Abstract
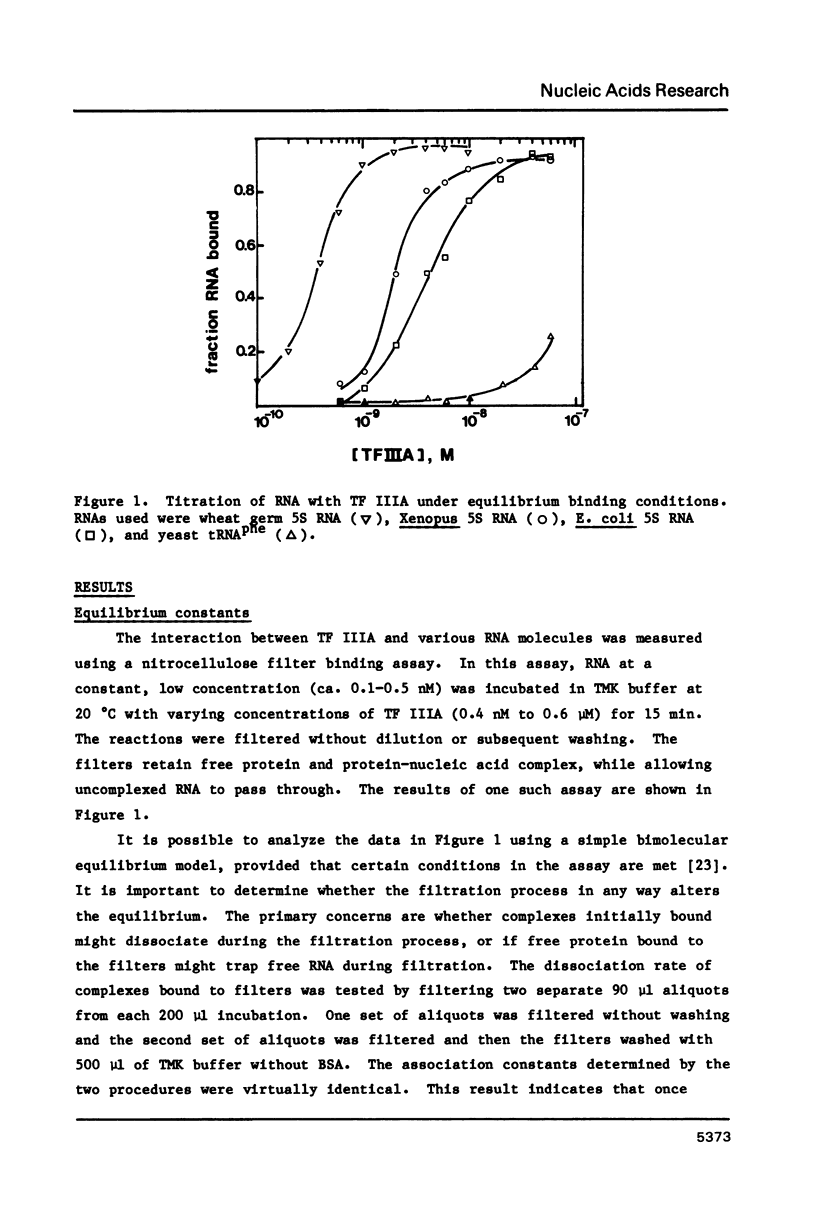
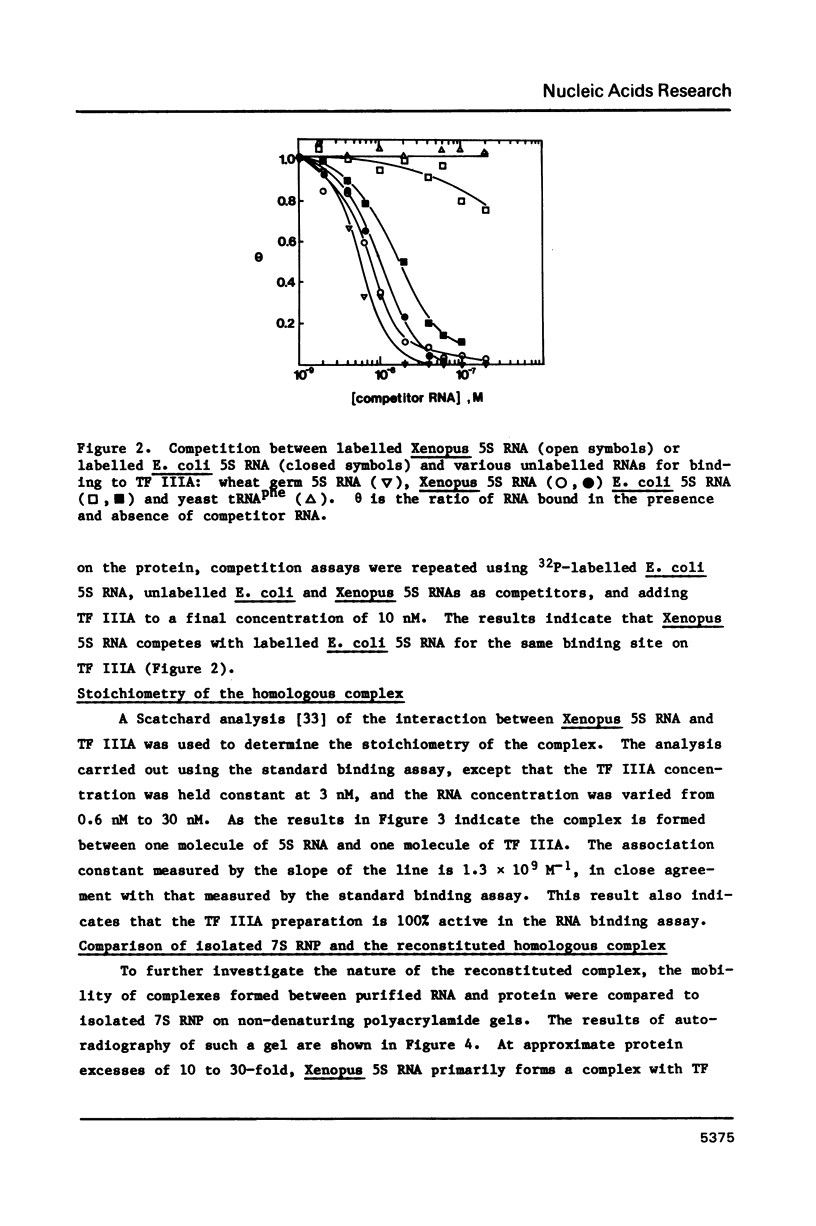
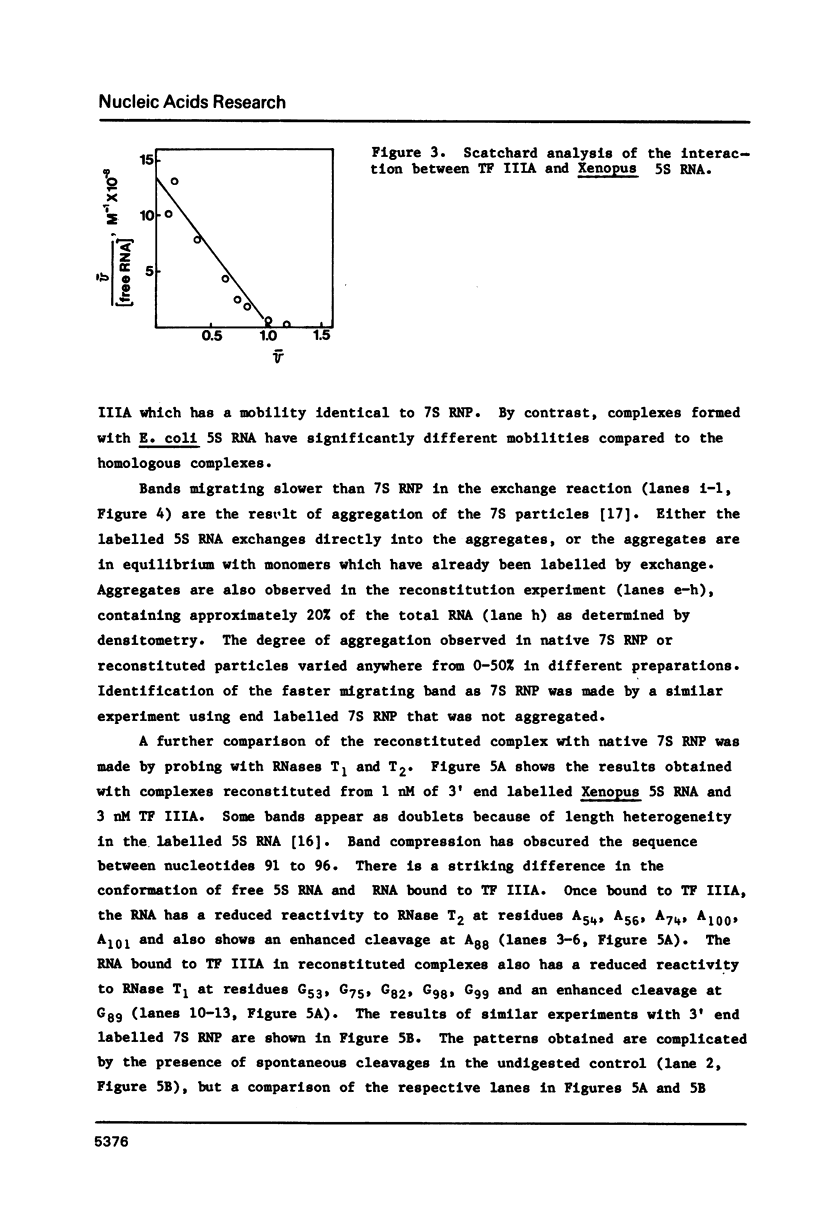
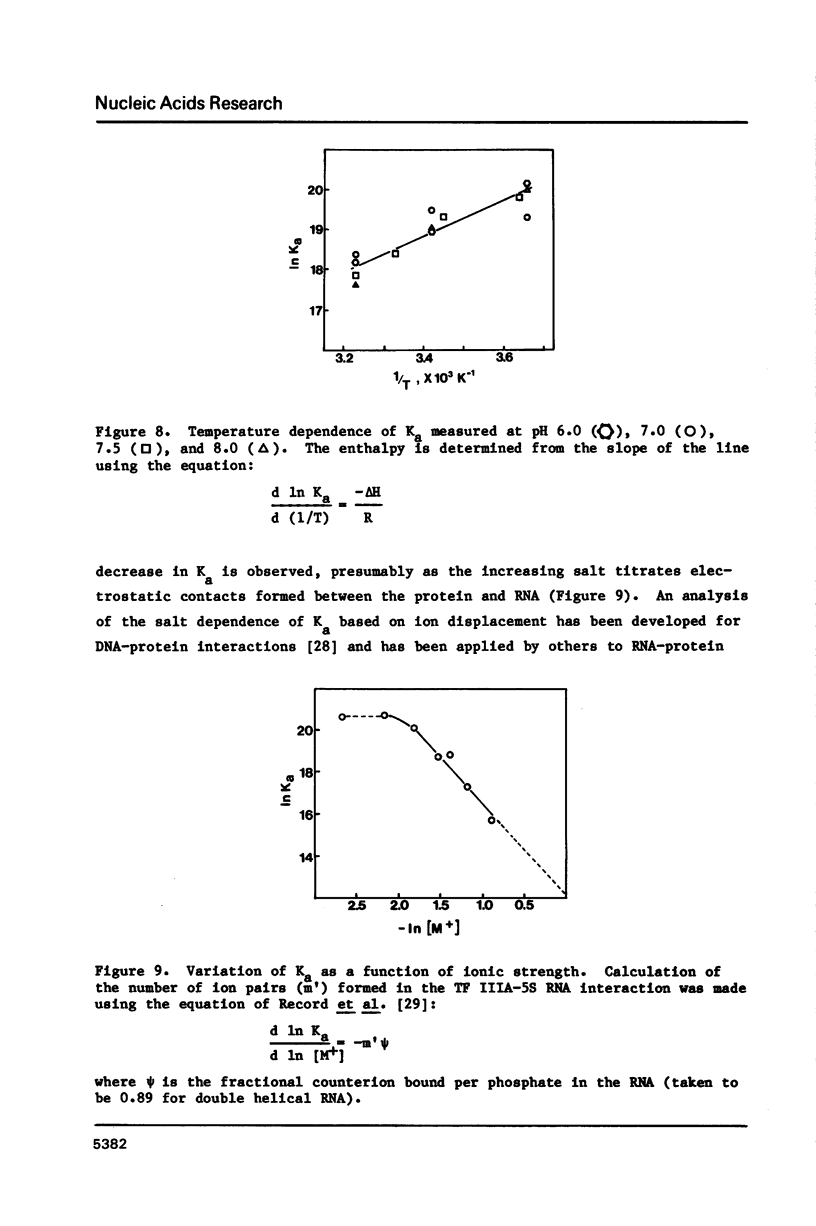
A nitrocellulose filter binding assay has been developed to study the interaction of Xenopus transcription factor IIIA with 5S RNA. The protein binds Xenopus oocyte 5S RNA with an association constant of 1.4 X 10(9) M-1 at 0.1 M salt, pH 7.5 at 20 degrees C. TF IIIA binds wheat germ 5S RNA with a two-fold higher affinity, E. coli 5S RNA with a four-fold weaker affinity, and has a barely detectable interaction with yeast tRNAphe. The preference for binding eukaryotic 5S RNA is enhanced in competition assays. The homologous reconstituted complex contains one molecule each of protein and 5S RNA and is indistinguishable from native 7S RNP in mobility on non-denaturing polyacrylamide gels. The conformation of the RNA in reconstituted particles is identical to the conformation of RNA in native 7S RNP. Further analysis of the homologous interaction reveals that complex formation is a favoured both by enthalpy and entropy. The 5S RNA binding activity has a broad pH optimum spanning pH 6.0 to pH 8.0. Determination of the salt dependence of Ka reveals that as many as 5 lysine-phosphate type ionic bonds may be formed in the homologous complex. Approximately 68% of the free energy of complex formation is contributed by non-electrostatic interactions between TF IIIA and Xenopus 5S RNA.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J., Delihas N., Hanas J. S., Wu C. W. 5S RNA structure and interaction with transcription factor A. 1. Ribonuclease probe of the structure of 5S RNA from Xenopus laevis oocytes. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5752–5759. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen J., Delihas N., Hanas J. S., Wu C. W. 5S RNA structure and interaction with transcription factor A. 2. Ribonuclease probe of the 7S particle from Xenopus laevis immature oocytes and RNA exchange properties of the 7S particle. