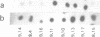Abstract
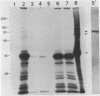
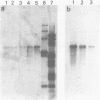
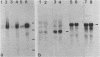
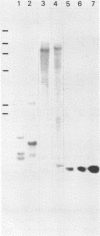
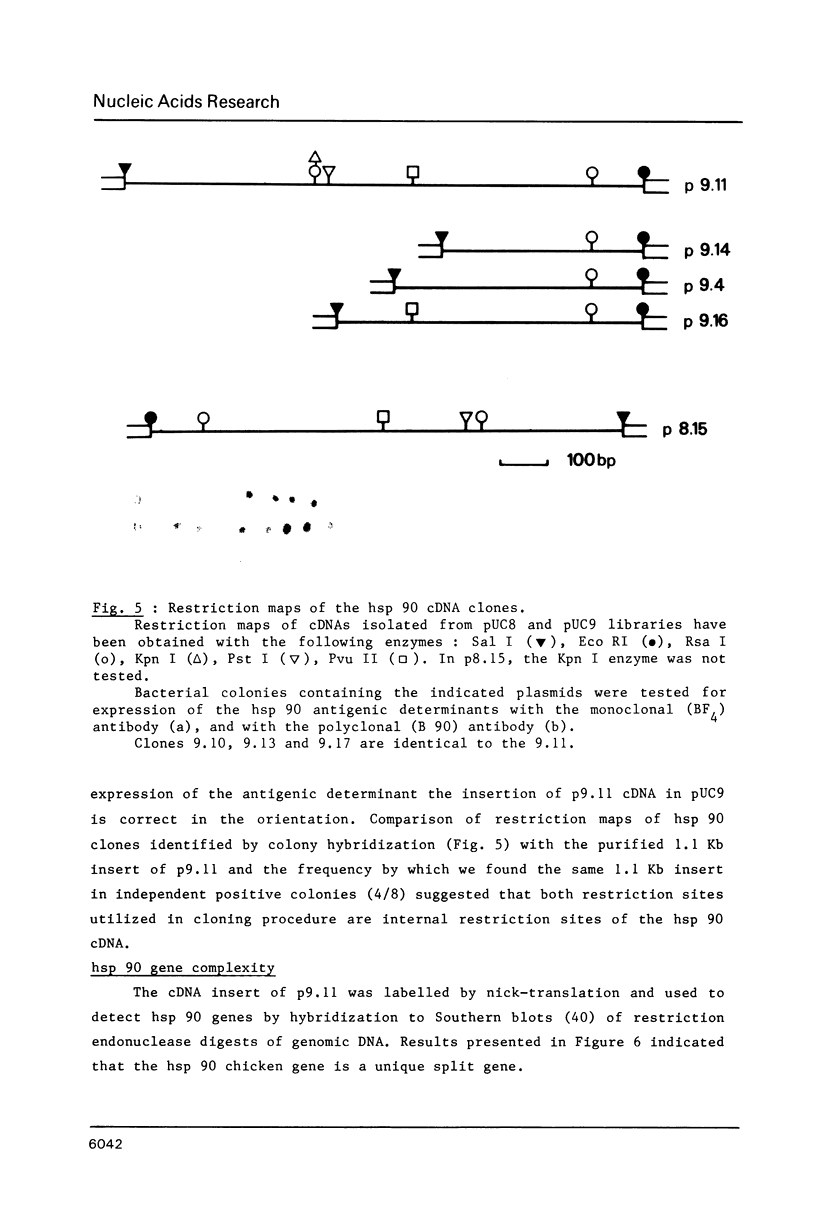
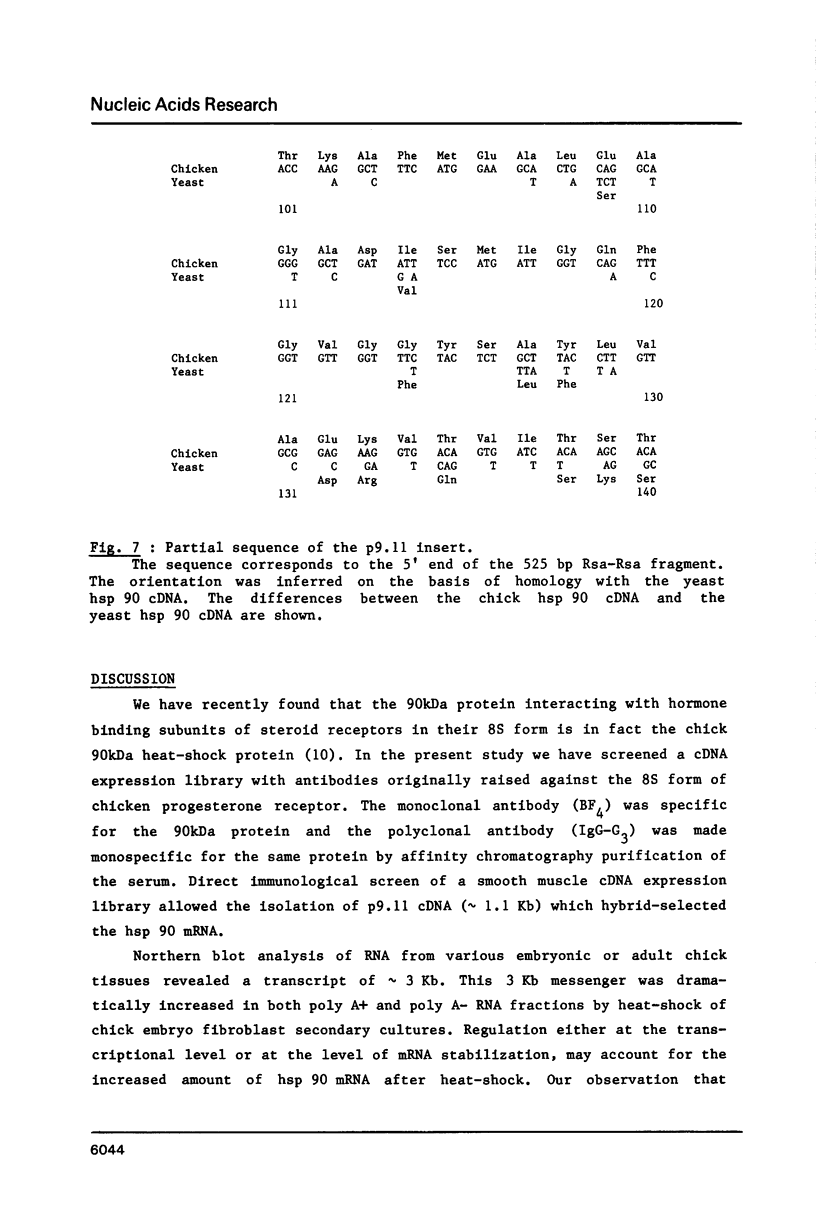
A cDNA clone for the 90kDa heat-shock protein, which we have recently identified as a component of steroid hormone receptors in their heteromeric 8S form, was isolated by direct immunological screening of a chicken smooth muscle cDNA expression library, prepared in the expression plasmids pUC8 and pUC9. Using polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies against the 90kDa protein a colony was identified that reacted with both antibodies. Plasmid 9.11 (p9.11, approximately 1100 base pair insert) was found to hybrid-select mRNA for the 90kDa heat-shock protein. Northern blot analysis revealed that RNA isolated from various chicken tissues contain a single transcript of approximately 3 Kb hybridizing to a [32P]labelled cDNA probe made from p9.11. Heat-shock treatment of chick embryonic fibroblasts resulted in increased steady-state levels of a 3 Kb transcript in both poly A+ and poly A- RNA fractions. Southern blot analysis of chicken genomic DNA indicated that the cDNA hybridizes to a single copy sequence. Sequence data show that the p9.11 cDNA displays a high degree of homology with the 5' portion of yeast heat shock protein 90 cDNA.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J., Yonemoto W., Darrow D. Interaction between the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein and two cellular phosphoproteins: analysis of the turnover and distribution of this complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):9–19. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K. Direct identification of specific glycoproteins and antigens in sodium dodecyl sulfate gels. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:54–64. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Transit of pp60v-src to the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7117–7121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty J. J., Puri R. K., Toft D. O. Polypeptide components of two 8 S forms of chicken oviduct progesterone receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):8004–8009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrelly F. W., Finkelstein D. B. Complete sequence of the heat shock-inducible HSP90 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5745–5751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasc J. M., Renoir J. M., Radanyi C., Joab I., Tuohimaa P., Baulieu E. E. Progesterone receptor in the chick oviduct: an immunohistochemical study with antibodies to distinct receptor components. