Previously in this journal, we published a phase 1 study of nebulized heparin in patients with acute lung injury [1]. Patients were administered heparin at doses of 50,000, 100,000, 200,000, or 400,000 U/day for 2 days, and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid samples were taken at baseline and after the last heparin dose. The study demonstrated a trend to reduced coagulation activation (prothrombin fragments) in BAL fluid after the last dose of nebulized heparin [1].
Following publication of these data, we were offered the possibility of further analysis of the BAL fluid with additional markers of coagulation activation, including thrombin-antithrombin complexes (TATcs), fibrin degradation products (FDPs), and plasminogen activator activity (PAI-1) levels. We wish to publish the results of this further analysis. The 400,000 U/day group had one patient more than the same group in the previously published data.
We found that TATc and FDP levels were significantly reduced in patients treated with 400,000 U/day of nebulized heparin, but not PAI-1 (Figure 1 overleaf). We believe that these data are important as they demonstrate for the first time that nebulized heparin significantly reduces coagulation activation in the lungs of critically ill patients with acute lung injury. This may be important knowledge as inflammatory mechanisms related to coagulation activation, such as hyaline membrane formation and microvascular thrombosis, may mediate lung injury [2,3].
Figure 1.
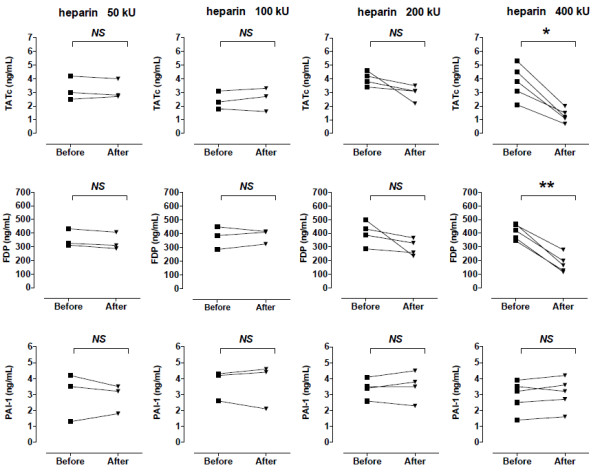
Changes in markers of coagulation activation in bronchoalveolar fluid before and after 2 days of nebulized heparin. Each line represents a single patient (*P < 0.01, **P < 0.001, paired t test). FDP, fibrin degradation product; NS, not significant; PAI-1, plasminogen activator activity; TATc, thrombin-antithrombin complex.
Abbreviations
BAL: bronchoalveolar lavage; FDP: fibrin degradation product; PAI-1: plasminogen activator activity; TATc: thrombin-antithrombin complex.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
See related research by Dixon et al., http://ccforum.com/content/12/3/R64
Contributor Information
Barry Dixon, Email: barry.dixon@svhm.org.au.
Marcus J Schultz, Email: marcus.j.schultz@gmail.com.
Jorrit J Hofstra, Email: j.j.hofstra@amc.uva.nl.
Duncan J Campbell, Email: dcampbell@svi.edu.au.
John D Santamaria, Email: john.santamaria@svhm.org.au.
References
- Dixon B, Santamaria JD, Campbell DJ. A phase 1 trial of nebulised heparin in acute lung injury. Crit Care. 2008;12:R64. doi: 10.1186/cc6894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon B. The role of microvascular thrombosis in sepsis. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2004;32:619–629. doi: 10.1177/0310057X0403200502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaisdell FW. Pathophysiology of the respiratory distress syndrome. Arch Surg. 1974;108:44–49. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1974.01350250036009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


