Abstract
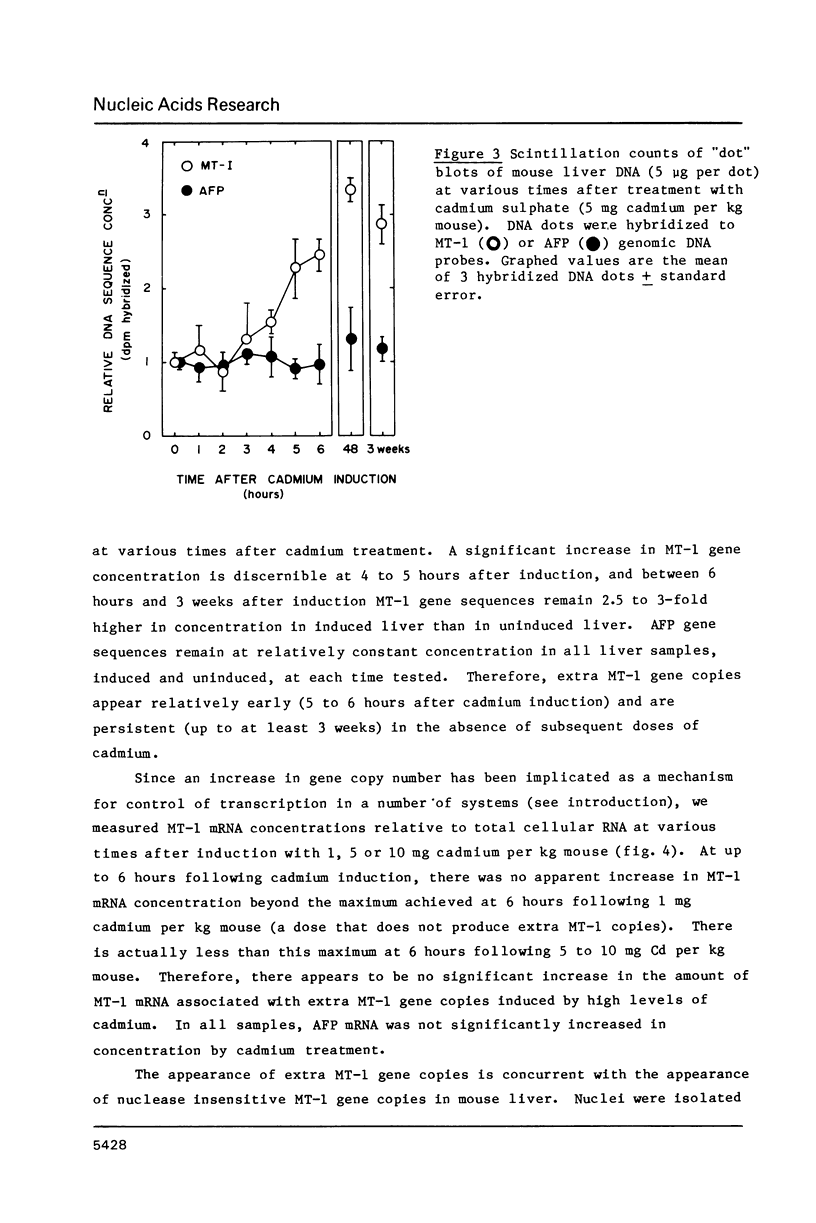
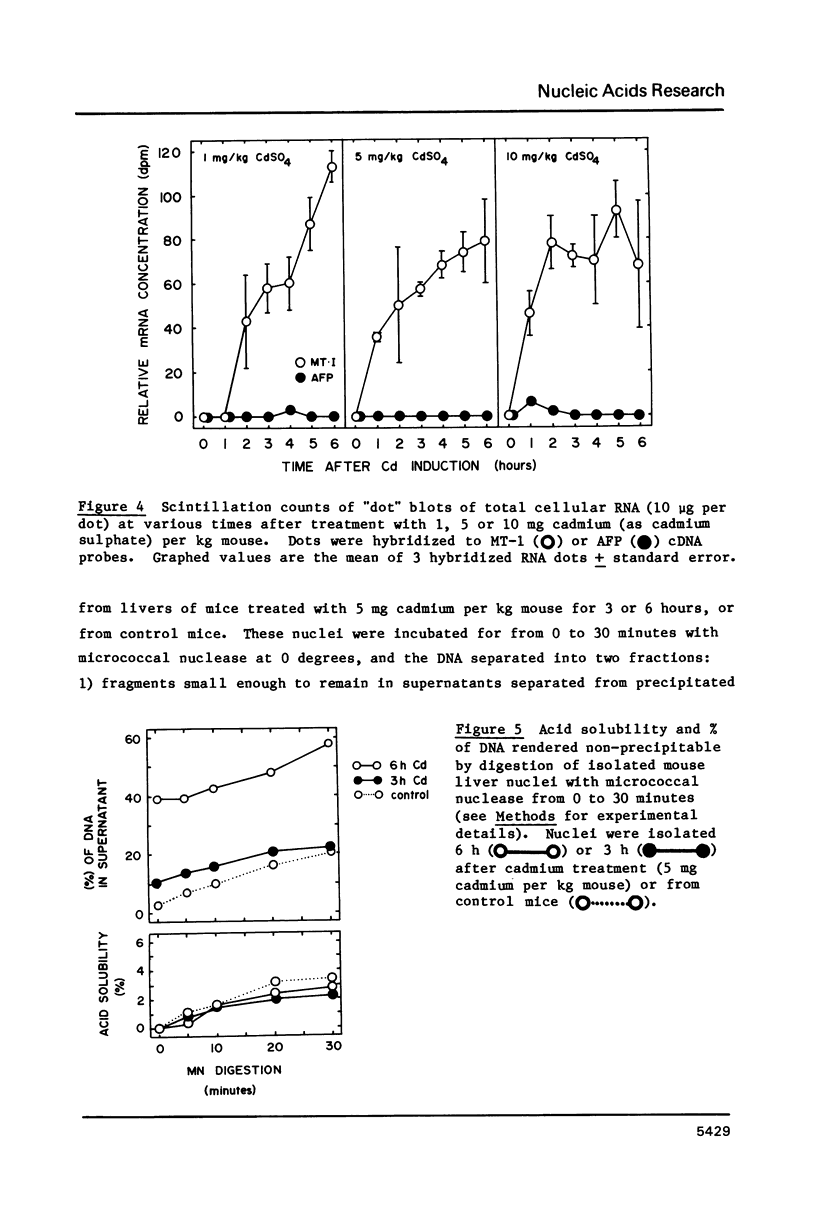
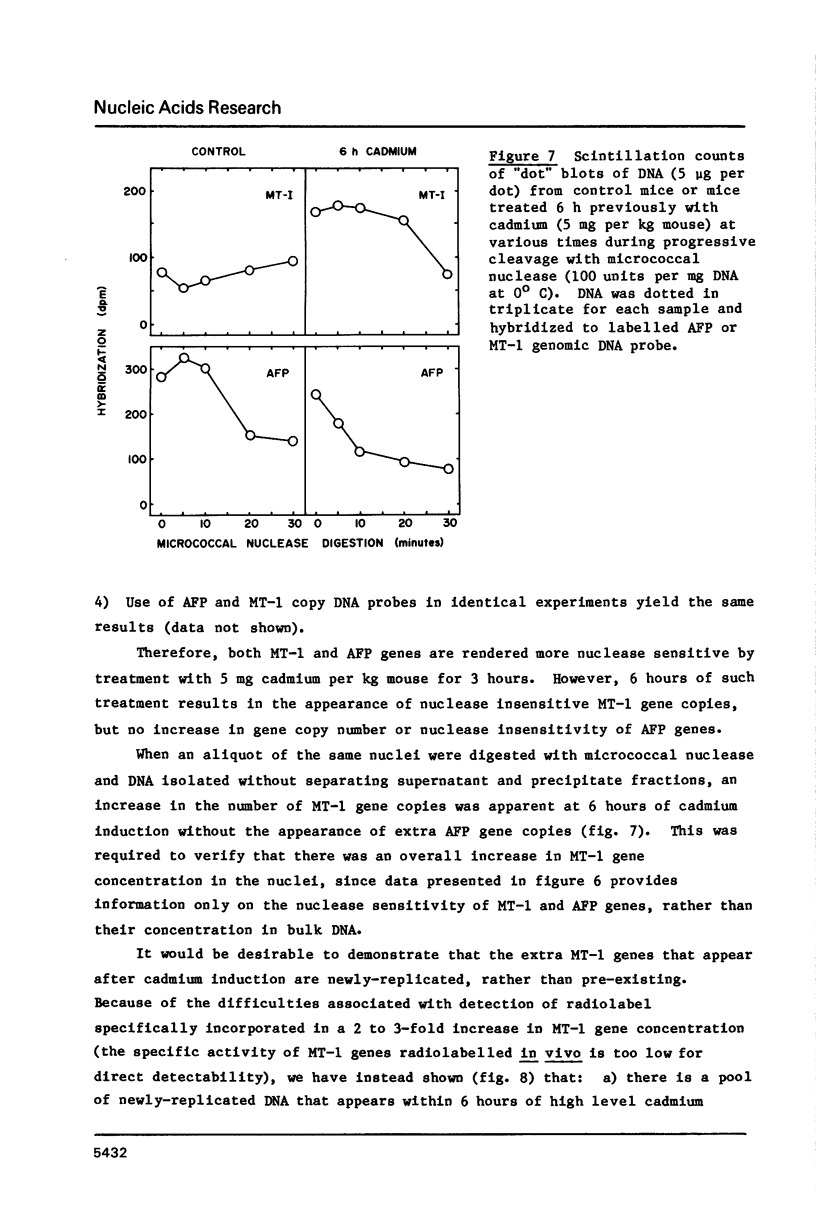
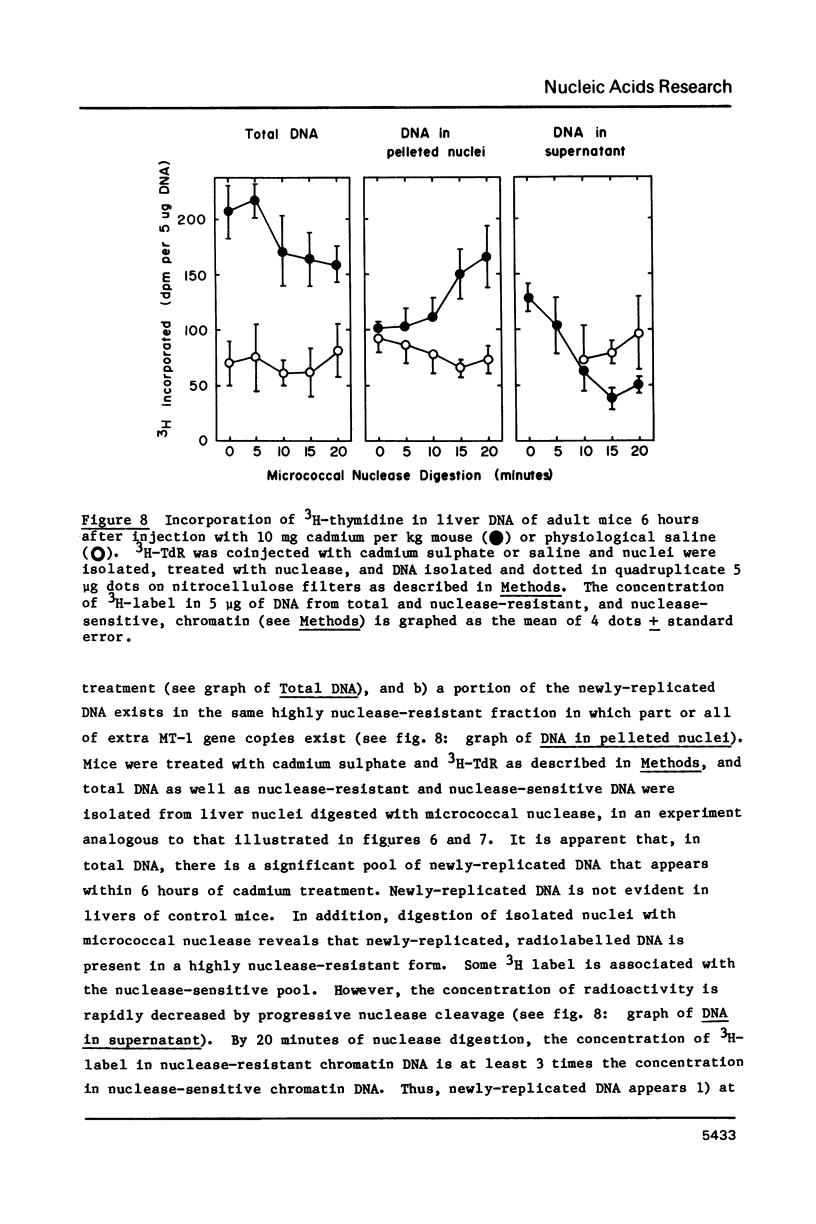
A variety of genes have been shown to change copy number during development, including rRNA genes in amphibians and chorion proteins in insects. Dihydrofolate reductase and metallothionein-1 (MT-1) genes are present in high copy number in cultured mammalian cells subjected to low levels of agents that will select for cells with amplified copies of specific genes. Recent studies have shown that the metallothionein-1 gene in mouse liver is regulated at the transcriptional level by treatment with heavy metals. We report here that, at cadmium concentrations 5 to 10-fold higher than that required to induce maximal transcription of the MT-1 gene, there is a 2 to 3-fold increase in MT-1 gene concentration in liver nuclear DNA by 6 hours after induction, and extra copies persist up to 3 weeks in the absence of further heavy metal treatment. The extra MT-1 gene copies that appear 6 hours after cadmium treatment are in a conformation that renders them relatively nuclease insensitive.
