308765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]