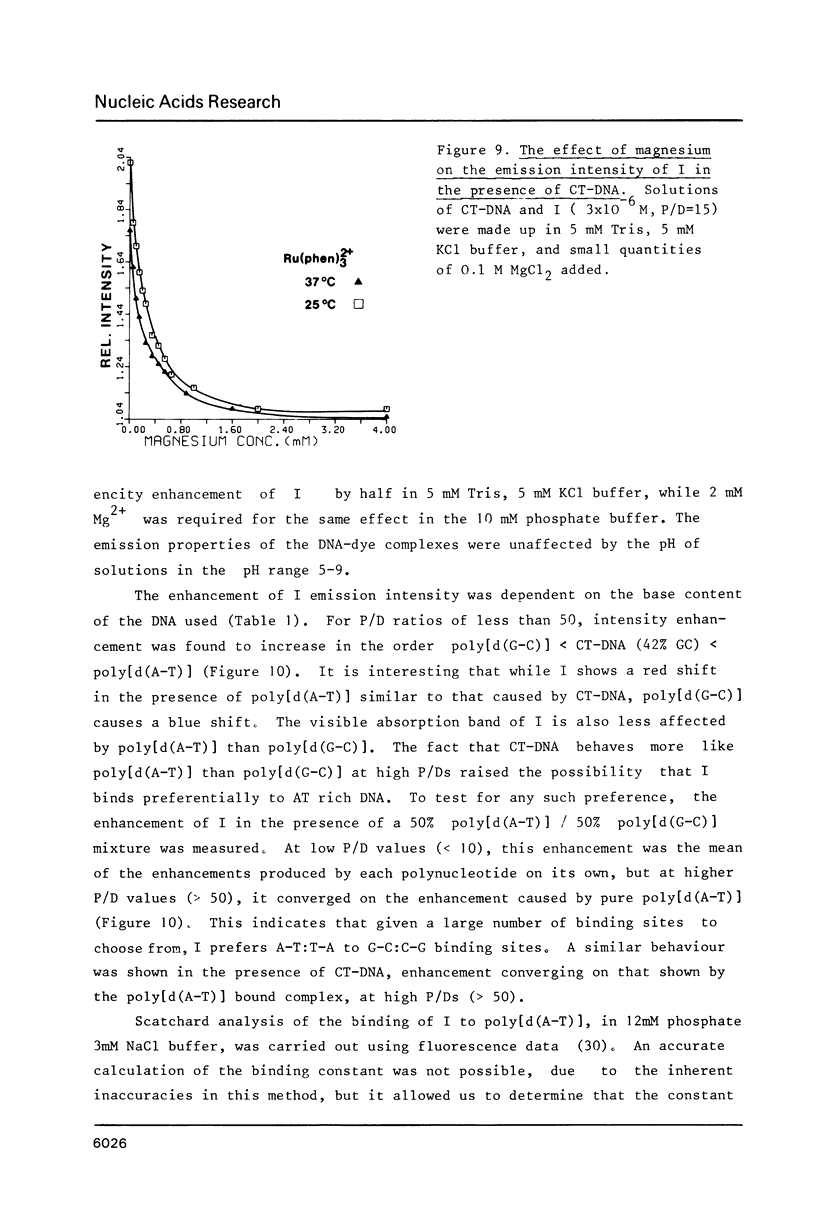
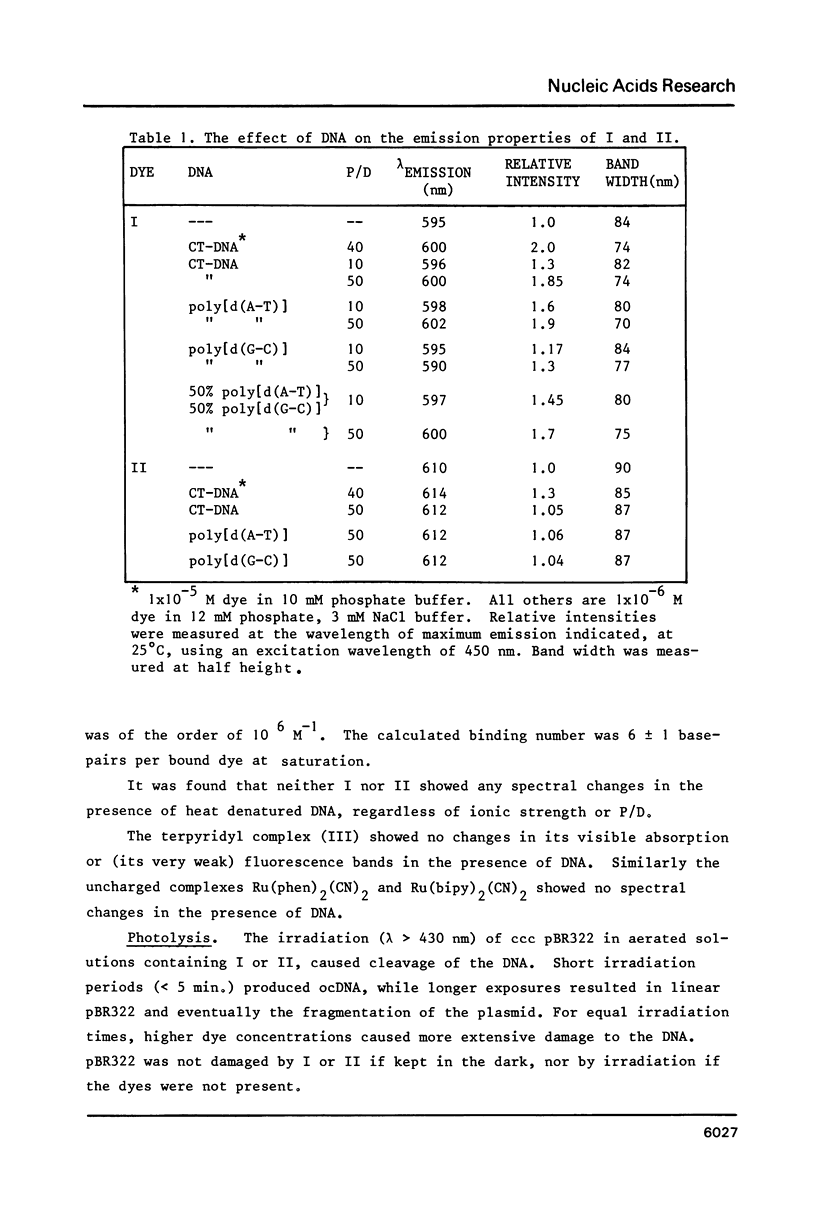
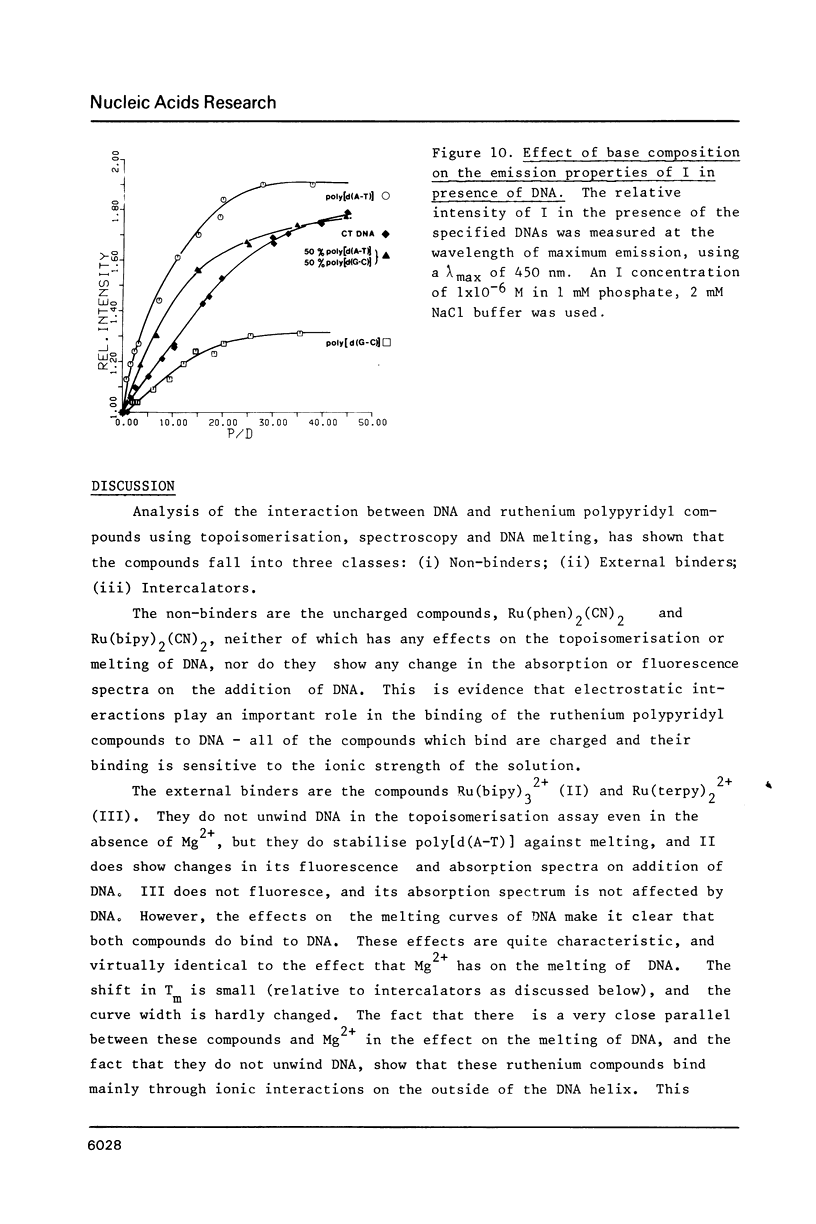
Abstract
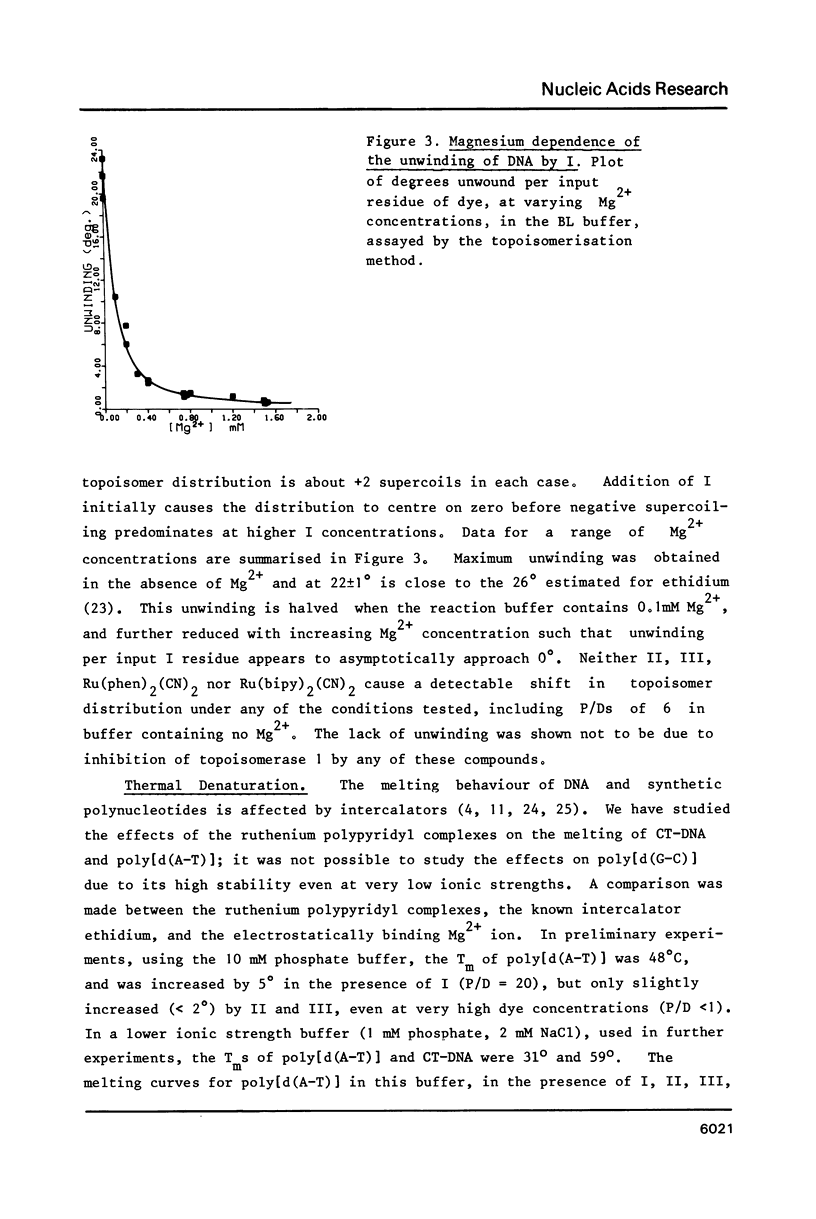
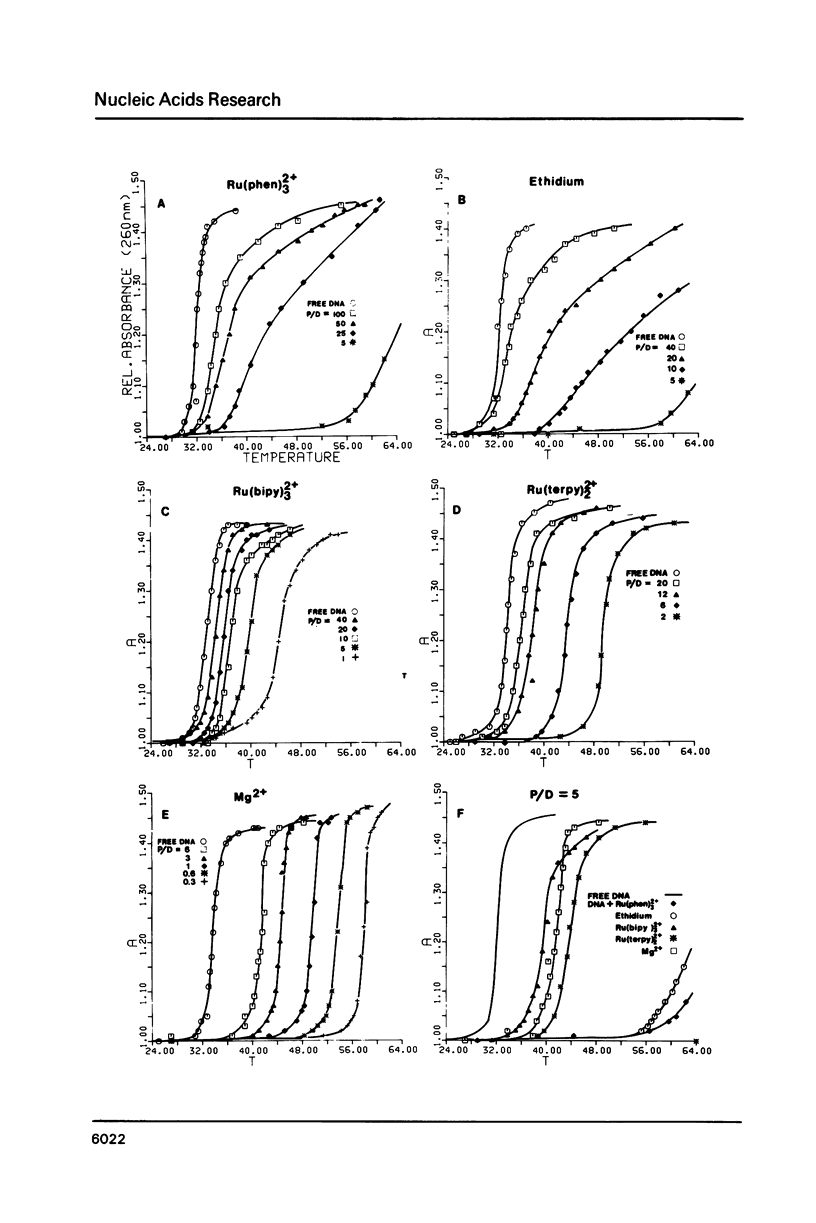
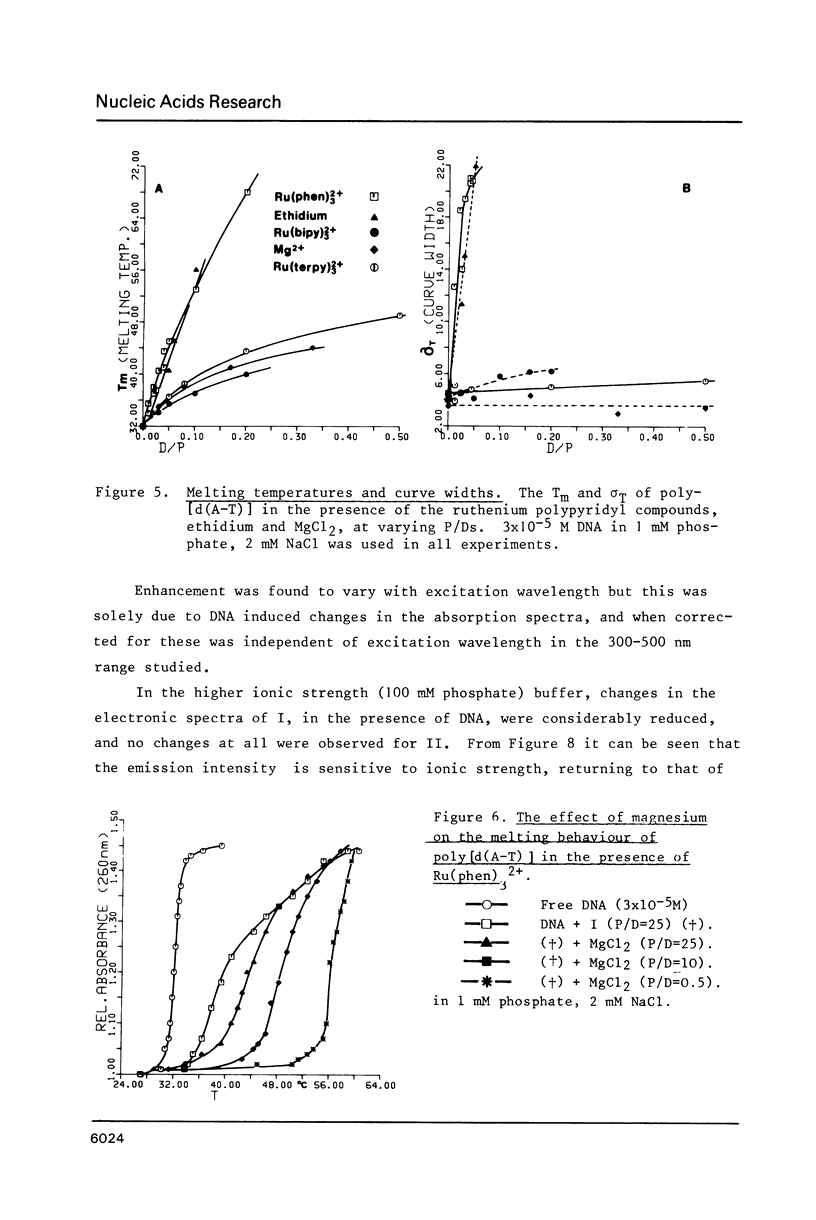
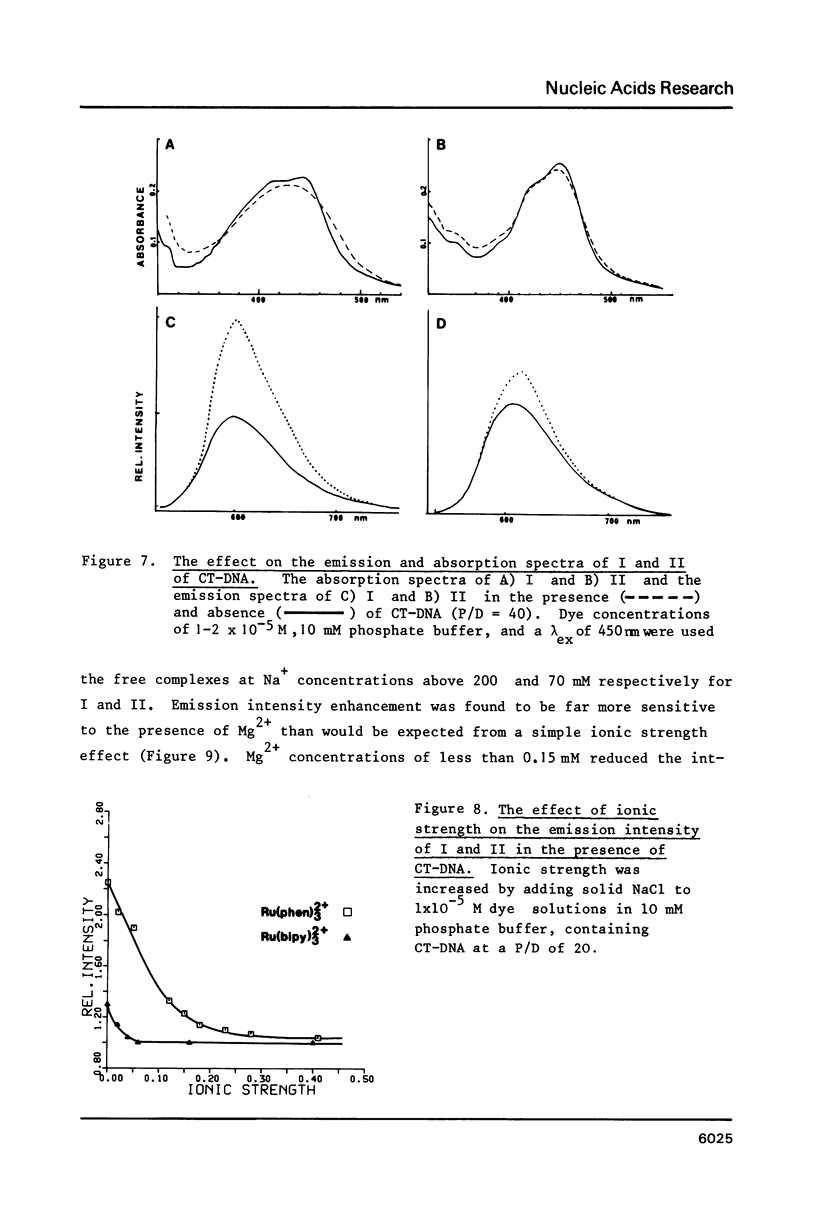
The nature of binding of Ru(phen) 2+ (I), Ru(bipy) 2+ (II), Ru(terpy) 2+ (III) (phen = 1,10-phenanthroline, bipy 3 = 2,2'-bipyridyl, 3 terpy = 2,2'2," - 2 terpyridyl) to DNA, poly[d(G-C)] and poly[d(A-T)] has been compared by absorption, fluorescence, DNA melting and DNA unwinding techniques. I binds intercalatively to DNA in low ionic strength solutions. Topoisomerisation shows that it unwinds DNA by 22 degrees +/- 1 per residue and that it thermally stabilizes poly[d(A-T)] in a manner closely resembling ethidium. Poly[d(A-T)] induces greater spectral changes on I than poly[d(G-C)] and a preference for A-T rich regions is indicated. I binding is very sensitive to Mg2+ concentration. In contrast to I the binding of II and III appears to be mainly electrostatic in nature, and causes no unwinding. There is no evidence