Full text
PDF


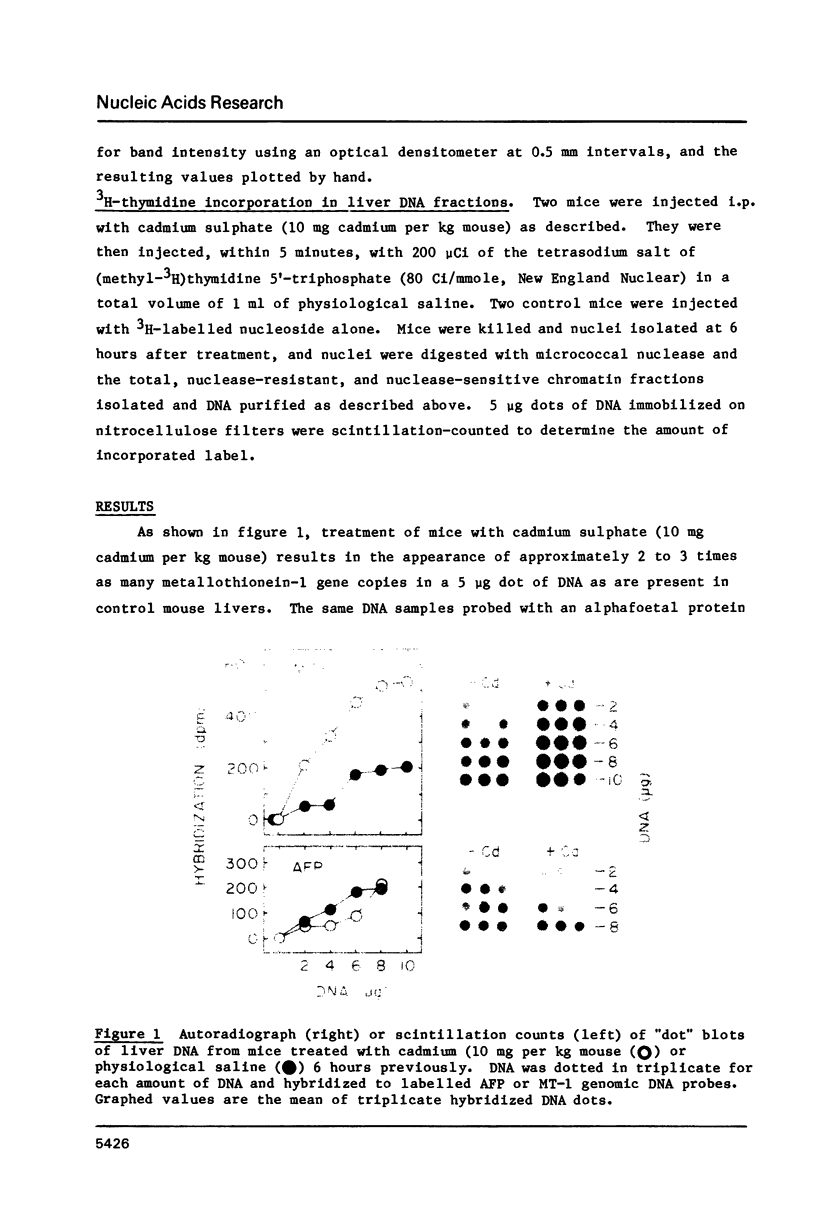
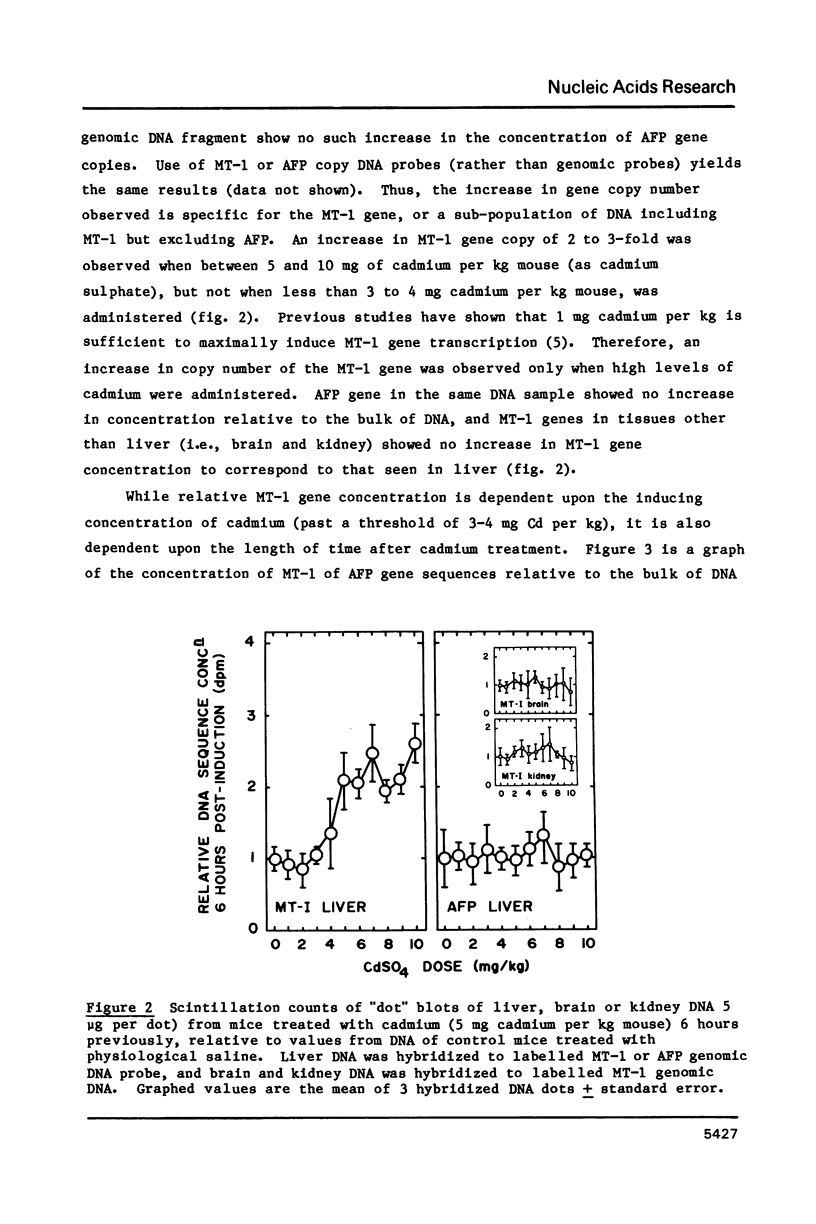








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Kellems R. E., Bertino J. R., Schimke R. T. Selective multiplication of dihydrofolate reductase genes in methotrexate-resistant variants of cultured murine cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1357–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach L. R., Palmiter R. D. Amplification of the metallothionein-I gene in cadmium-resistant mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the mouse metallothionein-I gene by heavy metals. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5712–5716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Perrin F., Gannon F., Palmiter R. D. Isolation and characterization of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6511–6515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin M. B., Tilghman S. M. Structure of the alpha-fetoprotein gene in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1351–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Brown P. C., Schimke R. T. Amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes in unstably methotrexate-resistant cells are associated with double minute chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5669–5673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koropatnick J., Andrews G., Duerksen J. D., Varshney U., Gedamu L. Mouse hepatic metallothionein-I gene cleavage by micrococcal nuclease is enhanced after induction by cadmium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3255–3267. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani B. D., Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in a single cell cycle in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1901–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst G. S., Bousquet W. F., Miya T. S. Kinetics of cadmium-induced hepatic and renal metallothionein synthesis in the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Jan;39(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(77)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification, drug resistance, and cancer. Cancer Res. 1984 May;44(5):1735–1742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Mahowald A. P. Amplification of genes for chorion proteins during oogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1096–1100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C. The organization and amplification of two chromosomal domains containing Drosophila chorion genes. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90373-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Nutter R., Montoya A. L., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Integration and organization of Ti plasmid sequences in crown gall tumors. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):729–739. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]