Abstract
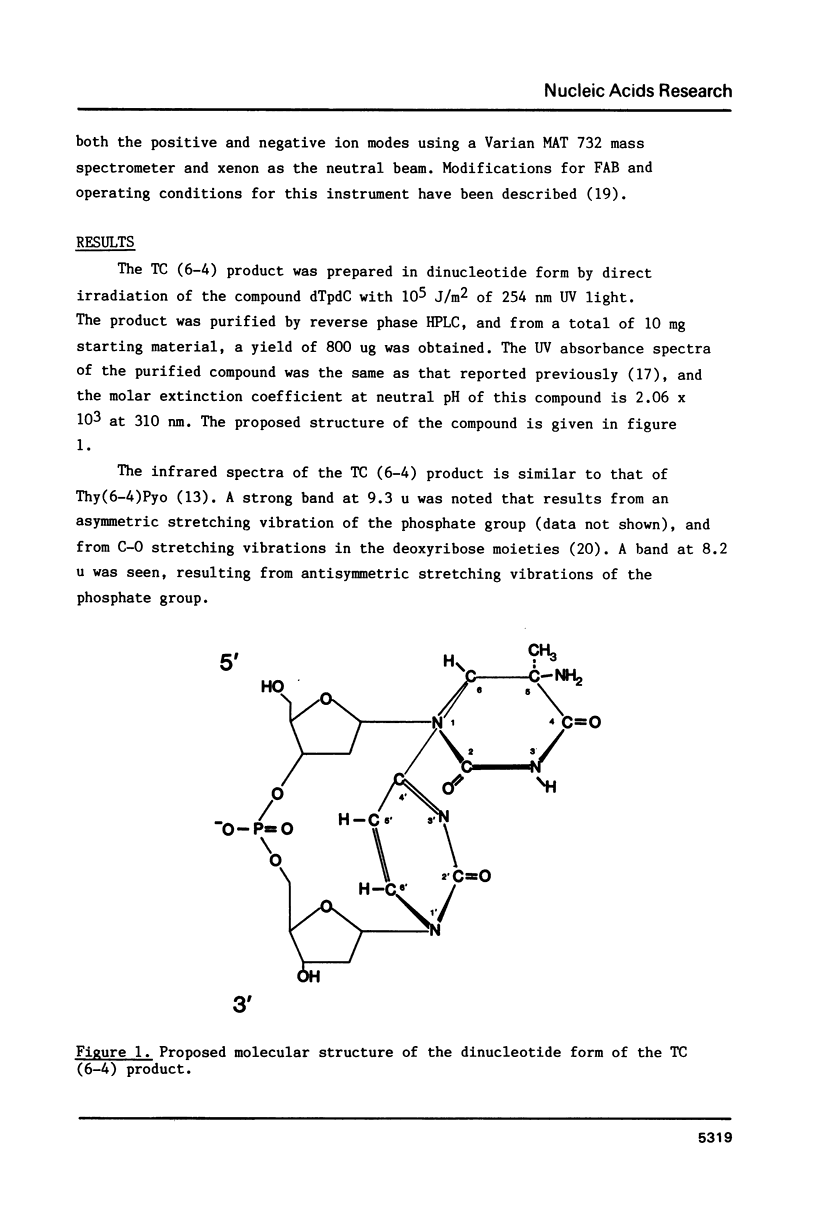
Ultraviolet light induces damage to DNA, with the majority of the damage expressed as the formation of cyclobutane dimers and pyrimidine-pyrimidone (6-4) photoproducts. The (6-4) photoproducts have been implicated as important UV light-induced premutagenic DNA lesions. The most abundant of the (6-4) products is the thymine-cytosine pyrimidine-pyrimidone (6-4) photoproduct, or TC (6-4) product. The structure of the TC (6-4) product was deduced by proton NMR, IR, and fast atom bombardment mass spectroscopy, and the product was found to differ from the previously described photoadduct, Thy(6-4)Pyo, by the presence of an amino group at the 5 position of the 5' pyrimidine. The implications of this structure on DNA base pairing and the induction of ultraviolet light-induced mutations are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brash D. E., Haseltine W. A. UV-induced mutation hotspots occur at DNA damage hotspots. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):189–192. doi: 10.1038/298189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. B., Danyluk S. S. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of 5'-ribo- and deoxyribonucleotide structures in solution. Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 8;13(21):4417–4434. doi: 10.1021/bi00718a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin W. A., Haseltine W. A. Removal of UV light-induced pyrimidine-pyrimidone(6-4) products from Escherichia coli DNA requires the uvrA, uvrB, and urvC gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3821–3824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin W. A., Lo K. M., Haseltine W. A. Alkaline lability of fluorescent photoproducts produced in ultraviolet light-irradiated DNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13535–13543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanawalt P. C., Cooper P. K., Ganesan A. K., Smith C. A. DNA repair in bacteria and mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:783–836. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A. Ultraviolet light repair and mutagenesis revisited. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90329-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karle I. L. Crystal structure of a thymine-thymine adduct from irradiated thymine. Acta Crystallogr B. 1969 Oct 15;25(10):2119–2126. doi: 10.1107/s056774086900522x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karle I. L., Wang S. Y., Varghese A. J. Crystal and molecular structure of a thymine-thymine adduct. Science. 1969 Apr 11;164(3876):183–184. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3876.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langhammer R., Piechocki R. Comparative analysis of UV-induced mutability of ten different codon units in position 211 of the Escherichia coli trpA gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):530–532. doi: 10.1007/BF00436204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippke J. A., Gordon L. K., Brash D. E., Haseltine W. A. Distribution of UV light-induced damage in a defined sequence of human DNA: detection of alkaline-sensitive lesions at pyrimidine nucleoside-cytidine sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3388–3392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Yang N. C. Photochemistry of cytosine derivatives. 1. Photochemistry of thymidylyl-(3' leads to 5')-deoxycytidine. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):4865–4876. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H. Mutational specificity in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:215–238. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades D. F., Wang S. Y. Uracil-thymine adduct from a mixture of uracil and thymine irradiated with ultraviolet light. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4416–4420. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagher D., Strauss B. Insertion of nucleotides opposite apurinic/apyrimidinic sites in deoxyribonucleic acid during in vitro synthesis: uniqueness of adenine nucleotides. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4518–4526. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Rupp W. D. A novel repair enzyme: UVRABC excision nuclease of Escherichia coli cuts a DNA strand on both sides of the damaged region. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):249–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90354-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese A. J., Patrick M. H. Cytosine derived heteroadduct formation in ultraviolet-irradiated DNA. Nature. 1969 Jul 19;223(5203):299–300. doi: 10.1038/223299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese A. J. Photochemistry of nucleic acids and their constituents. Photophysiology. 1972;(7):207–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese A. J., Wang S. Y. Thymine-thymine adduct as a photoproduct of thymine. Science. 1968 Apr 12;160(3824):186–187. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3824.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese A. J., Wang S. Y. Ultraviolet irradiation of DNA in vitro and in vivo produces a 3d thymine-derived product. Science. 1967 May 19;156(3777):955–957. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3777.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Y., Varghese A. J. Cytosine-thymine addition product from DNA irradiated with ultraviolet light. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Nov 30;29(4):543–549. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90519-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. D., Skopek T. R., Hutchinson F. Changes in DNA base sequence induced by targeted mutagenesis of lambda phage by ultraviolet light. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 5;173(3):273–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