for the binding of the neutral Ru(phen)2 (CN)2 or Ru(bipy)2 (CN)2 complexes. DNA is cleaved, upon visible irradiation of aerated solutions, in the presence of either I or II.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baguley B. C., Falkenhaug E. M. The interaction of ethidium with synthetic double-stranded polynucleotides at low ionic strength. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jan;5(1):161–171. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton J. K., Basile L. A., Danishefsky A., Alexandrescu A. Chiral probes for the handedness of DNA helices: enantiomers of tris(4,7-diphenylphenanthroline)ruthenium(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1961–1965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman H. M., Young P. R. The interaction of intercalating drugs with nucleic acids. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1981;10:87–114. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.10.060181.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaires J. B. Equilibrium studies on the interaction of daunomycin with deoxypolynucleotides. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 30;22(18):4204–4211. doi: 10.1021/bi00287a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deniss I. S., Morgan A. R. Studies on the mechanism of DNA cleavage by ethidium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Feb;3(2):315–323. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiel R. J., Datta-Gupta N., Mark E. H., Howard J. C. Induction of DNA damage by porphyrin photosensitizers. Cancer Res. 1981 Sep;41(9 Pt 1):3543–3545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiel R. J., Howard J. C., Mark E. H., Datta Gupta N. Interaction of DNA with a porphyrin ligand: evidence for intercalation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):3093–3118. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.3093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann T., Brown D. M. Base-specific reactions useful for DNA sequencing: methylene blue--sensitized photooxidation of guanine and osmium tetraoxide modification of thymine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Feb;5(2):615–622. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossweiner L. I., Kepka A. G. Photosensitization in biopolymers. Photochem Photobiol. 1972 Oct;16(4):305–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INMAN R. B., BALDWIN R. L. Helix-random coil transitions in synthetic DNAs of alternating sequence. J Mol Biol. 1962 Aug;5:172–184. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennette K. W., Lippard S. J., Vassiliades G. A., Bauer W. R. Metallointercalation reagents. 2-hydroxyethanethiolato(2,2',2'-terpyridine)-platinum(II) monocation binds strongly to DNA by intercalation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3839–3843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. M., Murphy M. J., McConnell D. J., OhUigin C. A comparative study of the interaction of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis (N-methylpyridinium-4-yl)porphyrin and its zinc complex with DNA using fluorescence spectroscopy and topoisomerisation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 11;13(1):167–184. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERMAN L. S. Structural considerations in the interaction of DNA and acridines. J Mol Biol. 1961 Feb;3:18–30. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LePecq J. B., Paoletti C. A fluorescent complex between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. Physical-chemical characterization. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):87–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens P. A., Clayton D. A. Strand breakage in solutions of DNA and ethidium bromide exposed to visible light. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1393–1407. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. J., Newlin D. D. Interactions of molecules with nucleic acids. VI. Computer design of chromophoric intercalating agents. Biopolymers. 1982 Mar;21(3):633–652. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Crothers D. M. Interactions of heteroaromatic compounds with nucleic acids. 1. The influence of heteroatoms and polarizability on the base specificity of intercalating ligands. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May;54(1):267–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Gautier F. Interactions of heteroaromatic compounds with nucleic acids. A - T-specific non-intercalating DNA ligands. