Abstract
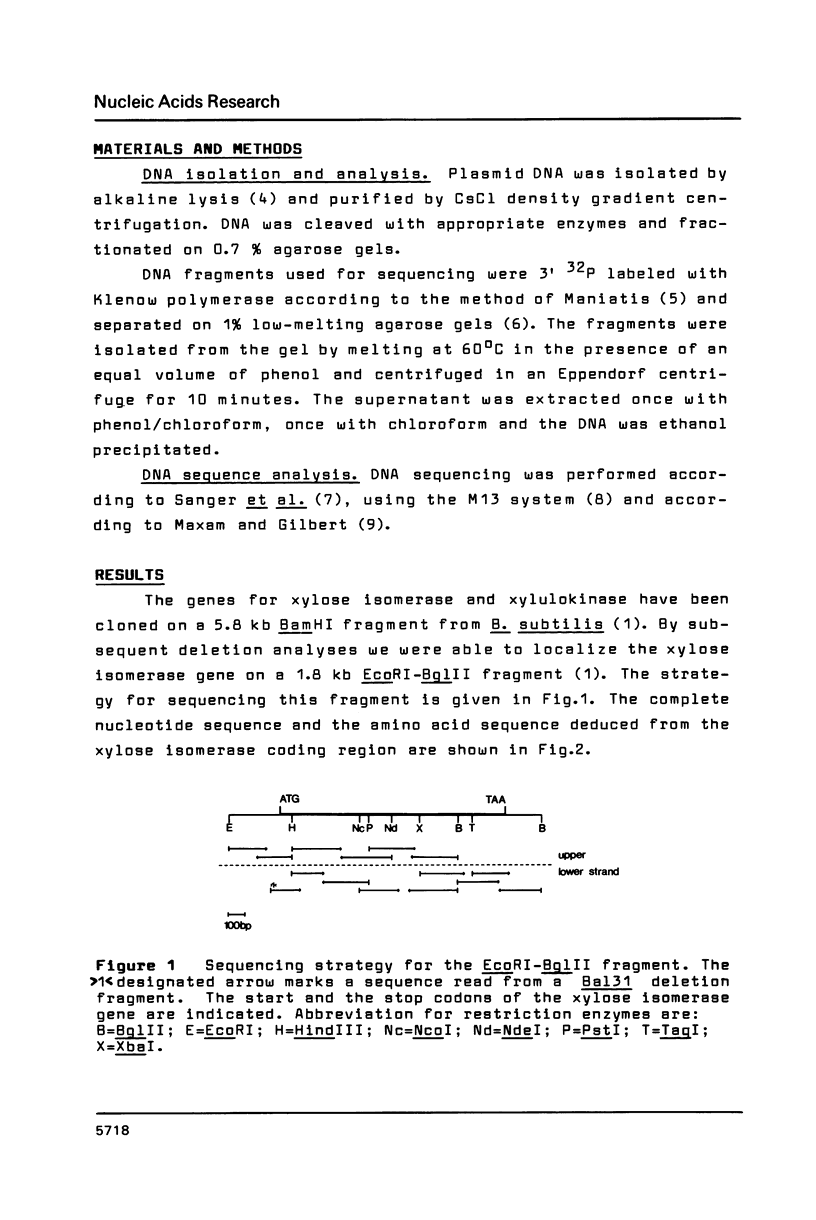
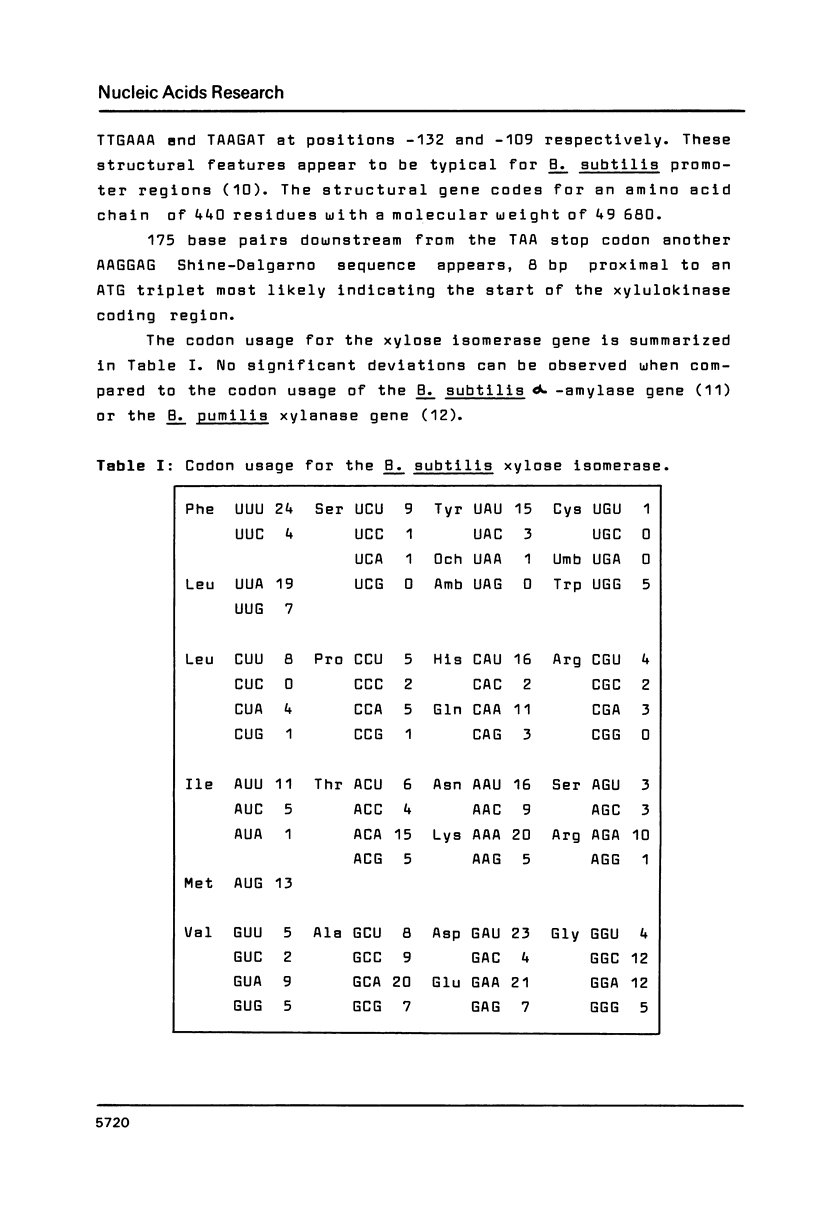
The xylose isomerase gene from Bacillus subtilis was cloned from a genomic BamH1 library by complementation of an isomerase defective Escherichia coli strain as previously described. The ATG initiation codon is preceded by a Shine-Dalgarno sequence and two hexamers being characteristic for the promoter region of Bacillus genes. The structural gene consists of 1320 base pairs, thus coding for a polypeptide chain of 440 amino acids with a molecular weight of 49 680. The polypeptide primary structure shows over 50% homology to that of the E. coli xylose isomerase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs K. A., Lancashire W. E., Hartley B. S. Molecular cloning, DNA structure and expression of the Escherichia coli D-xylose isomerase. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):611–616. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01856.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann R. G., Whitfeld P. R., Bottomley W. Construction of a SalI/PstI restriction map of spinach chloroplast DNA using low-gelling-temperature-agarose electrophoresis. Gene. 1980 Jan;8(2):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogue-Angeletti R. A. Subunit structure and amino acid composition of xylose isomerase from Streptomyces albus. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7814–7818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg G. D., Sarthy A., Larson A. E., Backer M. P., Crabb J. W., Lidstrom M., Hall B. D., Furlong C. E. Xylose isomerase from Escherichia coli. Characterization of the protein and the structural gene. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6826–6832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm M., Hollenberg C. P. Selective cloning of Bacillus subtilis xylose isomerase and xylulokinase in Escherichia coli genes by IS5-mediated expression. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2555–2560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02173.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki H., Ohmura K., Nakayama A., Takeichi Y., Otozai K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G., Yamane K. Alpha-amylase genes (amyR2 and amyE+) from an alpha-amylase-hyperproducing Bacillus subtilis strain: molecular cloning and nucleotide sequences. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):327–337. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.327-337.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