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1193–1201. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring U., Arndt H. Heteromeric nature of glucocorticoid receptors. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 1;179(1):138–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett R. W., Lis J. T. Localization of the hsp83 transcript within a 3292 nucleotide sequence from the 63B heat shock locus of D. melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7011–7030. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Fiddes J. C., Thomas G. P., Hughes S. H. Identification of clones that encode chicken tropomyosin by direct immunological screening of a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Ricci W. M., Hughes S. H. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone that contains the entire coding region for chicken smooth-muscle alpha-tropomyosin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14136–14143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren R., Livak K., Morimoto R., Freund R., Meselson M. Studies of cloned sequences from four Drosophila heat shock loci. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1359–1370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N. E., Groner B., Sippel A. E., Nguyen-Huu M. C., Schütz G. mRNA complexity and egg white protein mRNA content in mature and hormone-withdrawn oviduct. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):923–932. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90303-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joab I., Radanyi C., Renoir M., Buchou T., Catelli M. G., Binart N., Mester J., Baulieu E. E. Common non-hormone binding component in non-transformed chick oviduct receptors of four steroid hormones. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):850–853. doi: 10.1038/308850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Schlesinger M. J. Antibodies to two major chicken heat shock proteins cross-react with similar proteins in widely divergent species. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):267–274. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morange M., Diu A., Bensaude O., Babinet C. Altered expression of heat shock proteins in embryonal carcinoma and mouse early embryonic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):730–735. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D., Lis J. T. Two closely linked transcription units within the 63B heat shock puff locus of D. melanogaster display strikingly different regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):5075–5092. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.5075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson W., Bishop J. M. A cellular protein that associates with the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus is also a heat-shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1067–1071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Velan B., Felsenfeld A., Ramanathan L., Ferrini U., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Mouse beta 2-microglobulin cDNA clones: a screening procedure for cDNA clones corresponding to rare mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2253–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radanyi C., Joab I., Renoir J. M., Richard-Foy H., Baulieu E. E. Monoclonal antibody to chicken oviduct progesterone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2854–2858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renoir J. M., Radanyi C., Yang C. R., Baulieu E. E. Antibodies against progesterone receptor from chick oviduct. Cross-reactivity with mammalian progesterone receptors. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Sep;127(1):81–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06840.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. R., Stevens J. Structure of mammalian steroid receptors: evolving concepts and methodological developments. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:83–105. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.000503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storti R. V., Scott M. P., Rich A., Pardue M. L. Translational control of protein synthesis in response to heat shock in D. melanogaster cells. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):825–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90559-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voellmy R., Bromley P., Kocher H. P. Structural similarities between corresponding heat-shock proteins from different eucaryotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3516–3522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., Reddy E. P., Duesberg P. H., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chicken c-myc gene reveals homologous and unique coding regions by comparison with the transforming gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29, delta gag-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2146–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. N., Hightower L. E. Stress mRNA metabolism in canavanine-treated chicken embryo cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1534–1541. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]