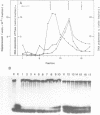
Abstract
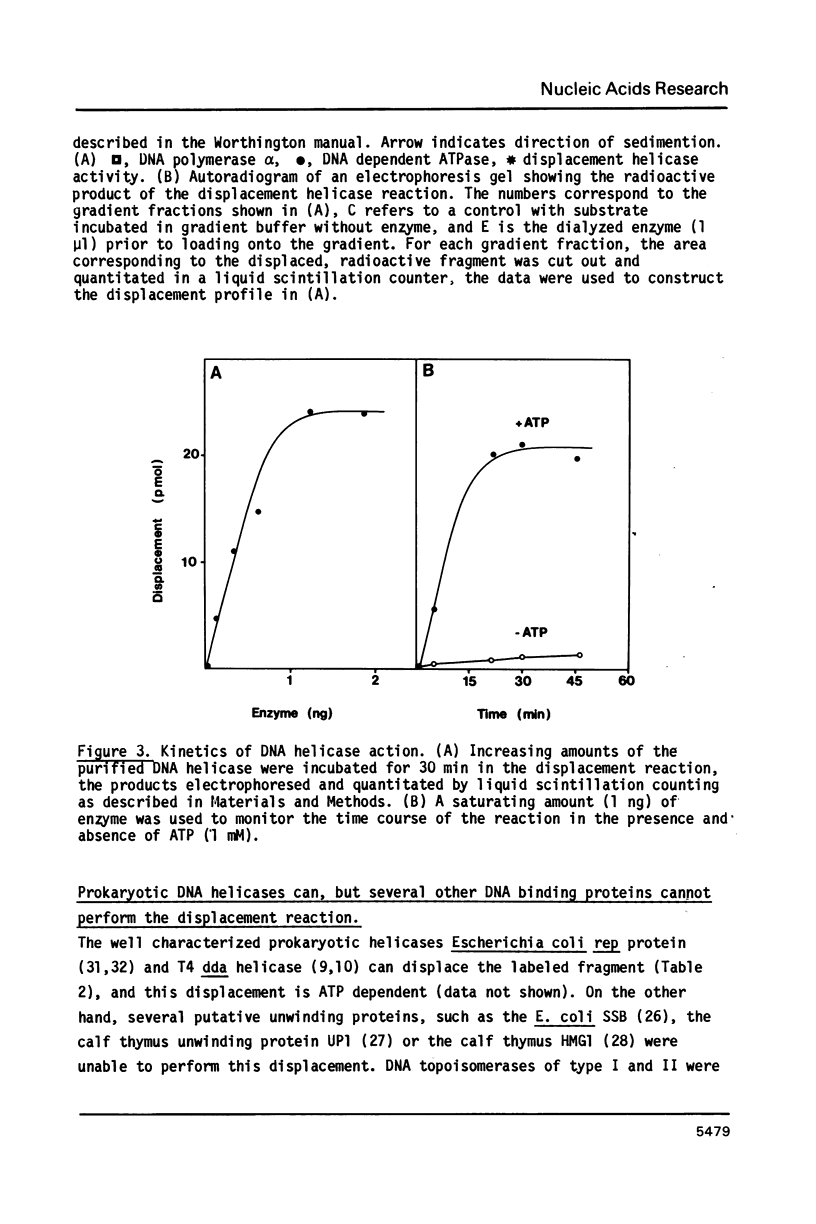
A forked DNA was constructed to serve as a substrate for DNA helicases. It contains features closely resembling a natural replication fork. The DNA was prepared in large amounts and was used to assay displacement activity during isolation from calf thymus DNA polymerases alpha holoenzyme. One form of DNA polymerase alpha holoenzyme is possibly involved leading strand replication at the replication fork and possesses DNA dependent ATPase activity (Ottiger, H.-P. and Hübscher, U. (1984) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 3993-3997). The enzyme can be separated from DNA polymerase alpha by velocity sedimentation in conditions of very low ionic strength and then be purified by chromatography on Sephacryl S-200 and ATP-agarose. At all stages of purification, DNA dependent ATPase and displacement activity profiles were virtually superimposable. The DNA dependent ATPase can displace a hybridized DNA fragment with a short single-stranded tail at its 3'hydroxyl end only in the presence of ATP, and this displacement relies on ATP hydrolysis. Furthermore, homogeneous single-stranded binding proteins from calf thymus as well as from other tissues cannot perform this displacement reaction. By all this token the DNA dependent ATPase appears to be a DNA helicase. It is suggested that this DNA helicase might act in concert with DNA polymerase alpha at the leading strand, possibly pushing the replication fork ahead of the polymerase.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Monem M., Arthur H. M., Benz I., Hoffmann-Berling H., Reygers U., Seiter A., Taucher-Scholz G. Functions of DNA helicases in the DNA metabolism of Escherichia coli. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;179:385–393. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-8730-5_40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai N., Kornberg A. Rep protein as a helicase in an active, isolatable replication fork of duplex phi X174 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5294–5298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assairi L. M., Johnston I. R. A DNA-dependent ATPase of calf-thymus. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 15;99(1):71–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biamonti G., Cobianchi F., Falaschi A., Riva S. Total purification of a DNA-dependent ATPase and of a DNA-binding protein from human cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):161–165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01399.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. M., Korn D. Structural and enzymological characterization of a deoxyribonucleic acid dependent adenosine triphosphatase from KB cell nuclei. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2623–2633. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäumel I., Meyer T. F., Geider K. Functional aspects of Escherichia coli rep helicase in unwinding and replication of DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):247–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobianchi F., Biamonti G., Mastromei G., Falaschi A., Riva S. A DNA dependent ATPase from HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 29;104(2):402–409. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90651-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jong P. J., Tommassen J. P., Van der Vliet P. C., Jansz H. S. Purification and characterization of DNA-dependent ATP phosphohydrolases from KB cells. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun;117(1):179–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguet M., de Recondo A. M. A deoxyribonucleic acid unwinding protein isolated from regenerating rat liver. Physical and functional properties. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1660–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geider K., Hoffmann-Berling H. Proteins controlling the helical structure of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:233–260. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachmann H. J., Lezius A. G. An ATPase depending on the presence of single-stranded DNA from mouse myeloma. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jan 15;61(2):325–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrick G., Alberts B. Purification and physical characterization of nucleic acid helix-unwinding proteins from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2124–2132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta Y., Stern H. DNA unwinding protein from meiotic cells of Lilium. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1872–1880. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongeneel C. V., Formosa T., Alberts B. M. Purification and characterization of the bacteriophage T4 dda protein. A DNA helicase that associates with the viral helix-destabilizing protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12925–12932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg A., Scott J. F., Bertsch L. L. ATP utilization by rep protein in the catalytic separation of DNA strands at a replicating fork. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3298–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzle C. C., Heizmann C. W., Hübscher U., Hobi R., Winkler G. C., Jaeger A. W., Morgenegg G. Chromatin changes accompanying neuronal differentiation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 2):493–499. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn B., Abdel-Monem M. DNA synthesis at a fork in the presence of DNA helicases. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jun 15;125(1):63–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Alberts B. M. Characterization of the DNA-dependent GTPase activity of T4 gene 41 protein, an essential component of the T4 bacteriophage DNA replication apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2813–2820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W., Tabor S., Richardson C. C. The gene 4 protein of bacteriophage T7. Characterization of helicase activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14017–14024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. R., Glassberg J., Scott J. V., Kornberg A. A temperature-sensitive single-stranded DNA-binding protein from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2897–2901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottiger H. P., Hübscher U. Mammalian DNA polymerase alpha holoenzymes with possible functions at the leading and lagging strand of the replication fork. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3993–3997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto B. DNA-dependent ATPases in concanavalin A stimulated lymphocytes. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80377-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevani P., Badaracco G., Chang L. M. Purification and characterization of two forms of DNA-dependent ATPase from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4957–4963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski P. D., Hurwitz J. Enzymatic breakage of deoxyribonucleic acid. II. Purification and properties of endonuclease IV from T4 phage-infected Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6192–6198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawaragi Y., Enomoto T., Watanabe Y., Hanaoka F., Yamada M. Multiple deoxyribonucleic acid dependent adenosinetriphosphatases in FM3A cells. Characterization of an adenosinetriphosphatase that prefers poly [d(A-T)] as cofactor. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 31;23(3):529–533. doi: 10.1021/bi00298a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. C., Meyer R. R. Deoxyribonucleic acid dependent adenosinetriphosphatases from the Novikoff hepatoma. Characterization of a homogeneous adenosinetriphosphatase that stimulates DNA polymerase beta. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 28;21(20):5060–5068. doi: 10.1021/bi00263a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma K., Koike K. Properties of a DNA-dependent ATPase from rat mitochondria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1949–1961. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Shimura K. Unwinding of DNA by nonhistone chromosomal protein HMG(1 + 2) from pig thymus as determined with endonuclease. J Biochem. 1984 Jan;95(1):117–124. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]