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5759–5766. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker J. J., Roeder R. G. Physical properties and DNA-binding stoichiometry of a 5 S gene-specific transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6158–6164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey J., Cameron V., de Haseth P. L., Uhlenbeck O. C. Sequence-specific interaction of R17 coat protein with its ribonucleic acid binding site. Biochemistry. 1983 May 24;22(11):2601–2610. doi: 10.1021/bi00280a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey J., Uhlenbeck O. C. Kinetic and thermodynamic characterization of the R17 coat protein-ribonucleic acid interaction. Biochemistry. 1983 May 24;22(11):2610–2615. doi: 10.1021/bi00280a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delihas N., Andersen J. Generalized structures of the 5S ribosomal RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7323–7344. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis H., le Maire M. Thesaurisomes, a novel kind of nucleoprotein particle. Subcell Biochem. 1983;9:263–297. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-3533-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-terminal labelling of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):560–561. doi: 10.1038/275560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg A. M., King B. O., Roeder R. G. Xenopus 5S gene transcription factor, TFIIIA: characterization of a cDNA clone and measurement of RNA levels throughout development. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):479–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90455-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu C. W. Binding of Xenopus transcription factor A to 5S RNA and to single stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2745–2758. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu C. W. Cooperative model for the binding of Xenopus transcription factor A to the 5S RNA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2142–2145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu C. W. DNA unwinding ability of Xenopus transcription factor A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1265–1276. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Hazuda D. J., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu F. Y., Wu C. W. Xenopus transcription factor A requires zinc for binding to the 5 S RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14120–14125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kime M. J., Moore P. B. NMR evidence for the existence of two native conformations of 5S RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):4973–4983. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.4973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Wegnez M. Isolation of a 7S particle from Xenopus laevis oocytes: a 5S RNA-protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):241–245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Erdmann V. A., Appel B. Structural requirements for the interaction of 5S rRNA with the eukaryotic transcription factor IIIA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8393–8406. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Erdmann V. A. Isolation and characterization of a 7 S RNP particle from mature Xenopus laevis oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 4;157(2):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80562-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Anderson C. F., Lohman T. M. Thermodynamic analysis of ion effects on the binding and conformational equilibria of proteins and nucleic acids: the roles of ion association or release, screening, and ion effects on water activity. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):103–178. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000202x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Lohman M. L., De Haseth P. Ion effects on ligand-nucleic acid interactions. J Mol Biol. 1976 Oct 25;107(2):145–158. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds W. F., Gottesfeld J. M. 5S rRNA gene transcription factor IIIA alters the helical configuration of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1862–1866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D. Contact points between a positive transcription factor and the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D., Engelke D., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. The binding of a transcription factor to deletion mutants of a 5S ribosomal RNA gene. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):665–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Jackson I. J., Brown D. D. Domains of the positive transcription factor specific for the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90396-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spierer P., Bogdanov A. A., Zimmermann R. A. Parameters for the interaction of ribosomal proteins L5, L18, and L25 with 5S RNA from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 12;17(25):5394–5398. doi: 10.1021/bi00618a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. A., Pace B., Marsh T., Pace N. R. The ribonucleoprotein substrate for a ribosomal RNA-processing nuclease. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11448–11453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss H. S., Burgess R. R., Record M. T., Jr Binding of Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid polymerase holoenzyme to a bacteriophage T7 promoter-containing fragment: evaluation of promoter binding constants as a function of solution conditions. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 22;19(15):3504–3515. doi: 10.1021/bi00556a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormington W. M., Bogenhagen D. F., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A quantitative assay for Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription in vitro. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):809–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]