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):385–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlin D. D., Miller K. J., Pilch D. F. Interactions of molecules with nucleic acids. VII. Intercalation and T.A specificity of daunomycin in DNA. Biopolymers. 1984 Jan;23(1):139–158. doi: 10.1002/bip.360230111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack R. F., Gibbs E. J., Villafranca J. J. Interactions of porphyrins with nucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2406–2414. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack R. F., Gibbs E. J., Villafranca J. J. Interactions of porphyrins with nucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1983 Nov 8;22(23):5409–5417. doi: 10.1021/bi00292a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porumb H. The solution spectroscopy of drugs and the drug-nucleic acid interactions. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1978;34(3):175–195. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(79)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley G. J., Wang A. H., Ughetto G., van der Marel G., van Boom J. H., Rich A. Molecular structure of an anticancer drug-DNA complex: daunomycin plus d(CpGpTpApCpG). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7204–7208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. The degree of unwinding of the DNA helix by ethidium. I. Titration of twisted PM2 DNA molecules in alkaline cesium chloride density gradients. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 15;89(4):783–801. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J. Complex formation between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1965 Aug;13(1):269–282. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J. DNA modification and cancer. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:159–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. Variation of the supercoils in closed circular DNA by binding of antibiotics and drugs: evidence for molecular models involving intercalation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):247–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




